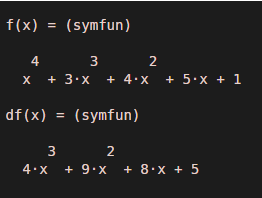Updated February 27, 2023
Introduction to MATLAB Derivative
MATLAB is a programming environment that is interactive and is used in scientific computing. It is extensively used in a lot of technical fields where problem-solving, data analysis, algorithm development, and experimentation is required. The discipline-specific software is extensively written using MATLAB. MATLAB provides us the ability to perform numerous mathematical operations, In this topic, we are going to learn about MATLAB Derivative.
How does MATLAB Derivative work?
Differentiation is a calculus tool that calculates small changes in a function. Differentiation or derivative is the rate of change of a function w.r.t. some variable. It calculates how sensitive our output is concerning any change in our input.
Mathematically, it can be represented as f(x)/dx, where dx represents the change in the value of function f (x), concerning the variable x.
Let us now understand how derivative works in MATLAB.
Syntax of derivative:
- diff (f)
- diff (f, n)
- diff (f, var)
- diff (f, var, n)
Examples of MATLAB Derivative
Here are the following examples mention below
Example #1 – diff (f)
This function will differentiate ‘f’ with the variable x
Here is an example where we compute the differentiation of a function using diff (f):
Lets us take a polynomial function defined as:
x ^ 4 + 3 x ^ 3 + 4 x ^ 2 + 5 x + 1
Syntax
df = diff (f, x)
The function diff will return derivative value of the functionx ^ 4 + 3 x ^ 3 + 4 x ^ 2 + 5 x + 1:
4x^3 + 9x^2 + 8x + 5
Input:
syms f(x)
f(x) = x ^ 4 + 3*x ^ 3 + 4*x ^ 2 + 5*x + 1
df = diff (f, x)
Output:
Example #2 – diff (f, n)
This function is used to calculate the nth derivative of the input function. ‘n’ here is passed as an argument.
Here is an example where we compute ‘nth’ derivative of a function using diff (f, n):
Lets us take another polynomial function defined as:
3 x ^ 3 + 2 x ^ 2 + 7 x + 5
For our example, we will calculate the 2nd derivative.
Mathematically, our output should be:
18x + 4
Input:
syms f(x)
f(x) = 3*x^3 + 2*x^2 + 7*x + 5
df = diff (f, 2)
Output:
As we can see, diff (f, n) has calculated the 2nd derivative of our input function.
Example #3 – diff (f, var)
This function will find the derivative of ‘f’ w.r.t the variable in the argument.
Here is an example where we compute differentiation of a function using diff (f, var):
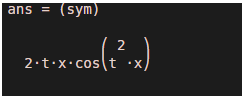
Lets us take a sine function defined as:
Sin(x*t^2)
For our example, we will calculate the derivative w.r.t ‘t’
Mathematically, our output should be:
2txcos(t^2x)
Input:
syms x t
diff(sin(x*t^2),t)
Output:
As we can see, the derivative is calculated w.r.t. ‘t’ as expected by us.
[Notice that we have passed ‘t’ as an argument. Diff function will now take the derivative w.r.t ‘t’]Example #4 – diff (f, var, n)
This function will calculate the ‘nth’ derivative of the input function w.r.t the variable we pass as an argument.
Below is the example where we calculate the derivative of a function using diff (f, var, n):
Lets us take a sine function defined as:
Sin(x*t^4)
For our example, we will calculate the ‘2nd’ derivative w.r.t ‘t’
Mathematically, our output should be:
12t^2xcos(t^4x) - 16t^6x^2sin(t^4x)
Input:
syms x t
diff(sin(x*t^4),t,2)
Output:
As we can see, we have got the 2nd derivative of our input function w.r.t ‘t’, as expected.
[Notice the arguments ‘t’ and ‘2’, for derivative w.r.t and nth derivative respectively]Conclusion
‘diff’ function is used in MATLAB to calculate the differentiation or derivative of a function. We can calculate the derivative w.r.t the default variable or the variable we pass as an argument. Also, the degree of differentiation or derivative can be controlled using the argument.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to MATLAB Derivative. Here we discuss how does MATLAB Derivative work along with appropriate syntax and respective examples. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –