Updated March 4, 2023
Introduction to JSON in Oracle
JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation is an open standard data interchange format that stores data objects in attribute-value pair which makes it very readable and value here can be a JSON object )a comma-separated attribute value pairs placed inside curly brackets), JSON array (comma-separated list of JSON objects placed inside square brackets), number, string, Boolean, null due to which it reduces complex parsing as it is very easy to convert a JSON object into a JavaScript object and similarly a JavaScript object to JSON and send JSON to the server. In this topic, we are going to learn about JSON in Oracle.
Syntax
In the case of using JSON in oracle, we will discuss two ways of using json in a relational oracle database. We will discuss the syntax of inserting json in oracle as well as querying json data from the oracle database.
Insert JSON In Oracle
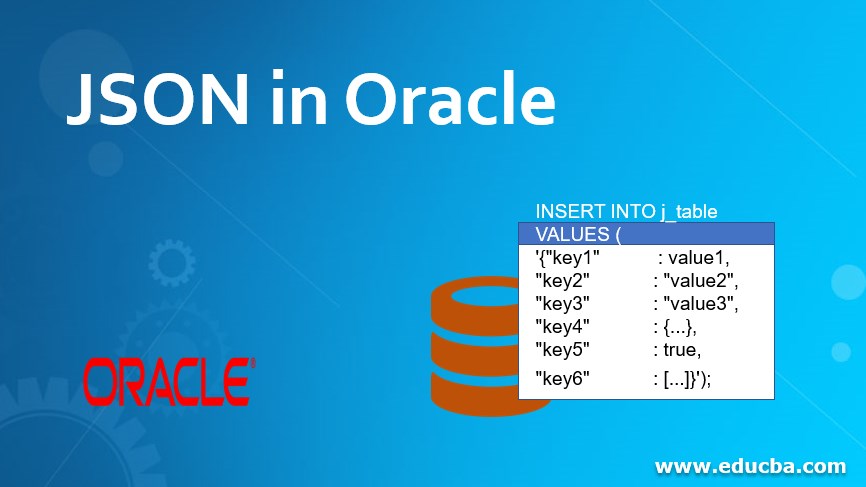
INSERT INTO j_table
VALUES (
'{"key1" : value1,
"key2" : "value2",
"key3" : "value3",
"key4" : {...},
"key5" : true,
"key6" : [...]}');
Parameters
- j_table: A table having one or more JSON column.
- Key: These are strings in the JSON objects surrounded by curly braces
- Value: These are valid data types (string, Boolean, integer, null) separated by a colon from the key in the JSON object.
Query JSON Data in Oracle
SELECT j_table.j_column.jsonKey FROM j_table;
Parameters
- j_table: A table with one or more json column
- j_column: The column having json data
- jsonkey: This will return from each document of the json column the value of the key.
How JSON works in Oracle?
In the previous section, we discussed the syntax of the various cases. Let us now look into How JSON works in oracle. Oracle database places no restrictions to tables that can store json objects which means that a column which has JSON data can co-exist with other columns in the table which do not have JSON data or with other columns which have json data. While creating tables in Oracle database having columns to store json documents we should add a constraint named is_json so that the table only accepts a json document when inserting values in the table as the data type while declaring the json should remain VARCHAR2. While querying the json data from the database, It is very simple as we just need to write a normal SQL SELECT statement the only difference is we need to provide the key for which we want the data. Suppose there is a column named column_json which stores json documents. In that case, we need all the phone numbers as the phone number is stored in the json document along with other fields. So we just mention column_name. phone_number (key) in the select query, this will extract the phone numbers from all the json documents present in that column. The return value will always be a VARCHAR2.
How to Insert Json Data in Oracle with Example?
We are going to look into these using two examples, the first example is How we will create a table which will store JSON data and then we will see how to use insert statement to store data.
We are first going to create a table j_customer which will have three columns. The cust_id column will be the primary key having unique ids for each customer, date when the customer is first inserted and then a json column named cust_doc which will store customer details of every customer in json format.
Query
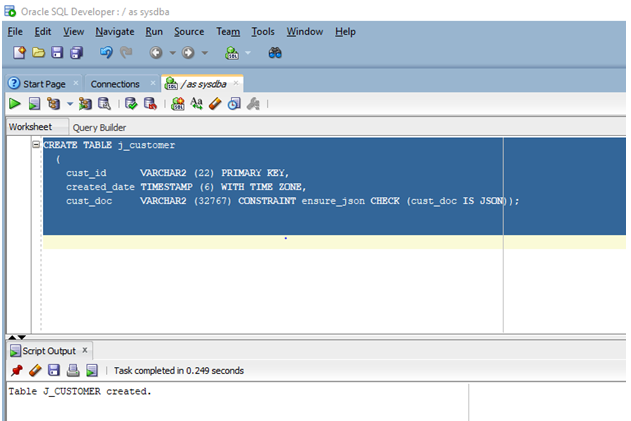
CREATE TABLE j_customer
(
cust_id VARCHAR2 (22) PRIMARY KEY,
created_date TIMESTAMP (6) WITH TIME ZONE,
cust_doc VARCHAR2 (32767) CONSTRAINT ensure_json CHECK (cust_doc IS JSON)
);
If we see the above query we can see that we have used a check constraint is_json to check that only json objects are inserted in the column as the data type of the column is varchar2.
Let us now execute the query in SQL developer.
The screenshot above shows the J_CUSTOMER table has been created successfully.
Let us now insert a column into the J_CUSTOMER table we just created.
We will insert a json document in the column cust_doc along with non json data object in the other two columns of the table j_customer. The insert query is shown below.
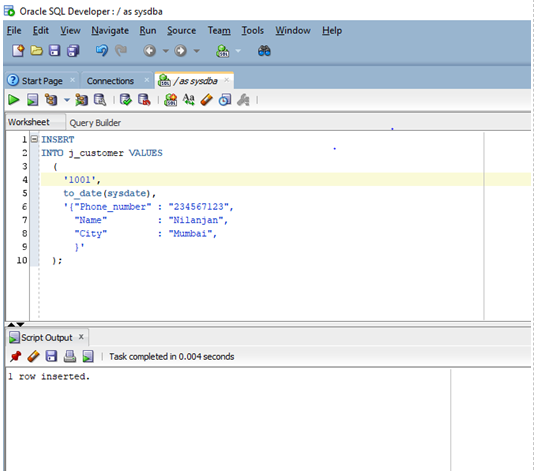
INSERT
INTO j_customer VALUES
(
'1001',
'to_date(sysdate)',
'{"Phone_number" : "234567123",
"Name" : "Nilanjan",
"City" : "Mumbai",
}'
);
In the above query, the json document consists of three key-value pairs. The values of the keys are separated through the colon and the curly braces signify the start and end of the json document.
We will execute the above query in SQL developer.
As we can see in the above screenshot the row has been successfully inserted.
How to Query JSON Data with Example?
In the previous section, we discussed how we can create a table and then insert JSON data. In this section, we will discuss the extraction of json data from a table.
In this example, we are going to extract the values of the key ‘name’ present in the json document stored in column cust_doc.
Let us look at the query for the same.
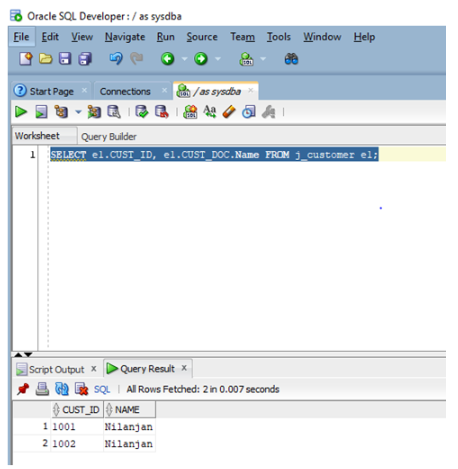
SELECT e1.CUST_ID, e1.CUST_DOC.Name FROM j_customer e1;
In the above query, we are extracting from each document the value of the field/key name which is returned as varchar2.
Let us execute the query in SQL developer.
In the screenshot, we can see the values of the field name along with customer id.
Advantages
Oracle database queries are declarative which means we can join the json data with relational data and similarly query it along with other relational data. We can access JSON data stored in the database the same way we access other data in the database using OCI, JDBC.
Conclusion
In this article we discussed the definition of JSON and how does it actually work in Oracle. Later on in the article we discussed the creating, inserting and extracting of Json data from oracle database using examples from each case.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to JSON in Oracle. Here we discuss How JSON works in Oracle and How to Insert and Query Data in Oracle with examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –