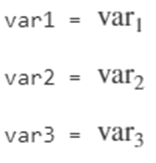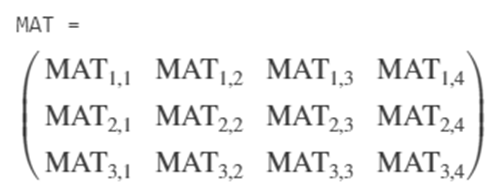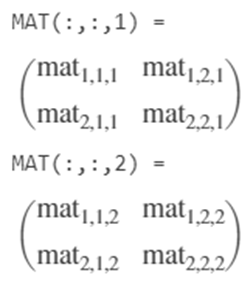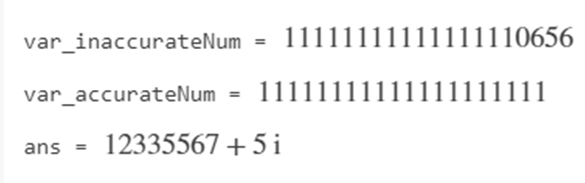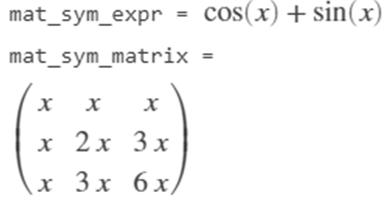Introduction to Matlab sym()
When any symbolic variable is created being associated with an assumption, the symbolic variable and its assumption get stored separately by MATLAB. The sym() in MATLAB is used to create numbered symbolic variables or symbolic variables in different MATLAB functions. Symbolic numbers generated from the sym() function are the exact representations of the input numbers.
Sym() can also be used to refer to an existing symbolic variable and current assumption associated with the variable. If the expected symbolic variable is not used in any MATLAB function previously, then sym() creates the variable without associating any assumptions.
Syntax of Matlab sym()
Syntax of matlab sym() is given: below:
| Syntax | Description |
s = sym('s') |
This command can be used to create a symbolic variable’. |
Mat = sym('m',[n1 ... nM]) |
This command can be used to create an array of symbols of size n1-by-…-by-nM consisting of automatically generated elements.
When the syntax MAT = sym(‘mat’,[n1 … nM]) is used, only the symbolic array MAT gets assigned to the MATLAB workspace by the sim() function. In order to assign also the automatically generated elements of MAT, the syms function needs to be used instead of sym(). For example, syms mat[1 3] ->
|
Mat = sym('m',n) |
This command can be used to create an array of symbols of sizen-by-n consisting of automatically generated elements. |
sym(___,set) |
This command can be used to create any symbolic variable or an array, setting the assumption that the variable or the array elements belong to the‘set’. |
sym(___,'clear') |
This command can be used to clear assumptions that are set on any symbolic variable or an array. |
sym(numb) |
This command can be used to convert any number or a numeric matrix, specified as numb, to corresponding symbolic number or matrix with symbolic elements. |
sym(numb ,flag) |
This command can be used to use the technique being specified by ‘flag’ to convert floating-point numbers into symbolic numbers. |
sym(str_num) |
This command can be used to convert a character string or vector, given as str_num, to an accurate symbolic number that avoids any approximation. |
Expr_sym = sym(h) |
This command can be used to create a symbolic expression or matrix Expr_sym from an anonymous MATLAB function associated with the function handle h. |
Note:
In the case of multidimensional arrays, sym() function generates automatically generated elements, having the prefix followed by the index for the element being added with ‘ _’ as a delimiter.
Example: a1_3_2.
Adding the command ‘clear x’ actually does not clear the symbolic object with respect to assumptions associated with the variable, such as real, positive, or any assumptions, etc. Hence, to remove assumptions, one of the below options is recommended:
- assume(x,’clear’): all assumptions that affect x, are being removed.
- clear all: clears all MATLAB workspace objects resetting the symbolic engine.
- assume and assumeAlso: Add further flexibility for applying assumptions on the variable.
Expressions such aspi = sym(pi),theta = sym(‘1/10’) etc. create symbolic numbers which enable the program to avoid floating-point approximations. The variable is created as a workspace variable to hold the symbolic value given within the sym() function. It temporarily replaces the name for built-in numeric function having the same name.
Examples of Matlab sym()
Following are the examples of matlab sym() are given below:
Example #1
var1=sym('var1')var2=sym('var2')var3=sym('var3')
Output:
Example #2
var = sym('var',[1 4])
Output:
Example #3
MAT = sym('MAT',[3 4])
Output:
Example #4 – Create Symbolic Multidimensional Arrays
MATLAB enables its program to create multidimensional array containing symbolic elements at one time, using sym() function.
MAT = sym('mat',[2 2 2])
Output:
Example #5 – Converting Expressions to Symbolic Expressions
Application of sym() function on the complete expressions makes the conversion inaccurate as MATLAB converts the expression to a floating-point number, which results in reducing accuracy and recovery of the lost accuracy is not possible by sym() all the time. Hence in order to extract symbolic expressions with respect to expressions, sym() needs to be applied on subexpressions instead of the entire expression to achieve better accuracy.
var_inaccurate1 = sym(1/1234567)
var_accurate1 = 1/sym(1234567)
var_inaccurate2 = sym(sqrt(1234567))
Output:
Example #6 – Generating Large Symbolic Numbers
In case of generating symbolic number having 15 or more digits, quotation marks are used to represent the numbers with optimum accuracy.
var_inaccurateNum = sym(11111111111111111111)
var_accurateNum = sym('11111111111111111111')
sym('12335567 + 5i')
Output:
Note: Sym() treats the imaginary symbol ‘i’ as an identifier in a character vector input. Hence in order to provide imaginary number I as an input, it is suggested to use 1i instead.
Example #7 – Generating Symbolic Expressions out of Function Handles
MATLAB supports creating any symbolic expression or a symbolic matrix from anonymous functions that are associated with MATLAB handles.
mat_expr = @(x)(sin(x) + cos(x));
mat_sym_expr = sym(mat_expr)
mat_matrix = @(x)(x*pascal(3));
mat_sym_matrix = sym(mat_matrix)
Output:
Example 8 – Setting of Assumptions While Generating Symbolic Variables
MATLAB supports creating symbolic variables adding a different set of assumptions about characteristics of the variable such as the number being real or positive or rational etc.
p = sym('p','real');
q = sym('q','positive');
r = sym('r','rational');
s = sym('s',{'positive','integer'});
assume([p q r s],'clear')
assumptions
Output:
Example #9 – Selecting Conversion Technique for Floating-Point Values
The functionality of the sym() function is extended to choose any conversion technique. It is achieved by specifying the second argument which is optional by nature. The value for the arguments can be ‘r’, ‘f’, ‘d’, or ‘e’. However, the default value remains ‘r’.
p = sym(pi)
q = sym(pi,'f')
r = sym(pi,'d')
s = sym(pi,'e')
Output:
Conclusion
When one or more elements of a numeric vector or matrix is/are replaced with a symbolic number, MATLAB treats the number as a double-precision number, but those elements of a numeric vector or matrix do not support replacement with a symbolic variable, function or expression as these elements cannot be converted to double-precision numbers. The functions Sym() and syms() share similar functionality but differs as:
The syms() function creates a symbolic object, automatically assigning to a MATLAB variable having the same name, whereas, a symbolic object referred by sym() function can be assigned to a MATLAB variable with the same name and to a different name as well.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab sym(). Here we also discuss the introduction and syntax of matlab sym() along with different examples and its code implementation. you may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –