Updated March 24, 2023

Introduction to Java ZoneId
ZoneId is a class in Java. time package, which has been introduced to specify the rules that are needed for conversion between Instant and LocalDateTime. This class is a subclass of ZoneOffset class and also serializable as it implements a Serializable interface. This class uses a particular format that is used to store the offset from UTC/Greenwich only. Being a value-based class, the use of identity-sensitive operations may lead to unpredictable results. This class represents most of the fixed offset IDs that use the same offset for all local date-times.
Syntax of Java ZoneId
Following is a syntax of java zoneid:
Syntax:
public abstract class ZoneId
extends Object
implements SerializableField: public static final Map<String,String> SHORT_IDS – This is an unmodifiable map that consists of mapping of IDs that are in line with TZDB 2005r and later.
This map is as follows:
- EST: -05:00
- HST: -10:00
- MST: -07:00
- ACT: Australia/Darwin
- AET: Australia/Sydney
- AGT: America/Argentina/Buenos_Aires
- ART: Africa/Cairo
- AST: America/Anchorage
- BET: America/Sao_Paulo
- BST: Asia/Dhaka
- CAT: Africa/Harare
- CNT: America/St_Johns
- CST: America/Chicago
- CTT: Asia/Shanghai
- EAT: Africa/Addis_Ababa
- ECT: Europe/Paris
- IET: America/Indiana/Indianapolis
- IST: Asia/Kolkata
- JST: Asia/Tokyo
- MIT: Pacific/Apia
- NET: Asia/Yerevan
- NST: Pacific/Auckland
- PLT: Asia/Karachi
- PNT: America/Phoenix
- PRT: America/Puerto_Rico
- PST: America/Los_Angeles
- SST: Pacific/Guadalcanal
- VST: Asia/Ho_Chi_Minh
Methods of Java ZoneId
Methods of java zoneid are given below:
1. public static ZoneId systemDefault()
This function is used to get the system default time- zone. This invokes TimeZone.getDefault() function to retrieve the value to default timeZone for that system, which means any updation made to system default Time-Zone will be reflected in the results. The output is converted to ZoneID format. Below 2 exceptions are thrown by this function must be handled:-
- DateTimeException: This indicates converted zone ID has an invalid format
- ZoneRulesException: This indicates converted zone region ID cannot be found
Code:
import java.time.ZoneId;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zone = ZoneId.systemDefault();
System.out.println("Output of systemDefault()-" +zone);
}
}Output:

2. public static Set<String> getAvailableZoneIds()
This function is used to return all available region-based IDs. The list is returned as a set of String. The string returned can be converted to the format of Zone-Id using Of(String) function. Offset-Ids are not included in the result of a set of Strings.
Code:
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> zoneIds = ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds();
List<String> zoneList = new ArrayList<String>(zoneIds);
Collections.sort(zoneList);
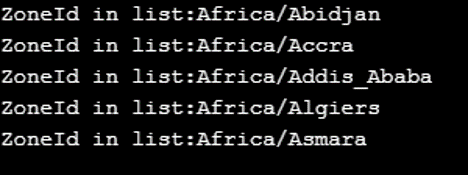
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("ZoneId in list:" +zoneList.get(i) );
}
}
}Output:
3. public static ZoneId of(String zoneId)
This function returns ZoneID or ZoneOffset for a valid ID passed as a string as an output to the function. ZoneOffset is returned based on the string’s starting character (if it is ‘Z’ or ‘+’ or ‘-‘). The ZoneID being returned always follow the ZoneRules. This conversion takes place using a complete parsing algorithm. In case the format of the argument is invalid, DateTimeException is thrown, and in the case of the region, ID can not be found, then ZoneRulesException is thrown.
Code:
import java.time.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.time.format.TextStyle;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("Asia/Calcutta");
System.out.println("Output of zoneid obtained using of function: "+ zoneId.normalized());
}
}Output:

4. public static ZoneId ofOffset(String prefix,ZoneOffset offset)
This method is used to obtain ZoneID when prefix and an offset are being passed as arguments. Zone ID with prefix and non zero Offset ID is returned. In this case, the prefix is “” ZoneOffset is returned.
The prefix must be ‘GMT’, ‘UTC’ or ‘UT’ or ‘’ otherwise, IllegalArgumentException is thrown by the method.
Code:
import java.time.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
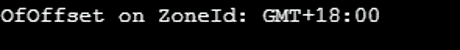
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.ofOffset("GMT", ZoneOffset.MAX);
System.out.println("OfOffset on ZoneId: " + zoneId);
}
}Ouput:
5. public static ZoneId from(TemporalAccessor temporal)
This method is used to convert a TemporalAccessor, an arbitrary set of date and time, object to an instance of ZoneId. This function works in a similar manner to TemporalQueries.zone() that extracts offset base zone id. Thus this method matches the signature of Temporal Query that is being used via ZoneId::from() function.
Code:
import java.time.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
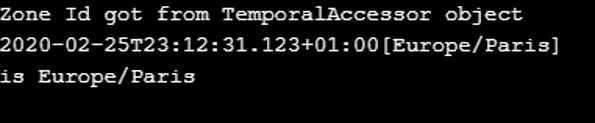
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZonedDateTime zoneddatetime
= ZonedDateTime.parse("2020-02-25T23:12:31.123+02:00[Europe/Paris]");
ZoneId result = ZoneId.from(zoneddatetime);
System.out.println("Zone Id got from "+ "TemporalAccessor object \n"
+ zoneddatetime + "\nis " + result);
}
}Output:
6. public abstract String getId()
This function is used to get a unique time-zone ID for a particular object. The format for an offset-based ID is defined by the getId() method in the Timezone class. The ID given as an output helps to uniquely define the object.
Code:
import java.time.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("Asia/Calcutta");
System.out.println("Id using getID(): "+ zoneId.getId());
}
}Output:
![]()
7. public String getDisplayName(TextStyle style,Locale locale)
This method helps to provide the textual representation of the zone. The style required as well as the locale of the output required is given as arguments. And thus, the suitable textual representation of the time-zone id is given as an output. In case no textual representation is present, a complete ID is returned as an output.
Code:
import java.time.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.time.format.TextStyle;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("Asia/Calcutta");
String result = zoneId.getDisplayName(TextStyle.SHORT, Locale.ENGLISH);
System.out.println("Name of ID using getDisplayName(): "+ result);
}
}Output:

8. public abstract ZoneRules getRules()
This function is used to retrieve the rules that are applied for the given ID. These rules give an idea about the calculations to be performed as well as the functionality associated with time-zone like finding an offset for an instant. ZoneRulesProvider supplies these rules. An advanced provider can also make a dynamic update to these rules, but the results may change over time in this case. In case no rule is available or the rules of JRE is different from that of time-zone, a call made to this function may lead to ZoneRulesException.
Code:
import java.time.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.time.format.TextStyle;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("Asia/Calcutta");
System.out.println("Rules are: "+ zoneId.getRules());
}
}Output:
![]()
9. public ZoneId normalized()
This method is used to check if the given zoneID contains a fixed Offset and if yes, a ZOneOffset equal to that fixed offset is returned; otherwise, this is returned. The returned ID will also have ZoneRules similar to the given offset, but the result we get from the getId() function is different from what we get here.
Code:
import java.time.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.time.format.TextStyle;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("Asia/Calcutta");
System.out.println("Normalized Id: "+ zoneId.normalized());
}
}Output:
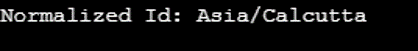
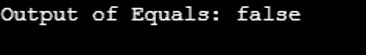
10. public boolean equals(Object obj)
This method helps to compare 2 different times ZoneId objects. This method overrides the equals method in the Object class, which is used to compare value stored in 2 objects. Similarly, here the value of these ZoneID is compared to see if 2 objects are equal or not. And, Accordingly, true and false is returned.
Code:
import java.time.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.time.format.TextStyle;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("Asia/Calcutta");
ZoneId zoneId2 = ZoneId.of("Europe/Paris");
System.out.println("Output of Equals: "+ zoneId.equals(zoneId2));
}
}Output:
11. public int hashCode()
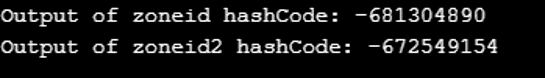
This function is used to get the hash code for a particular ZoneID object. This hashcode is returned in int format.
Code:
import java.time.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.time.format.TextStyle;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("Asia/Calcutta");
ZoneId zoneId2 = ZoneId.of("Europe/Paris");
System.out.println("Output of zoneid hashCode: "+ zoneId.hashCode());
System.out.println("Output of zoneid2 hashCode: "+ zoneId2.hashCode());
}
}Output:
12. public String toString()
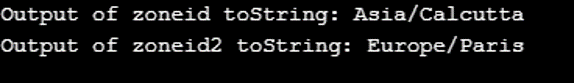
This function is used to get the string representation of the time -zone ID that is stored in the particular Offset ID. This function overrides the method toString() of Object class.
Code:
import java.time.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.time.format.TextStyle;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("Asia/Calcutta");
ZoneId zoneId2 = ZoneId.of("Europe/Paris");
System.out.println("Output of zoneid toString: "+ zoneId.toString());
System.out.println("Output of zoneid2 toString: "+ zoneId2.toString());
}
}Output:
Conclusion
ZoneID is a serialized class that is used to store the IDs that identify different ZoneRules that the government frequently updates. Thus at the time of serialization, rules are used instead as they contain the entire data set. Also, calling normalized() on ZoneId returns fixed offset ID in the format of ZoneOffset.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java ZoneId. Here we discuss the Introduction and Methods of Java zoneid along with its code implementation, respectively. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


