Updated April 12, 2023
Introduction to MariaDB Encryption
MariaDB provides the encryption functionality to the user, in which we can encrypt customer data, product design, tables, database and construction plan etc. We can also store the other information that is stored into the text on system storage media. Everyone is able to read data, write data or we can say modify the data. If all stored data or any other information falls into the wrong hands that is competitors in our area or criminal, so this may cause serious issues. They can make any changes or they can hack our system. But with the help of an encryption method we protect our databases, tables or any other information.
Syntax:
MariaDB [] alter table specified table name encrypted = YES;Explanation:
- In the above syntax we use alter table command with specified table name that table we need to encrypt with parameter YES as shown in above syntax.
How to Perform Encryption in MariaDB?
Normally all data means database, table and other information not fall into the possible attackers hands, so we need to encrypt some information that information should be protected from attackers such as personal information, customers details, financial and credit card details and other important information we can encrypt.
For encryption we required the key management that we called encryption plugin as below:
When we encrypt the data at that time we require the use of key management and encryption plugin. This key management is responsible for encryption key as well as actual encryption and decryption data. MariaDB supports the multiple key encryption method. a 32 bit integer identifier is used to each encryption key then the plugin is rotated after that encryption key is also rotated. The key management and encryption plugin it reads the keys from a plain text file. Encryption of data is the most important feature to maintain security of data.
There are two main types of data encryption as follows:
1. Data – At – Rest Encryption
Stored data in a system we called data at rest. In this type we can encrypt data by using a different algorithm to convert plain text into the unreadable text or we can say code. When we need to decode that code we must have an encryption key to decode that code. We also encrypt the entire database but it causes a serious performance impact, so that reason we encrypt database individuals or tables. In this type we can protect data from physical theft of hard drives or unauthorized access of storage, this type we also maintain the security regulation standards.
2. Data – In – Transit Encryption
When we send data from one location to another location or we can say data is moving between the different transactions this process is known as data in transit encryption method. The best example of this type is data moving between client and server while browsing web pages. In this type data is always in a moving state so we need to protect them by using different algorithms to avoid theft or alteration of data before it reaches its destination. The main thing in this type to protect data is to encrypt that before moving data in the network and it only decodes when it reaches the desired destination.
Examples of MariaDB Encryption
Given below are the examples of MariaDB Encryption:
Follow the following steps to configure encryption support.
a. First we need to edit the configuration file depending on our installation types that is location of configuration file, the name of file is my.cnf that we need to edit.
b. After that we will need to add some lines in my.cnf file with the mysqld section, to activate the keyring file plugin.
early – plugin – load=keyring_file.so
keyring_file_data= system path
c. After adding the above line into the my.cnf file, we must restart the MariaDB server. Note here the keyring file is automatically created in the mentioned path when the first table is encrypted.
d. In the next step we need to confirm the keyring file plugin is activated by executing the query.
Now we are able to create an encrypted table as follows:
Example #1
Code:
create table demo (id int, name varchar(200), address varchar(200)) encryption='Y';Explanation:
- In the above example we use the create table command to create a new table name as a demo with different attributes such as id, name and address as shown in the above statement. At the end of the statement we add an encryption keyword with Y clause to encrypt the demo table.
- The end output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Suppose we have already created a table and we need to encrypt that table.
At that time we use the following syntax as follows:
Syntax:
alter table specified table name encryption='Y';Explanation:
- In above syntax we use alter table command with specified table name means actual table name and at the end of syntax we add encryption keyword with Y clause as shown in above syntax.
Example #2
We have an already created table name emp with different attributes, now we need to encrypt the emp table so that we can use the following statement as follows.
Code:
alter table emp encryption='Y';Explanation:
- In the above example we use the alter table command to encrypt the emp table with encryption keyword and Y clause as shown in above statement.
- The end output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
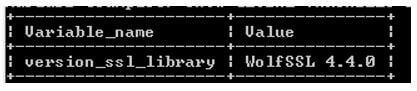
When we need to encrypt data between client and server using Transport Layer Security Protocol, we must ensure that MariaDB server compiled TLS protocol and that can be checked by using the following statement.
Code:
SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'version_ssl_library';Explanation:
- The end output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
Conclusion
From this article we saw the basic syntax of encryption and we also saw different examples of encryption. From this article we saw how and when we use MariaDB encryption.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB Encryption” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.