Updated July 4, 2023
Introduction to MariaDB Boolean
The MariaDB Boolean Type is a data type in MariaDB that stores values for Boolean query operations, defining them as TRUE or FALSE. In Maria, while we design a database, we have to consider several present data types to choose the finest ones for saving the data records, including numerical type, Temporal, string, and Spatial data types. The numeric type contains different data types supported: TINYINT, SMALLINT, MEDIUMINT, INT, BIGINT, DECIMAL, FLOAT, DOUBLE, and BIT. Hence, MariaDB implements the TINYINT (1) to represent the server operations’ Boolean values. But here, for true, we will use non-zero (1); for false, we will use zero (0). We can denote BOOL and BOOLEAN as synonyms of TINYINT (1).
Syntax:
Let us discuss the syntax for Boolean Data type in MariaDB as follows:
To apply Boolean literals, a user needs to implement the constants TRUE and FALSE, which calculate to 1 and 0 simultaneously as coded below:
SELECT true, false, False, True, FALSE, TRUE;Here, we have typed a command above using the SELECT statement to view the case sensitivity, which gives output as 100101, where 1 associate with the true value and 0 associates with a false one.
We will use the Boolean type while adding a column to hold the Boolean values in table creation which has the syntax structure as follows:
CREATE TABLE TableName (Column1 data type constraints, Column2 data type constraints,….., Column5 BOOLEAN,……..ColumnN data type constraints);Here, the TableName denotes the table name, and the column with data type as BOOLEAN defines the table column having the Boolean value as True and False.
How does the Boolean Type Work in MariaDB?
In MariaDB, the Boolean type holds the following syntax structure BOOL, BOOLEAN. These data types describe the substitutes for the TINYINT(1), where the value 0 is considered false and non-zero ones are considered true. We know the true and false values as the pseudonyms for 1 and 0. You can use the IS operator for testing the values against a Boolean type.
For illustration, let us write the query as:
CREATE TABLE Bool(j, BOOLEAN);
DESC Bool;It provides the output where the field j in the table bool has type as TINYINT(1), NULL as YES; the Default value is NULL. The TINYINT data type holds the integer values within the range of -128 to 127 signed in MariaDB.
Examples of MariaDB Boolean
Let us illustrate the MariaDB Boolean type commands in the server and view their respective outputs as follows:
MariaDB stores this Boolean value in the database table as an integer. We will demonstrate the statement with the example below by creating a table defined as Task using data types related to table columns as specified:
CREATE TABLE Task (TaskID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, Task_Title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, Task_Completed BOOLEAN);Output:
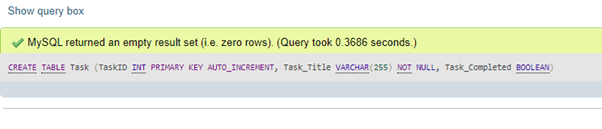
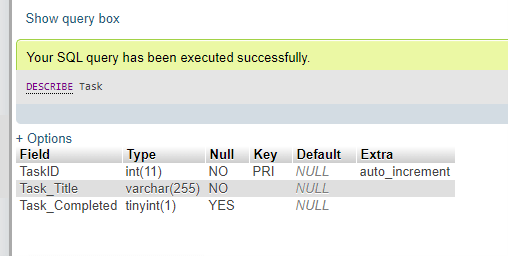
The above table creates a Boolean column with Boolean values to be stored along with other related table columns in the MariaDB table named Task_Completed. But we will view the table definition using the DESCRIBE TABLE keyword command; then it will show the column data type as TINYINT(1) even when defined the column is BOOLEAN type.
So, let us have a look at the query executed as:
DESCRIBE Task;Output:
Now, we will enter some record rows in the table using the INSERT query statement:
INSERT INTO Task(Task_Title, Task_Completed) VALUES('MariaDB Boolean value', True),('Create Table in database', False);The query execution in MariaDB will insert the column value into the table Task. Before storing the row values in the Boolean columns, the system will convert the Boolean values into 0 or 1 in MariaDB. Hence, we can view the table contents using the SELECT keyword to retrieve the Task table data, as shown below:
SELECT Task_ID, Task_Title, Task_Completed FROM Task;Output:
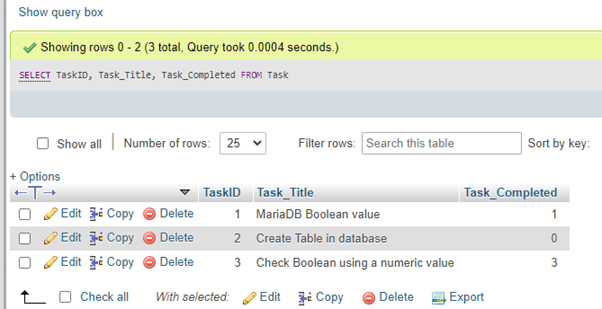
As you can see that the Boolean Table column value is converted as 1 for true and 0 for false. Since Boolean is TINYINT(1) therefore, we can enter a value other than 0 and 1 into the Task table Boolean column, which can be illustrated with the query below:
INSERT INTO Task(Task_Title, Task_Completed) VALUES('Check Boolean using a numeric value',3);
select * from task;Let us view the output, which is functioning fine as:
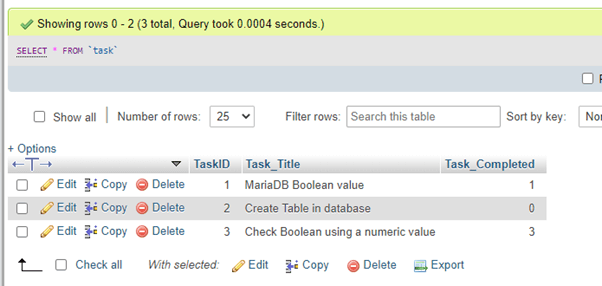
Suppose if you need to produce the output result as TRUE and FALSE; then, we can involve the IF function in MariaDB with the previous query as follows:
SELECT TaskID, Task_Title, IF(Task_Completed,'True','False') Task_Completed FROM Task;Output:
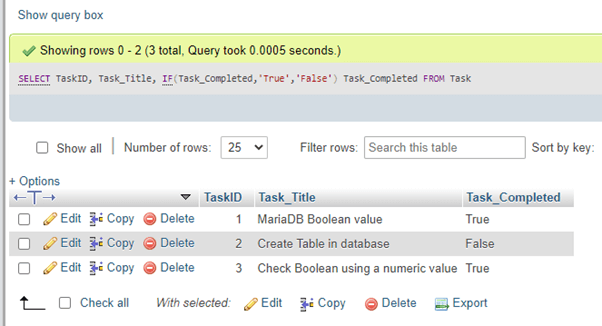
As you can see, we present the Boolean values as True and False values.
MariaDB Boolean Operators
To retrieve all the tasks that are completed from the Task table, you can use the following query code:
SELECT TaskID, Task_Title, Task_Completed FROM Task WHERE Task_Completed = TRUE;Output:
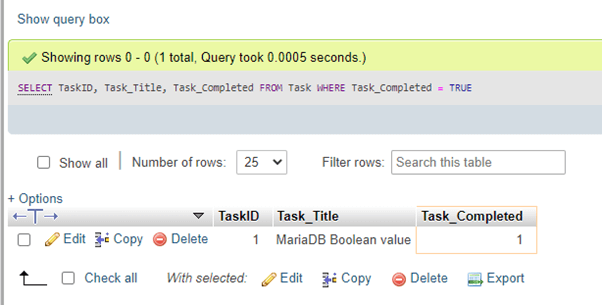
As you can see from the above result, only the completed task holds a value as 1(true) and is returned when the query is executed. You can fix this. We must apply the IS operator in the query statement as:
SELECT TaskID, Task_Title, Task_Completed FROM Task WHERE Task_Completed IS TRUE;Output:
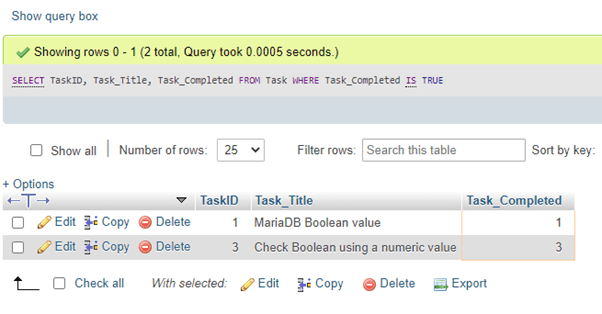
In this instance, we have used the operator IS in the SELECT query statement to check a value against the Boolean type value.
To retrieve the values of the pending or remaining task from the Task table, we will use the keywords “IS FALSE” or “IS NOT TRUE” in the following manner:
SELECT TaskID, Task_Title, Task_Completed FROM Task WHERE Task_Completed IS NOT TRUE;Output:
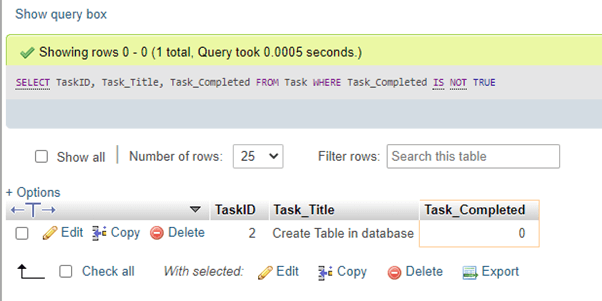
As you can see, the query displayed the row with the Boolean value 0, i.e., false, because it used the keyword “IS NOT TRUE.”
Conclusion
MariaDB Boolean Type is a MariaDB data type from the numeric type, which denotes the TINYINT type where a zero value defines the false part, and a non-zero value means for true one in the query operations. Since MariaDB or MySQL does not support any built-in numeric type as Boolean values, perhaps it provides the TINYINT data type to conveniently use BOOL or BOOLEAN as a substitute for TINYINT (1).
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB boolean” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

