Updated June 3, 2023
Definition of MariaDB IF Statement
MariaDB provides an IF conditional statement to the user, In which we can implement a basic IF conditional statement, IF search condition shows true or false statement during the SQL query execution. If the search condition does not match the specified value, then the SQL statement executes the else statement and consists of one or more words. IF () function totally differs from the IF statement as explained above statement. Normally IF statements have three different forms: IF – THEN statement, IF – THEN – ELSE statement, and IF-THEN – ELSEIF – ELSE statement. With the conditional statement, we can perform different operations.
Syntax:
If condition
begin
if above-mentioned condition is true then it execute following expression
true expression;
end
else
begin
if above-mentioned condition is false then it execute following expression
false expression
end;Explanation:
In above syntax, we use an IF conditional statement with the condition, here IF condition is true, then it executes the true expression otherwise, it goes to the else part, and it runs the false expression when the IF condition is false, and we also use begin and end keywords to identify the IF – ELSE statement as shown in above syntax.
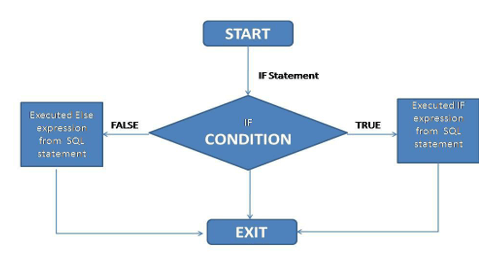
Flow Chart
Let’s set how the IF statement is working with the help of a flow chart as follows.
Explanation:
MariaDB IF statement should return a Boolean value.
After that, we can specify the select statement with an expression we need to execute, but it should be in parentheses.
In the above flowchart, we use START and EXIT in the IF statement to determine the IF statement.
The ELSE condition of the IF statement is optional and depends on the user.
How if statement works in MariaDB?
Let’s see how the IF statement works in MariaDB as below.
In IF statements, all the specified conditions with IF statements are executed sequentially, which means it executes the first condition from the statement. So let’s see how we can use IF statements in three different ways as follows.
1. IF – THEN statement
In this type, we only use IF – THEN statement, in which it executes only the IF part if the condition is true otherwise, it executes the THEN part, that means if the condition is false.
2. IF – THEN – ELSE statement
In this type, we use IF – THEN – ELSE statement, in which if condition is true, then it executes if expression, and if condition is false, then it executes the else part of the IF statement.
3. IF – THEN – ELSEIF statement.
In this, we used an ELSEIF statement with different expressions, and it executed the same as the above types.
When a condition is found that means true, then the IF-THEN-ELSE statement will execute related expressions otherwise not evaluate any expression.
If the condition is false, that means the ELSE part of the IF-THEN-ELSE statement will be executed. This is very impotent, not that the ELSEIF and ELSE both condition are optional.
Examples
Let’s see the different examples of IF statements in MariaDB below.
set @myId = (SELECT IF ((SELECT count(2) FROM `emp` WHERE `emp_id` = 2 AND `emp_dept`='2') = 3, TRUE, FALSE));Explanation:
In the above example, we use the IF statement with the select and where clause, as shown in the above statement. Here we set the different values for the specified column mentioned in the above statement with a Boolean expression. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
DELIMITER $$
USE sample $$
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS my_demo $$
CREATE PROCEDURE
my_demo ()
BEGIN
IF 1=1
THEN
SELECT 1;
END IF;
END $$Explanation:
In the above example, we use a delimiter to create a new procedure using an if statement. We use a sample database in this example, as shown in the above statement. After that, we create a new procedure using the create procedure statement, here, we create my_demo procedure. After that, we use IF – THEN statement as shown in the above statement. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
Now let’s see how we can combine all IF statements as follows.
DELIMITER //
CREATE FUNCTION sample_demo ( count INT )
RETURNS varchar(20) DETERMINISTIC
BEGIN
DECLARE size varchar(20);
IF count < 500 THEN
SET size = 'Low';
ELSEIF count >= 500 AND count <= 4000 THEN
SET size = 'Medium';
ELSE
SET size = 'High';
END IF;
RETURN size;
END; //
DELIMITER ;Explanation:
In the above example, we create a function name as sample_demo as shown in the above statement in which we set different values by using the IF statement such IF count is less than 500, THEN we set size is low, similarly ELSE IF count >= 500 AND count <= 4000 THEN we set size is medium and ELSE size is high. After that, we return the size, then the end function, and the end IF statement. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
Now see a simple example of an IF – ELSE statement as follows.
DELIMITER $
CREATE PROCEDURE my_pr()
BEGIN
IF 2 = 2 THEN
SELECT 'TRUE';
ELSE
SELECT 'FALSE';
END IF;
END $
DELIMITER ;
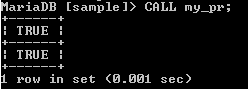
CALL my_pr;Explanation:
In the above example, we created a procedure name demo1, as shown in the above statement, in which we use the IF ELSE statement, here condition is that IF we have 4 = 4, then select the true value otherwise, it returns the false values. When we execute the above statement, it simply shows the query is ok, so we need to execute the procedure by using the above-mentioned statement, such as call my_pr. We illustrate the final output of the above query using the following snapshot.
In the above screenshot, we show the procedure result, and when we run the call my_pr, the result is shown in the screenshot below.
CALL my_pr;Conclusion
We hope from this article, you have understood the MariaDB IF statement. From this article, we have learned the basic syntax of the MariaDB IF statement, and we also see different examples of the MariaDB IF statement. This article taught us how and when to use MariaDB IF statements.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB IF” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.