Updated April 12, 2023

Introduction to MariaDB alters table.
MariaDB provides alter table functionality to the user, in which we can change the structure of existing tables. For example, we can add columns into the specified table or delete a column from the table, create or delete indexes; we can change the datatype of the existing column, rename column name, and we can also change the storage engine of the table. If we use another connection for the alter command, if the metadata lock is active, then the alter statement will wait until the lock is released. When we need to add a unique index on a column that specified duplicate values, then alter command shows an error message, and statement execution will be stopped. The alter command is also used to rename the table name.
Syntax:
alter table table_name add new colm name column structure or definition [before colm name | after colm name];Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we used the alter table command to add a new column name into the table.
- In this syntax, table name means specified table name and add the keyword used to add a new column into the specified table with column definition or structure that means null or not null etc.
- Here before column name and after column name is an optional part of this syntax, and it is used to indicate where in the table we need to create the column.
How to alter the table in MariaDB?
- Basically, alter table command comes under the data definition language.
- In MariaDB, alter table statements are useful to change the structure of tables, or we can change the definition of columns. Altering tables in the column is a big task, or we can say this is not very difficult; but some database developers are not familiar with the alter command, but with the help of alter command syntax, we can easily perform different operations.
- We can use different clauses to alter table statements.
Examples of MariaDB alter table.
Given below are the examples of MariaDB alter table:
First, we need a table to perform different operations of the alter table command, so by using the following statement, we can create a table.
Code:
create table stud1(
stud_id int auto_increment,
stud_name varchar(255) not null,
address varchar(255) not null,
primary key (stud_id));Explanation:
- In the above example, we created a table name as a stud1 with different attributes. The stud1 table has a 3 column as shown in the above statement.
- The stud_id is an integer column with auto_increment property, so MariaDB will automatically increment a sequential number when we insert a new row into the table. In addition, the stud_id column is a primary key specified by using the primary key constraint as shown at the end of the statement, and the primary key constraint is useful to identify unique rows in the table.
- stud_name is a variable-length character with a maximum size of the character. The stud_name has a not-null constraint that means we cannot insert null values into this column.
- The address is a variable-length character with a maximum size of the character, and it also has a not-null constraint.
Output:
![]()
After that, we insert some records into the stud1 table by using insert into statement. The final definition of the stud1 table is shown in the below snapshot.
Code:
select * from stud1;Output:
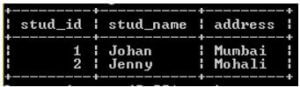
Example #1
Change Column.
Suppose we need to modify the stud_id column definition, in which we modify the data type of the stud_id column by using the following statement.
Code:
ALTER TABLE stud1 MODIFY stud_id BIGINT UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT;Explanation:
- In the above example, we use the alter table command to modify the data type of the stud_id column, here we add a new data type BIGINT UNSIGNED instead of INT data type as shown in the above statement.
- The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:

Example #2
Change Column.
In this type of example, we can change the column as follows.
Code:
ALTER TABLE stud1 ALTER address SET DEFAULT 'Mumbai';Explanation:
- In the above example, we alter the address column; in this example, we set the default value of the address column as Mumbai, as shown in the above statement.
- The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
![]()
Example #3
Rename column of Table.
In this type of example, we can change the table’s column name by using the alter table command as follows.
Code:
ALTER TABLE stud1 RENAME column stud_id TO roll_no;Explanation:
- In the above example, we use the rename column command to change the column name as in this example; we changed the column name of stud_id to roll_no by using the alter table command with rename column clause as shown in the above statement.
- The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Code:
select * from stud1;Output:

In the above screenshot, we can see the updated column name.
Example #4
Drop by default clause.
Code:
ALTER TABLE stud1 ALTER address DROP DEFAULTExplanation:
- In the above example, we use the alter table command to drop the default value column. In this example, we drop the default value of the address column as shown above example.
- The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:
![]()
Example #5
Rename Table Name.
We can also change the table name by using the following statement.
Code:
ALTER TABLE stud1 RENAME TO college_stud;Explanation:
- In the above example, we change the table name by using rename keyword here; we change table name stud1 to college_stud as shown in the above statement.
- The final output of the above query we illustrate by using the following snapshot.
Output:

In this way, similarly, we can perform add primary key, drop primary key, add foreign key, drop foreign key, add an index, drop index etc.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MariaDB alter table” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

