Updated April 12, 2023

Introduction to MariaDB Replication
MariaDB Replication in SQL databases can be defined as a method to copy data from the source MariaDB database to other one or multiple ones and vice versa. Here, the data from a database server are to be frequently copied to single or multiple servers. MariaDB Replication is useful for distributing and balancing requests through a pool of replicated servers, delivering failover, and high obtainability of MariaDB databases. The MariaDB and also MySQL permits to apply two kinds of databases replication made such as the Master-Master and the Master-Slave. These terms as a master slave have been historically implemented, but now the preferred terms are primary and replica. Replication functioning gets the composition of few steps on both the master servers as well as the slave servers.
Syntax of MariaDB Replication
Let us see the syntax structure for MariaDB Replication in the server as follows:
We need to add the succeeding code into the my.cnf file and then restarting the MariaDB database.
[mariadb]
Log-bin
Server_id=1
Log-basename=master1
Binlog-format =mixedHere, the server id defines a unique number for every MariaDB or MySQL server in the network. To specify how the statements are logged, we will use the binlog-format. It generally disturbs the binary log size, which is directed between the Master and the Slaves.
Now, we can execute the above SQL query code along with the mysql command line client as follows:
CREATE USER 'replication_user' @'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'bigs3cret';
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'replication_user'@'%';Whereas for MySQL, we will enable Replication following the procedure, which will be nearly identical to the MariaDB servers so that if the user requires to activate the replication feature from MySQL to MariaDB, then it can be accomplished. The major alteration is that support for log-basename is not provided in the MySQL server.
[mysql]
Log-bin
Server_id=1How to Perform Replication in MariaDB?
In MariaDB, Replication represents a feature permitting the contents of single or multiple primary servers to be minored on single or multiple replica servers. While using replication on different versions of MariaDB, it is the finest that the master is a previous version than the slave. Since these elder versions may not be often forward-compatible therefore, MariaDB versions are normally backward compatible.
We will configure the Master as follows:
- If not already enabled, we will active binary logging for its formats.
- We need to provide the master with a distinctive server_id as well as all the slaves should also be provided with a server_id which may be an integer from 1 to 232 -1 that must be distinct for every server in the replicating group.
- State a distinctive name for the replication logs along with –log-basename. By chance, if this is not provided, the hostname will be implemented, but if the hostname ever modifies, then there may rise some problems.
- Here, slaves may require permission to associate and start replicating from a server. Normally, this can be applied by making a dedicated slave user and then yielding that user’s permission to replicate i.e. REPLICATION SLAVE permission.
Example of MariaDB Replication
Given below is the example mentioned:
Data replication is necessary to save the data records, make them protected, and confirm the high availability of data and the simplicity of access, specifically in the event of any unpredicted error like a system smash, software or hardware created error and so on. MariaDB Replication may take place with the help of several mechanisms like a master slave, master-master and the start and multi-source mechanism. Here, the replicated data may be a comprehensive set of either single or multiple databases or even the data tables delivered from the preferred database.
In the configuration of master-slave, any alterations that are completed to one of the slaves, reflect in the master record simultaneously in a matter of seconds, succeeding which entire slaves accept the data modernizing from the master slave being in an entirely computerized style.
Let us see some key features of this MariaDB Replication listed below:
- Scalability: To reduce the load on the master server, it is good to have one or multiple slave servers that permit data reads to be performed on them, allowing executing the write operation.
- Backup Assistance: It comprises copying data to a slave, which you can apply as backup data, which later can perform as the stand-alone server in a steady state.
- Data Analysis: The data record will be analysed on the slave server but not tallying further load to the master server with duplication in place.
- Data Distribution: In a place with replication, one can work on this data nearby without concerning to the master server. Now, upon succeeding connection, the rationalized data can get combined with the master.
Let us show to configure MariaDB as Master Server as follows:
Initially, we need to alter my.cnf file situated at /etc/mysql/ directory. Again, sudo nano /etc/mysql/my.cnf, now we will change the file as below:
Code:
[mysqld]
Bind-address = 192.168.15.237
Server_id =
Log-basename=master
Log-bin
Binlog-format=row
Binlog-do-db=<databasename>We need to note that the database name will be replaced with the current database available on the server. Now, save and then close the file and restart the MariaDB server to implement the modifications. ‘sudo systemctl restart mysql’. After that setting up the replication:
First of all, logging in to the MariaDB server by the below command as:
Code:
mysql –u root –pThe command above prompts for root password; therefore, enter it and then login.
Stopping the slave with the command as:
Code:
STOP SLAVE;Creating a fresh replication user with the name slaveuser as well as password as specified by the command as:
Code:
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'user_slave'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password1';Resulting with flush privileges:
Code:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
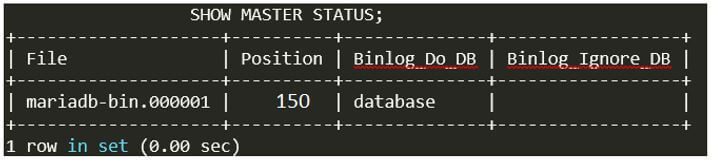
FLUSH TABLES WITH READ LOCK;Again, checking the status of the master server with the command as:
Code:
SHOW MASTER STATUS;Output:
Conclusion
MariaDB 10.0 version has presented a replication feature with global transactions ids, including a number of benefits, and normally it is being recommended to apply this feature using MariaDB 10.0. While using MariaDB Replication across its various versions, it is a good option that the master is available in the elder version than the slave because these versions of MariaDB are typically backward compatible, and also, the elder versions may not always be forward compatible.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB Replication” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

