Updated August 19, 2023
Definition of Loops in C
Loops in C programming language are a conditional concept used to execute a line or block of code consecutively.
Loops are essential for automating tasks and controlling program flow in C programming. They offer a structured method for accomplishing iterative operations. C programming has three loops: For Loop, While Loop, and Do While Loop. You can also combine loops in C with other control statements like Break, Goto, and Control statements. You can use these loops anywhere in the program, entry, or exit control units.
Table of Contents
Types of Loops in C Programming
There are three different types of Loops in C:
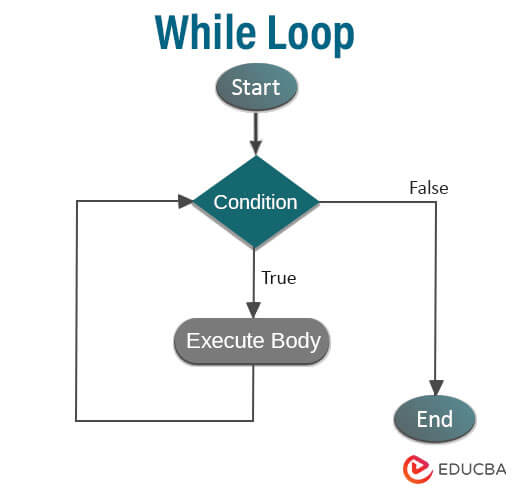
1. While Loop
In this, the condition is evaluated before processing the loop’s body. Only the loop’s body is executed if the condition is true. Then the control goes back to the beginning after completing the loop once. The statements in the loop will be executed again, and if the condition is true and checked, this process goes on until the condition becomes false. The control will go out of the loop if the condition is false. After completion of the loop, the control will go to the statement immediately after the loop, and the body can contain more than one statement. The curly braces are not that important if they have only one statement. If the condition is not true in the while loop, then loop statements won’t get executed.
Syntax:
while (condition) {
statements;
}Flowchart:
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int num=1;
while(num<=5)
{
printf("%d\n",num);
num++;
}
return 0;
}Output:
It will print the numbers from 1 to 5, like below.

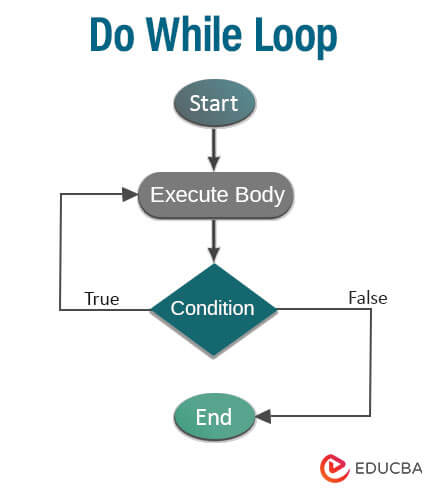
2. Do While Loop
In this loop, the statements need to be executed at least once. After that, it checks the condition. If the condition is true, it will again execute the loop; otherwise, it will exit it. It is known as an exit-controlled loop. It is similar to a while loop, and the condition is always executed after the loop’s body. The while loop is performed only when the condition is true, but sometimes the statement must be conducted at least once, so the do-while loop has to be used. The difference between the while and do-while loops is that in the while loop, the while is written at the beginning, and in the do-while, the condition is mentioned at the end and ends with a semicolon (;).
Syntax:
do {
statements
} while (expression);Flowchart:
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int num=1;
do
{
printf ("%d\n",2*num);
num++;
}
while(num<=5);
return 0;
}Output:
The output of the above program is:

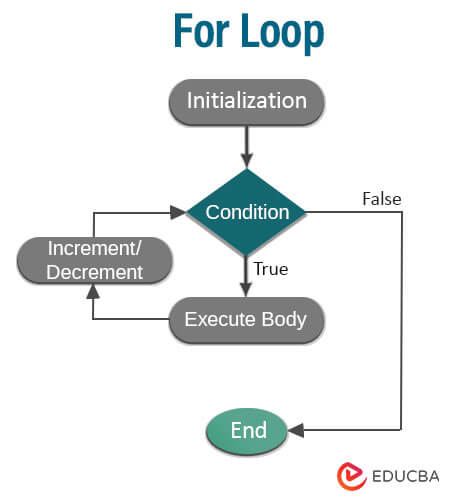
3. For Loop
It executes the set of statements until a particular condition is accomplished. It is known as the Open-ended loop. In the for loop, we can have more than one initialization or increment/decrement, separated using a comma operator and one condition. A for loop is used to evaluate the initialization part first, checking the condition for true or false. If the condition is true, it executes the statements in the for loop. After that, it evaluates the increment or decrement condition until it becomes false and repeats the same steps. It will exit the loop when the condition is false.
Syntax:
for (initial value; condition; incrementation or decrementation )
{
statements;
}Flowchart:
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int number;
for(number=1;number<=5;number++)
{
printf("%d\n",number);
}
return 0;
}Output:

Nested Loops in C
Nested loops refer to loops within loops, which enable the creation of complex repetitive structures. They come in handy when you must carry out specific tasks numerous times, each involving a different set of repetitive actions. In C programming, it’s possible to nest loops of any type, whether for, while, or do-while, within one another. Here’s an explanation of nested loops, along with examples:
1. Nested for Loops
Nested for loops are widely used to generate patterns and grids or to iterate over a two-dimensional array.
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
printf("+ ");
}
printf("\n");
}
}Output:
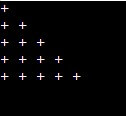
2. Nested while Loops
We use nested while loops to iterate through a condition that involves another condition.
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 2) {
int j = 1;
while (j <= 5) {
printf("%d x %d = %d\n", i, j, i * j);
j++;
}
printf("\n");
i++;
}
return 0;
}Output:
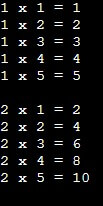
3. Nested do-while Loops
Nested do-while loops are similar to nested while loops. They are useful for tasks that require the repeated execution of specific actions based on a condition.
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int i = 1;
do {
int j = 1;
do {
printf("%d ", j);
j++;
} while (j <= i);
printf("\n");
i++;
} while (i <= 5);
}Output:

Control Statements
Some loop control statements need to be used in loops for different purposes and to achieve the result. Below are the other statements that are used:
1. Break statement
The break statement exits the loop immediately after executing a particular statement for a specific condition.
Syntax:
break;Example
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
if (i == 5) {
printf("Loop terminated at i = %d\n", i);
break;
}
printf("%d ", i);
}
}Output:
![]()
2. Continue Statement
It generally skips statements according to the condition, sends the control directly to the condition, and continues the loop process. It skips the current loop or statements for a particular condition and enters a new one.
Syntax:
continue;Example
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
if (i == 3) {
continue;
}
printf("%d ", i);
}
}Output:
![]()
3. Goto statement
People use it to transfer the protocol to a labeled statement. Although you can use goto to control loop flow, it’s generally not recommended because it can potentially complicate code and make it less readable.
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int number;
number=0;
repeat:
printf ("%d\n",number);
number++;
if(number<=5)
goto repeat;
return 0;
}Output:

Real-Case Examples
1. For Loop
In this example, the for loop simulates a countdown sequence from 3 to 1, with a half-second delay between each number using the usleep function. After completing the countdown, the program prints “Happy Birthday!”.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h> // for usleep function
int main() {
printf("Countdown Begins:\n");
for (int i = 3; i >= 1; i--) {
printf("%d\n", i);
usleep(500000); // Sleep for 500 milliseconds (0.5 seconds)
}
printf("Happy Birthday !\n");
return 0;
}Output:
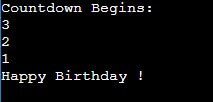
2. While Loop
In this case, the program will continually prompt the user to enter numbers. The loop will keep running until the user enters 0. The break statement will end the loop when the user enters 0. Finally, the program will calculate and display the sum of all the entered numbers.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number, sum = 0;
printf("Enter numbers to calculate their sum (enter 0 to stop):\n");
while (1) {
printf("Number: ");
scanf("%d", &number);
if (number == 0) {
break; // Exit the loop when user enters 0
}
sum += number; // Add the entered number to the sum
}
printf("Sum of the entered numbers is: %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}Output:
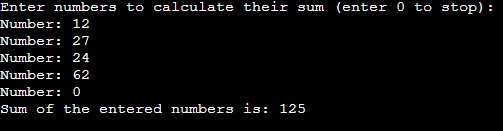
3. Do while Loop
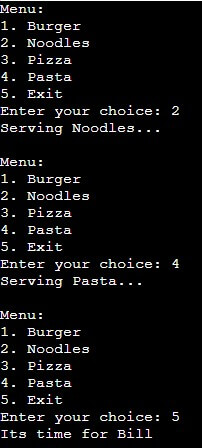
Here is an example of a Restaurant that gives you a menu and serves you according to your choice. The customer can choose from various options, and the loop continues until the user decides to exit by choosing option 5.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int choice;
do {
printf("Menu:\n");
printf("1. Burger\n");
printf("2. Noodles\n");
printf("3. Pizza\n");
printf("4. Pasta\n");
printf("5. Exit\n");
printf("Enter your choice: ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
switch (choice) {
case 1:
printf("Serving Burger...\n");
// Code for Burger
break;
case 2:
printf("Serving Noodles...\n");
// Code for Noodles
break;
case 3:
printf("Serving Pizza...\n");
// Code for Pizza
break;
case 4:
printf("Serving Pasta...\n");
// Code for Pasta
break;
case 5:
printf("Its time for Bill\n");
break;
default:
printf("Invalid choice. Please select a valid option.\n");
}
printf("\n");
} while (choice != 5);
return 0;
}Output:
Importance of Loops in C Programming
- Repetition and Automation: Loops allow you to repeat an operation without writing the same code each time. This proves particularly useful for repetitive activities, such as processing array elements or performing calculations.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Loops can optimize resource usage. Instead of writing repetitive code, developers define and repeat a single block of code as necessary, saving memory and reducing the chances of errors.
- Handling Data Structures: Loops play a vital role in traversing and manipulating arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, and other data structures. They provide an organized method of accessing and processing every element in a collection.
- Generating Patterns: Programmers widely use loops for generating patterns like stars, numbers, or characters, serving various contexts such as graphical representations or output formatting.
- Menu-Driven Programs: Loops are essential when designing interactive menu-driven software that enables users to make choices and perform actions repeatedly. This results in an improved user experience and greater program versatility.
- Calculations and Simulations: Loops play an essential role in iterative calculations and simulations, where programmers update variables based on specific criteria until achieving a desired result.
- Dynamic Program Flow: Loops are important in programming as they offer a way to control a program’s flow dynamically. They enable the creation of flexible structures that adapt to changing data or conditions, allowing for more efficient execution.
- Reduced Code Duplication: Loops prevent code duplication, resulting in cleaner and more maintainable programs. You write the logic once, and the loop does the rest.
- Conditional Execution: Loops run programs based on predefined circumstances. This allows you to make decisions within the loop, such as whether the loop should be continued or terminated based on specific criteria.
- Problem-Solving: Loops facilitate problem-solving by breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable steps that people can iterate over and solve systematically. They are essential tools for solving problems effectively.
FAQs
Q1. What are some common use cases for loops?
Answer: Developers often use loops to iterate through arrays, perform calculations, validate input, generate patterns, and create menu-driven programs.
Q2. How can I prevent infinite loops?
Answer: Ensure that you eventually meet the exit condition of your loop. Double-check your condition and variables to prevent unintentional infinite loops.
Q3. Are there any best practices for writing loop code?
Answer: Keep loop bodies short, use proper indentation, and use meaningful variable names for better code readability and maintenance.
Conclusion – Loops in C
Finally, loops are essential to C programming since they allow for recurring operations and regulated program flow. Understanding their different types – for, while, and do-while – enables developers to handle various scenarios more efficiently. Adhering to recommended practices and controlling loop conditions ensures well-structured and stable code, enabling effective problem-solving and program development.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “Loops in C” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


