Updated July 3, 2023

Introduction to Matlab Double Integral
Matlab Double Integral is the extension of the definite integral. In the double integral, the integration is carried out for functions that involve two variables. It is an extension of the concept of integration for functions with one variable. In MATLAB, we use ‘integral2 function’ to get the double integration of a function.
Syntax
Let us now understand the syntax of integral2 function in MATLAB:
I = integral2 (Func, minX, maxX, minY, maxY)
I = integral2 (Func, minX, maxX, minY, maxX, Name, Value)
Explanation:
I = integral2 (Func, minX, maxX, minY, maxY) will integrate the function ‘Func’ (here ‘Func’ is a function of 2 variables X and Y) over the region minX ≤ X ≤ maxX and minY ≤ Y ≤ maxY
I = integral2 (Func, minX, maxX, minY, maxX, Name, Value) can be used to pass more options to the integral2 function. These options are passed as paired arguments
Examples to Implement Matlab Double Integral
Let us now understand the code to calculate the double integral in MATLAB using ‘integral2 function’.
Example #1
In this example, we will take a function of cos with 2 variables, ‘x’ and ‘y’. We will follow the following 2 steps:
Step 1: Create a function of x and y
Step 2: Pass the function and required limits to the integral2 function
Code:
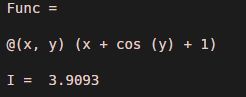
Func = @ (x,y) (x + cos (y) + 1)
[Creating the cos function in ‘x’ and ‘y’]
I = integral2 (Func, 0, 1, 0, 2)
[Calling the integral2 function and passing the desired limits as 0 <= x <= 1; 0 <= y <= 2)]
[Mathematically, the double integral of x + cos (y) + 1 is 3.9093]
Output:
Explanation: As we can see in the output, we have obtained a double integral of our input function as 3.9093, which is the same as we expected.
Example #2
In this example, we will take a function of sin with 2 variables, ‘x’ and ‘y’. We will follow the following 2 steps:
Step 1: Create a sin function of x and y
Step 2: Pass the function and required limits to the integral2 function
Code:
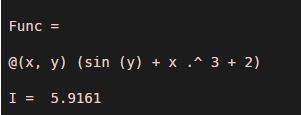
Func = @(x,y) (sin(y) + x.^3 + 2)
[Creating the sin function in ‘x’ and ‘y’]
I = integral2 (Func, 0, 1, 0, 2)
[Calling the integral function and passing the desired limits as 0 <= x <= 1; 0 <= y <= 2)]
[Mathematically, the double integral of sin(y) + x.^3 + 2 is 5.9161]
Output:
Explanation: As we can see in the output, we have obtained a double integral of our input function as 5.9161, which is the same as we expected.
Example #3
We will take a polynomial function of x and y in this example. We will follow the following 2 steps:
Step 1: Create a polynomial function of x and y
Step 2: Pass the function and required limits to the integral2 function
Code:
Func = @(x,y) (35*y.^3 - 15*x)
[Creating the polynomial function in ‘x’ and ‘y’]
I = integral2 (Func, 0, 1, 0, 2)
[Calling the integral function and passing the desired limits as 0 <= x <= 1; 0 <= y <= 2)]
[Mathematically, the double integral of 35*y.^3 - 15*x is 125]
Output:
Explanation: As we can see in the output, we have obtained a double integral of our input function as 125, which is the same as we expected.
Example #4
In this example, we will take a polynomial function of x, y, and degree 3. We will follow the following 2 steps:
Step 1: Create a polynomial function of x and y and degree 3
Step 2: Pass the function and required limits to the integral2 function
Code:
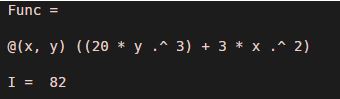
Func = @(x,y) ((20*y.^3) + 3*x.^2)
[Creating the polynomial function in ‘x’ and ‘y’]
I = integral2 (Func, 0, 1, 0, 2)
[Calling the integral function and passing the desired limits as 0 <= x <= 1; 0 <= y <= 2)]
[Mathematically, the double integral of (20*y.^3) + 3*x.^2 is 82]
Output:
Example #5
In this example, we will take a polynomial function with the division. We will follow the following 2 steps:
Step 1: Create a polynomial function of x and y with division
Step 2: Pass the function and required limits to the integral2 function
Code:
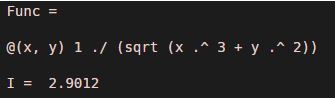
Func = @(x,y) 1./(sqrt(x.^3 + y.^2))
[Creating the polynomial function in ‘x’ and ‘y’ and division]
I = integral2 (Func, 0, 1, 0, 2)
[Calling the integral function and passing the desired limits as 0 <= x <= 1; 0 <= y <= 2)]
[Mathematically, the double integral of 1./(sqrt(x.^3 + y.^2)) is 2.9012]
Output:
Conclusion
Integral2 function can be used in MATLAB to get the double integral of a function. Double integral integrates the function of 2 variables over a 2-D region specified by the limits.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab Double Integral. Here we discuss an introduction to Matlab Double Integral, syntax, and examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –