Updated June 17, 2023
Introduction to Matlab Image Resize
MATLAB is designed to store most of the images in the form of two-dimensional matrices. Each element corresponds to a distinct, discrete pixel in the matrices in any stored image. The Image Processing Toolbox software available in MATLAB supports several operations that can be performed on images. The function of resizing images is one of those functionalities. Resizing any 2D image in MATLAB can be performed using the resize () procedure, whereas imresize3() is used for resizing 3-D volumetric intensity images.
| Syntax | Description |
| ImgOut = imresize(Img,scale) | This syntax is used to result in an image ImgOut which is a scaled-up version of the input image Img with respect to its size. The input image Img can be of type binary, grayscale, categorical image, or RGB.
Resizing an image using a GPU is optional for this syntax. |
| ImgOut= imresize(Img,[row_numcol_num]) | This syntax results in an image ImgOut created with a number of rows and columns specified by the input argument vector. |
| [ImgOut,newmap] = imresize(Img,map,___) | This syntax results in the resized form of the indexed image Img with the colormap map presented by ImgOut. By default, imresize results in an optimized colormapi.enewmap, along with the resized indexed image ImgOut. In order to result in the same colormap as that of the original colormap, the Colormap name-value pair argument needs to be used.
|
| ___ = imresize(___,method) | This syntax results in a resized image with the interpolation method being specified. |
| ___ = imresize(___,Name,Value) | This syntax results in resized images being customized by means of name-value pair arguments to control different aspects of the resizing operation. Application of this syntax on a GPU is not supported. |
Examples of Matlab Image Resize
There are different ways in which an image can be resized in a MATLAB program. They are:
1. Resizing using Magnification Value
The image can be magnified or shrunk by a specific factor mentioned within the imresize() command.
Code:
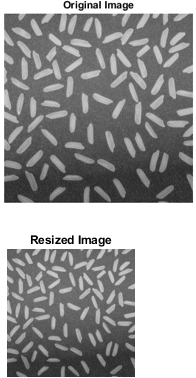
Img = imread('MyIMage.png');% Reading input image from workspaceimshow(Img) %Showing given image on the output windowtitle('Original Image')Out = imresize(Img,0.5);imshow(Out)title(' Resized Image') axis off
Output:
2. Resizing using fixed dimension Value
The image can be magnified or shrink to definite dimensions, mentioned within the imresize() command.
Code:
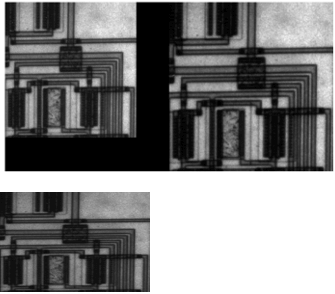
Img = imread('MyCircuit.png');imshow(Img)Out = imresize(Img,[100 150]);imshow(Out)axis off
Output:
3. Resizing using the specific interpolation method
The image can be magnified or shrink using a specific interpolation method mentioned within the imresize() command.
Code #1
Img = imread('MyIMage.png');imshow(Img)Out = imresize(Img,0.5, 'nearest'); %Applying the interpolation method ‘nearest- %neighbor’imshow(Out)axis off
Output:
Code #2
Img = imresize(I,.75,'Antialiasing’, false);figure, imshow(Img)
Output:
4. Resizing indexed images
An indexed image specified in the form of a numerical array can be magnified or shrink using a scaling factor mentioned within the imresize() command.
Code:
[M, map] = imread('trees.png');
[O, newmap] = imresize(M, map, 0.5);
figure
imshow(X,map)
figure
imshow(Y,newmap)
Output:
5. Resizing RGB Image to the Specified Size of Output Image
An RGB image specified can be magnified or shrink to a definite dimention, mentioned within the imresize() command.
Code:
RGB = imread('trees.png');
RGBOut = imresize(RGB, [64 NaN]);
figure
imshow(RGB,map)
figure
imshow(RGBOut,newmap)
Output:
Input Arguments and Attributes
Below is the table explaining arguments and attributes:
| Attribute/Argument | Description | Probable Values |
| Scale | It acts as Resizing factor by which the original image size gets changed. | 0>val<1 or val>1 |
| [numrowsnumcols] | This vector decides the number of rows and columns in which the resultant image should be created. | NaN or any positive integer |
| map | This attribute is associated with an indexed image presenting a color map for the same. | Values are in the range [0,1] |
| Method | This attribute talks about the Interpolation method or kernel to be used in the resizing operation. | Methods: nearest, bilinear, bicubic Kernel: box, triangle,cubic,lanczos2, lanczos3 |
| Antialiasing | The “antialiasing” attribute determines whether an antialiasing effect is applied to the output image when the input image undergoes shrinking or reduction in size. | True/False |
| Colormap | This output parameter returns a value of an optimized or original colormap with respect to the indexed image. | Original/optimized |
| Dither | The “color dithering” attribute is used to apply a form of noise to the image during the quantization process, which helps randomize and minimize quantization errors. | True/False |
| Newmap | This attribute is used for Optimized colormap. | [0,1] |
Additional Note
Below are the points explain additional information:
- The operation of imresize() method is carried out either by CPU or GPU. There is a numerical difference between the results of imresize that occurs on the bottom and rightmost borders of the resultant image.
- In the case of the resultant image not having size with an integer value, the imresize() function does not use the specified scaling factor. Imresize() uses ceil while calculating the size of the output image.
- If the input image has more than two dimensions, imresize() supports resizing operations only to the first two dimensions.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab Image Resize. Here we discuss an introduction to Matlab Image Resize, syntax with attributes, and examples to resize images. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –