Updated April 12, 2023
Definition of MariaDB Functions
- MariaDB functions are stated as the stored program in the server which a user can pass the required parameters into and after that returning a value as output. The MariaDB functions can be created and dropped out too.
- MariaDB includes many stored functions and procedures which consist of aggregate functions such as MIN, MAX, COUNT, SUM, AVG, and so on.
- The MariaDB functions also comprises of Date and Time type of functions like CURDATE(), DATE(), CURTIME(), DATEDIFF(), NOW(), DATE FROMAT(), HOUR(), MINUTE(), SECOND(), etc.
- Again, the MariaDB functions extends to have the numeric type also such as TRUNCATE(), COS(), DIV(), DEGREES(), EXP(), FLOOR(), LN(), LOG(), SQRT(), etc.
- The string functions are included in this MariaDB functions like RIGHT(), INSTR(), LENGTH(), INSERT(), LOCATE(), LOWER(), REPLACE(), REPEAT(), SUBSTRING(), TRIM() and so on.
MariaDB Functions
The functions can be created in other languages too, so a user can create his/her own functions in MariaDB. We have the following syntax for creating a function in the MariaDB server:
CREATE [ DEFINER = {UserName | Current_User } ]
FUNCTION FunctionName [ (datatype of parameter [, datatype of parameter])]
RETURNS datatype_of_return [ Language SQL | Deterministic | Non Deterministic | {NO SQL | CONTAINS SQL | MODIFIES SQL DATA | READS SQL DATA} | SQL SECURITY {INVOKER | DEFINER} | COMMENT ‘value_of_comment’]
BEGIN
Declaration_section
Executable_section
END;Let us explain the terms used in the above syntax structure:
- DEFINER: DEFINER is the clause that is optionally applied and if not present then the definer specifies the user that has created the MariaDB function. Whereas if anyone want to state the definer name as a specific one then, we must involve the clause DEFINER in the function where UserName denotes the definer.
- FunctionName: In MariaDB, it provides a name to the function while creating it.
- Parameter: It denotes the parameter either one or many that are passed into the MariaDB function. All parameters should be reflected to be IN parameters (INOUT or not OUT parameters) while building a function where these function parameters may be referenced by this function but cannot be overwritten by the MariaDB function.
- Datatype_of_return: It defines the datatype of the return value of the MariaDB function.
- Language SQL: It is present in the syntax code of the function for movability but this will cause no influence on the function.
- Deterministic: It is responsible for returning only one result always of the function provided a set of input function parameters.
- Non-Deterministic: It is responsible for returning an unalike result of the function provided a set of input function parameters. This output result will be affected by the data of table, server variables, or random numbers.
- CONTAINS SQL: It is a default type and an informative clause that conveys MariaDB server that the function includes SQL but the MariaDB database may not confirm that it is true.
- NO SQL: It is revealing clause which is not implemented and may not have any influence on the function in MariaDB.
- READS SQL DATA: This is also a helpful clause that instructs MariaDB server that the function will perform reading of data using the SELECT query statements but cannot alter the data.
- MODIFIES SQL DATA: It also denotes an illuminating clause which states MariaDB server that this function may change the SQL data by means of UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE, and other type of DDL statements.
- Declaration_section: It defines the area in the function in MariaDB where we declare_local_variables.
- Executable_section: It defines the area in the function in MariaDB where the user inserts the code for the function.
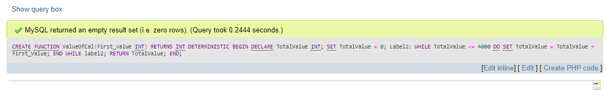
For demonstration, suppose we have the following syntax code to implement the function creation in the MariaDB server:
DELIMITER//
CREATE FUNCTION ValueOfCal(First_value INT)
RETURNS INT DETERMINISTIC
BEGIN
DECLARE TotalValue INT;
SET TotalValue = 0;
Label2: WHILE TotalValue <= 4000 DO
SET TotalValue =TotalValue + First_Value;
END WHILE label2;
RETURN TotalValue;
END; //
DELIMITER;Output:
Now, the user can reference the new function created as follows:
SELECT ValueOfCal (2000);Output:

After execution, the query above will provide the result as specified.
If the user wants to view all the stored functions in MariaDB, then we need to use the SHOW statement as follows:
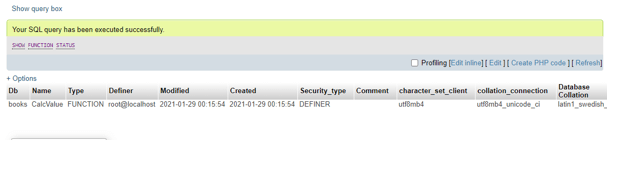
SHOW FUNCTION STATUS;Output:
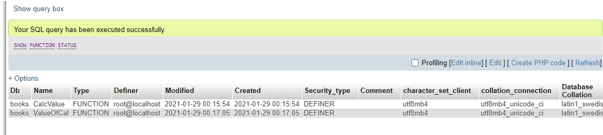
As you can see that in the MariaDB database named books there are two functions created and active to work with. This query command provides as result all the characteristics of stored functions. But do remember that this Show Function Status; command fetches the functions which we have been granted as privileges to access.
Suppose, if we want to view any particular stored functions in the database then we will apply the WHERE clause with the query holding a search condition for function name as:
SHOW FUNCTION STATUS WHERE searching_condition;Also, with LIKE clause one can put the search condition in the SHOW query to fetch specifically named functions using the pattern search as below:
SHOW FUNCTION STATUS LIKE '%Specific pattern%';Drop Function:
In MariaDB, once the MariaDB function is created, after some time the user might need to delete it from the database server. Then, for this the syntax will be written using the DROP keyword as follows:
DROP FUCNTION {IF EXISTS} Name_of_Function;Here, the Name_of_Function term defines the name of the MariaDB function that was created and now the user wishes to remove it.
Therefore, let us view an example illustrating the drop of a function in MariaDB server and how to code for it as follows:
DROP FUNCTION ValueOfCal;Output:
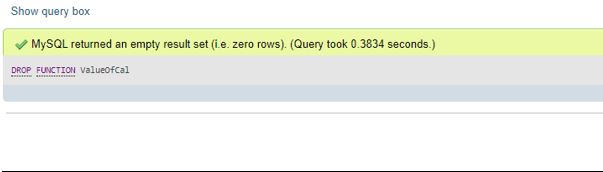
Here, we have mentioned the function created previously and that will be dropped now when the above function will be executed. If we run the show command, then the result will be as follows:
SHOW FUNCTION STATUS;Output:
Conclusion
- Contrasting to the procedures, a user should provide parameters to the MariaDB functions and this function should output a value as result. MariaDB maintenances the VALUES statement which makes it calmer for testing a function created as MariaDB functions in the server.
- MariaDB functions cover stored aggregate type functions composing structured values which help to read different table rows and return values.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB Functions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

