Updated April 12, 2023

Introduction to MariaDB max_allowed_packet
The following article provides an outline for MariaDB max_allowed_packet. MariaDB provides the different system variables and that can be used as per requirement as well as we can change them. max_allowed packet size is used to increase the response time of data recovery and it is a session variable and it also has a read only variable. Nowadays we are facing different problems related to max_allowed_packet size during the backup and recovery manager. Each system variable has a by default value and that value we can set at server side by using different options. Most of the time we can set max_allowed _packet size dynamically at runtime by using the set statement without stopping the server. If we need to set global system variables at that time we require the super user privilege.
Syntax:
set global max_allowed_packet=size of max_allowed_packet;Explanation:
- In the above syntax we use set global command to set max size of allowed packet, here max_allowed_packet is a system variable that can be set at server side and size of max_ allowed_ packet is used to actual size of packet shown in above syntax, here size of system variable is same or greater than at client side otherwise it shows error message.
How does max_allowed_packet Function Work in MariaDB?
Maximum size of max_allowed_packet is in bytes or it generates the intermediate string. In which we can set the packet message buffer value from the net_buffer_length but we can increase that value by using the max_allowed_packet bytes. If we changed the value at the server side then it should be changed on the client side as well. The scope of that variable is global.
When MariaDB server or MariaDB client received the packet and the size of system variable is larger than the max_allowed_packet size, this is the main issue and it shows errors like packet size too large and closes the connection. The default value of max_allowed_packet is low, so you need to increase the value of max_allowed_packet size by using the different parameters as follows.
Now let’s see how we can set the max_allowed_packet as follows:
- First open my.cnf file under the MariaDB server install directory by using any edit tool or we can simply open in notepad.
- After that we need to search the max_allowed_packet variable, sometimes this variable or parameter is not present in that file. At that time we add that parameter or variable into the file.
- In the third step we can set the max value of max_allowed_packet as per our requirement and restart the MariaDB server.
Default value as per different version are as follows:
- 16 M less than or equal to MariaDB 10.2.4 version.
- 4 M less than or equal to MariaDB 10.1.7.
- 1 MB greater than or equal to MariaDB 10.2.4 version.
- 1 GB for client side.
We can set the max_allowed_packet value by using two ways as follows:
- In the first way we can set it by using the set global max_allowed_packet value.
- In the second way we add the value of max_allowed_packet in my.cnf file but at the same time we need to restart the MariaDB server.
Example of MariaDB max_allowed_packet
Given below is the example of MariaDB max_allowed_packet:
First to check what the current value of max_allowed_packet is by using the following statement as follows:
Code:
show variables like 'max_allowed_packet';Explanation:
- In the above statement we use show variables command to see the current value of max_allowed_packet function, here like is used to search specified system variables, which is we need to search the max_allowed_packet function value.
- The end output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
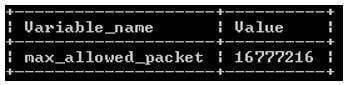
In the above screenshot the value of max_allowed_packet is 16777216, so we can change this value by using two ways as follows.
In the first way we can directly set max_allowed_packet size by using a query statement as follows.
Code:
set global max_allowed_packet=445878;Explanation:
- In the above example we use the set global variable command to set max_allowed_packet system variable, here we set 445878 value for the system variable that is max_allowed_packet as shown in above statement.
- The end output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:

Now we can check the current value of max_allowed_packet as follows.
We can again execute the following statement to see the current value.
Code:
show variables like 'max_allowed_packet';Explanation:
- In above statement we use show variables command to see the current value of max_allowed_packet function, here like clause is used to search specified system variable that is we need to search that is max_allowed_packet function value.
- The end output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
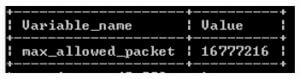
Now let’s see the second way to set max_allowed_packet system variable value by using my.cnf file as follows.
In which first we need to search the my.cnf file on our system location that is the install location of MariaDB server.
After that we need to open that file in any edit tool or we can also open in notepad and to check max_allowed_packet system variable is available or not, if this system variable is not present then we add manually in my.cnf within the mysqld file with size or we can say value of system variable.
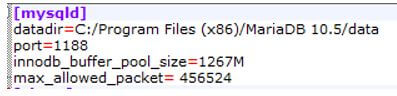
In the above screenshot we manually add the value of max_allowed_packet within the mysqld as shown in the above screenshot. After that we will need to restart the MariaDB server.
Notice here if we set a specific value of max_allowed_packet and we created a simple table, and we try to insert a greater value than max_allowed_packet size then it shows an error message. So we must have the same value at both sides and less than system variable size.
Conclusion
From this article we saw the basic syntax of max_allowed_packet and we also saw different examples of max_allowed_packet. From this article we saw how and when we use MariaDB max_allowed_packet.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB max_allowed_packet” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

