Updated February 28, 2023
Introduction to MATLAB Indexing
MATLAB provides us with plenty of functionalities, useful in various computational problems. In this article, we will study a powerful MATLAB functionality called ‘MATLAB Indexing’. Indexing is the way to select a particular element in an array. The selection is done based on the index or position of that element. Indexing is handy when we need to access/ edit or delete some cells and want to have an understanding of the value is present in that cell before implementing any change. When we use single subscript for pointing to an element in some array, it is referred to as linear indexing.
Now let us understand different approaches that can be used for indexing, with the help of examples.
Examples of MATLAB Indexing
Below are the examples of MATLAB Indexing:
Example#1
Let us first take a simple example without any condition.
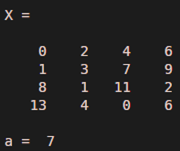
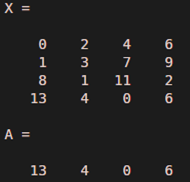
X = [0 2 4 6; 1 3 7 9; 8 1 11 2; 13 4 0 6]
Our input X, when implemented in MATLAB will result in the following 4 x 4 array:
For this example, let us try to find out the cell at position (2, 3).
The Syntax that we will use in MATLAB is:
a = X (2, 3)
The Output that we obtain will be a single value present at the position (2, 3) in the array X.
i.e, Output is 7
This is how our input and output will look like in MATLAB console:
Input:
X = [0 2 4 6; 1 3 7 9; 8 1 11 2; 13 4 0 6]
a = X (2, 3)
Output:
As we can clearly see in the output, only the value present at position (2, 3), i.e. 7 is selected from the input array
Example #2
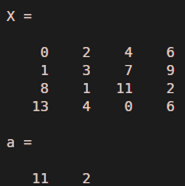
Let us now take the scenario where we want to reference more than one element of a row. We will use the same array as above for this example. For our understanding, let us try to get the 3rd and 4th element of 3rd row.
This is how our input and output will look like in MATLAB console:
Input:
X = [0 2 4 6; 1 3 7 9; 8 1 11 2; 13 4 0 6]
a = X (3, [3,4])
Output:
As we can clearly see in the output, we are able to get the 3rd and 4th elements of the 3rd row, i.e, 11 and 2. All we did is passed the indices of required elements with the help of a vector to MATLAB.
Example #3
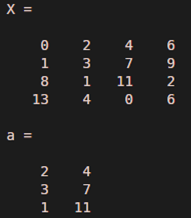
In the next scenario, let us assume that we need to get elements from the 1st row till the 3rd row, and from the 2nd column till the 3rd column.
For this purpose, we will specify the index range that we are looking for and will separate row and column ranges by a ‘colon’.
i.e. A = X(1: 3, 2: 3)
This is how our input and output will look like in MATLAB console:
Input:
X = [0 2 4 6; 1 3 7 9; 8 1 11 2; 13 4 0 6]
a = X (1 : 3, 2 : 3)
Output:
The output is an array with 1st, 2nd, and 3rd row selected, with elements from the 2nd and 3rd columns.
Example #4
Another way of using the index is to access all elements of a particular row or column.
For this, we will pass just the row or column number whose elements we require. So, if we need all the elements of 4th row, we just need to pass.
A = X (4, : )
This is how our input and output will look like in MATLAB console:
Input:
X = [0 2 4 6; 1 3 7 9; 8 1 11 2; 13 4 0 6]
A = X (4 , :)
Output:
Example #5
It is also possible to index arrays based on logical operators. Let us understand how this can be achieved.
In the scenario where we want to know which all elements of an array X are greater than or less than another array Y, we can use this feature of indexing.
All we need to do is pass the ‘<’ or ‘>’ sign between these 2 arrays as per our requirement.
Let us understand with an example:
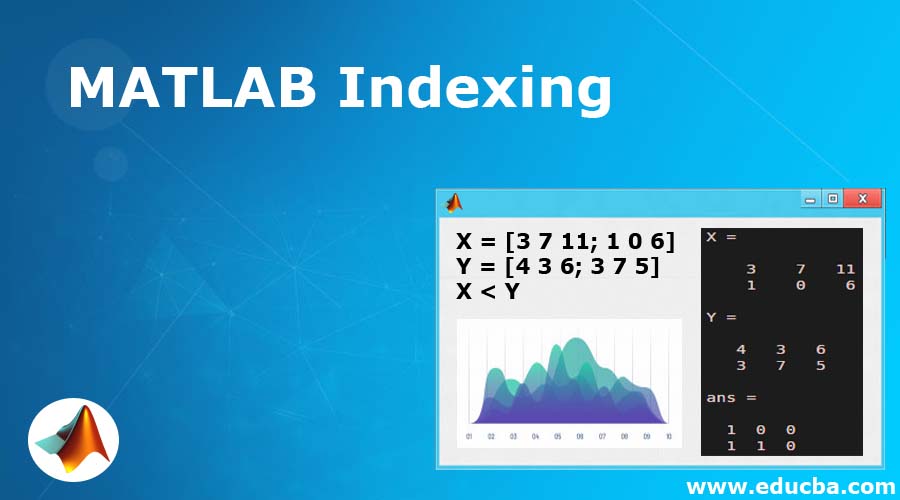
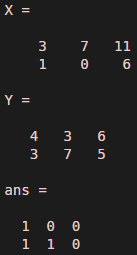
X = [3 7 11; 1 0 6]Y = [4 3 6; 3 7 5] We will pass the condition X < Y, to find out the elements in X, which are less than elements in Y.The output, in this case, will be an array of 0s and 1s. 0 showing value in X is not less than Y at that particular cell and 1 showing that value at X is less than Y.
This is how our input and output will look like in MATLAB console:
Input:
X = [3 7 11; 1 0 6]
Y = [4 3 6; 3 7 5]
X < Y
Output:
As we can clearly see in the output above, we have obtained a ‘1’ for all values in ‘X’ which are less than corresponding values in ‘Y’. For the values in ‘X’, which are greater than ‘Y’, the output array has a ‘0’.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learnt how the indexing works in MATLAB. We can use indexing to obtain the value present at any desired location in an array. As an additional feature, indexing can also be used to compare values of arrays.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MATLAB Indexing. Here we discuss the Introduction to MATLAB Indexing and its different Examples as well as its input and output. You can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –