Introduction to Management by Objectives
In a competitive business environment where efficiency, productivity, and innovation determine success, organizations cannot afford to run without a clear direction. Employees often lose motivation when they do not see how their work contributes to the bigger picture. To address this gap, businesses need a framework that aligns individual performance with organizational goals.
This is where Management by Objectives (MBO) becomes highly valuable. MBO, introduced by Peter Drucker in 1954, focuses on setting clear objectives agreed upon by both management and employees. Unlike traditional management methods that rely heavily on supervision and control, MBO empowers employees to take ownership of their performance.
In this article, we will cover everything about MBO: its meaning, process, features, advantages, limitations, best practices, and practical examples.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Management by Objectives (MBO)?
- Key Features of Management by Objectives (MBO)
- Process of Implementing Management by Objectives (MBO)
- Benefits of Management by Objectives
- Challenges and Limitations of MBO
- Best Practices for Effective MBO Implementation
- Real-World Applications of MBO
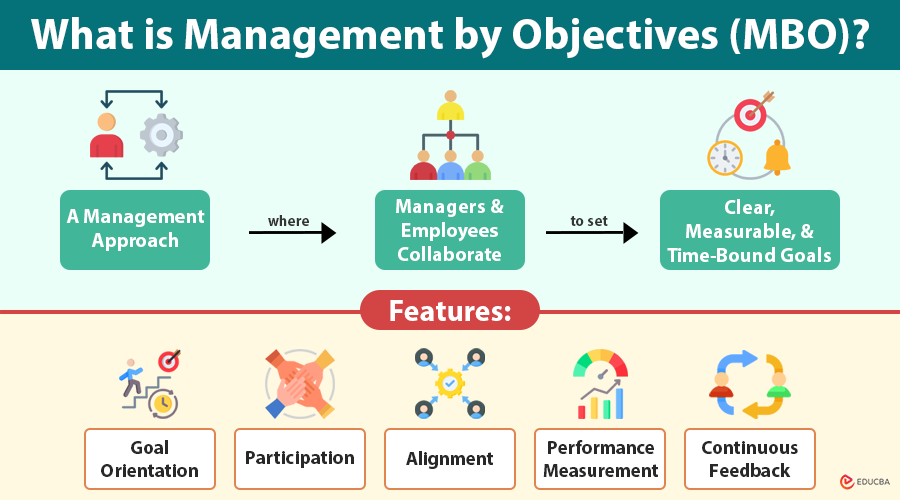
What is Management by Objectives (MBO)?
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a management approach where managers and employees collaborate to set clear, measurable, and time-bound goals. The company aligns these objectives with its broader mission and vision.
The philosophy behind MBO is simple:
- When employees clearly understand expectations, they perform at their best.
- Measuring goals allows us to track progress more objectively.
- When employees are part of the goal-setting process, they feel motivated and accountable.
For example, in a software company, the organizational goal might be to increase market share by 10% in the next fiscal year. To achieve this:
- The marketing team could set a target to improve brand visibility through five major campaigns.
- The sales team could aim for 1,000 new customer acquisitions within six months.
- The development team could plan two major feature upgrades in the product roadmap.
Thus, individual and departmental goals collectively support the company’s main objective.
Key Features of Management by Objectives (MBO)
Here are the key features of management by objectives:
1. Goal Orientation
MBO is fundamentally results-driven, with a primary focus on clearly defined objectives rather than routine tasks. These objectives are specific, measurable, and time-bound, ensuring that employees work toward well-established outcomes. By emphasizing results, organizations can avoid ambiguity and measure success with greater accuracy.
2. Participation
A distinguishing feature of MBO is its participatory nature, where employees are actively involved in setting their own objectives in consultation with their managers. This approach creates ownership and commitment, motivating employees to achieve goals they helped set.
Participation also encourages creativity and problem-solving, as employees feel empowered to suggest realistic and innovative ways to achieve their targets.
3. Alignment
MBO ensures a top-down alignment of objectives, linking organizational goals with departmental, team, and individual performance. This approach links every employee’s contribution directly to the organization’s larger mission and vision.
Such alignment minimizes duplication of effort and prevents departments from working in isolation. It creates synergy across different functions, ensuring that progress at the micro level contributes meaningfully to macro-level success.
4. Performance Measurement
MBO measures performance by comparing results against predetermined benchmarks. Regularly monitoring objectives helps managers identify progress and take timely corrective action when needed.
Organizations often track progress using metrics such as Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), productivity ratios, customer satisfaction scores, and financial targets. This systematic evaluation makes the appraisal process transparent and objective.
5. Continuous Feedback
An essential element of MBO is ongoing communication and feedback between managers and employees. Managers conduct regular performance reviews to keep employees aligned with organizational goals and adjust objectives when conditions change.
Continuous feedback also motivates employees by recognizing achievements and addressing gaps constructively. This two-way communication fosters trust, strengthens relationships, and creates a culture of continuous improvement.
Process of Implementing Management by Objectives (MBO)
The implementation of management by objectives follows a structured, systematic approach, ensuring alignment between organizational strategy and individual performance. The process typically involves the following stages:
1. Establish Organizational Objectives
The first stage involves defining the strategic goals of the organization. Senior management identifies long-term objectives that are consistent with the company’s vision, mission, and overall business strategy. These goals provide a framework for cascading objectives to lower levels of the organization.
Importance: Clear organizational objectives guide the organization, prioritize resources, and serve as a reference point for measuring all subsequent objectives.
2. Cascade Goals to Departments and Teams
After defining organizational objectives, managers translate them into departmental and team-level objectives. This ensures that every function contributes directly to the overall goals of the organization.
Importance: Cascading goals help align the organization, avoid duplication, and ensure everyone works together toward the same purpose.
3. Set Individual Objectives
In this stage, managers and employees collaboratively establish individual objectives. This participative approach ensures that employees clearly understand their responsibilities and feel a sense of ownership over their performance.
Importance: Jointly set objectives to increase employee motivation, foster accountability, and enhance clarity regarding expected outcomes.
4. Develop Action Plans
After setting objectives, teams develop detailed action plans that specify the steps to achieve the goals. Action plans define resource allocation, timelines, specific responsibilities, and performance indicators.
Importance: Action plans provide a roadmap for execution, reduce ambiguity, and ensure that employees have the resources and guidance necessary to succeed.
5. Monitor Progress
Continuous monitoring is critical to the MBO process. Managers track performance against the objectives through regular reviews, key performance indicators (KPIs), and progress reports. This stage also includes providing support or interventions if challenges arise.
Importance: Ongoing monitoring ensures timely adjustments, maintains focus on goals, and prevents deviation from desired outcomes.
6. Evaluate Performance
Performance evaluation involves comparing actual results against the predefined objectives. This assessment serves as the basis for appraisals, promotions, and other HR decisions. Organizations often formalize it through performance reviews or rating systems.
Importance: Evaluation ensures accountability, recognizes achievement, and identifies areas for improvement or training.
7. Provide Feedback and Recognition
The final stage emphasizes constructive feedback and recognition of accomplishments. Managers discuss performance with employees, acknowledge successes, and recommend improvements where necessary. Recognition may include promotions, bonuses, awards, or public appreciation.
Importance: Regular feedback and recognition encourage good behavior, lift employee morale, and support continuous improvement.
Benefits of Management by Objectives
The adoption of MBO provides several notable advantages:
- Clarity of roles and expectations: Employees understand their roles and how they contribute to the organization’s success.
- Enhanced motivation: Involvement in goal-setting fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, leading to increased motivation.
- Objective evaluation: Quantifiable goals reduce bias in performance assessments.
- Improved communication: Promotes two-way dialogue between managers and subordinates.
- Organizational alignment: Ensures that individual and departmental goals support strategic objectives.
- Focus on results: Encourages a performance-based culture rather than activity-based evaluation.
- Employee development: Feedback and goal-setting contribute to professional growth.
Challenges and Limitations of MBO
Despite its advantages, MBO is not without limitations:
- Time-intensive process: Goal-setting and review discussions require significant managerial effort.
- Overemphasis on quantifiable goals: Managers may overlook qualitative factors such as creativity and teamwork.
- Environmental uncertainty: Objectives may become irrelevant in rapidly changing business contexts.
- Conflict of interest: Individual goals may not always align seamlessly with organizational priorities.
- Measurement difficulties: Certain objectives, such as innovation or leadership, may not be easily measurable.
- Risk of short-term orientation: Employees may prioritize immediate results over long-term sustainability.
Best Practices for Effective MBO Implementation
To maximize the impact of management by objectives, organizations should follow these key practices:
- Set SMART goals: Define objectives that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound to provide clear direction and accountability.
- Stay flexible: Adapt objectives as needed to respond to changing business conditions, market dynamics, or internal priorities.
- Foster open communication: Maintain ongoing dialogue between managers and employees to ensure clarity, alignment, and timely feedback.
- Leverage technology: Use digital tools for tracking progress, reporting performance, and providing real-time insights.
- Provide resources & training: Provide employees with the skills, knowledge, and tools they need to reach their goals effectively.
- Recognize and reward achievement: Celebrate successes and incentivize high performance to reinforce positive behavior and motivation.
Real-World Applications of MBO
- Corporate goal alignment: Companies like Google and Intel utilize MBO to ensure that individual objectives align with the overall corporate strategy.
- Performance appraisals: Organizations implement MBO to make employee evaluations more objective, measurable, and transparent.
- Sales and marketing targets: Sales teams set specific revenue and lead-generation goals, improving accountability and performance tracking.
- Project management: MBO helps define clear milestones, deadlines, and deliverables, ensuring every team member knows their role in project success.
Final Thoughts
Management by objectives is a structured management approach that fosters collaboration, accountability, and performance alignment across all levels of an organization. While it requires significant effort in terms of planning and monitoring, its benefits in enhancing motivation, communication, and goal clarity are substantial.
By adopting best practices and maintaining flexibility, organizations can leverage MBO to cultivate a results-oriented, participative, and transparent work culture, thereby driving long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is MBO suitable for all types of organizations?
Answer: While MBO is highly effective for goal-driven organizations, it may be less suitable for very dynamic environments where objectives change frequently or for creative roles where output is harder to quantify.
Q2. How does MBO differ from traditional management styles?
Answer: Unlike traditional management, which often relies on supervision and routine task management, MBO emphasizes collaborative goal-setting, employee accountability, and measurable outcomes.
Q3. Can MBO improve employee engagement?
Answer: Yes. By involving employees in goal-setting and giving them ownership over their objectives, MBO can significantly boost engagement, motivation, and job satisfaction.
Q4. What role do managers play in MBO?
Answer: Managers guide employees in setting realistic objectives, provide resources, monitor progress, give feedback, and recognize achievements, ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
Q5. How is MBO different from OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)?
Answer: MBO focuses on setting specific objectives collaboratively and tracking achievement, while OKRs combine ambitious, stretch objectives with measurable key results to further push performance.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide to Management by Objectives (MBO) helped you understand how goal-setting drives organizational success. Explore our related articles on performance management, employee motivation, and effective goal-setting strategies to enhance workplace productivity.
