
Introduction to java.util.Date
The date and time in java are represented by a class called java.util.Date class, which provides methods and constructors to handle the time and date in java and Serializable, Comparable<Date> and Cloneable interfaces are implemented by java.util.Date class and java.sql.Date, java.sql.Time and java.sql.Timestamp interfaces are the base classes of the java.util.Date class.
Constructors of java.util.Date
The constructors of java.util.Date class are:
1. Date(): A date object is created, which represents the present time and date by using the Date() constructor.
2. Date(long milliseconds): A date object is created for the specified number of milliseconds since the time 1st January 1970, 00:00:00 GMT, by using the Date(long milliseconds) constructor.
Methods of java.util.Date
The methods of java.util.Date class are:
1. booleanafter(Date date): Boolean after(Date date) method is used to check whether the present date is after the specified date as a parameter.
2. booleanbefore(Date date): Boolean before(Date date) method is used to check whether the present date is before the specified date as a qparameter.
Below are the examples of java.util.Date:
Code:
import java.util.Date;
public class Example
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// a variable called dat1 is defined to store one date
Date dat1=new Date(2020,6,01);
//a variable called dat2 is defined to store another date
Date dat2=new Date(2021,6,01);
//boolean after(Date date) method is used to check if dat1 comes after dat2 date
System.out.println("The date represented by the variable dat1 is after the date represented by the variable dat2 : "+dat1.after(dat2));
//boolean before(Date date) method is used to check if dat1 comes before dat2 date
System.out.println("The date represented by the variable dat1 is before the date represented by the variable dat2 : "+dat1.before(dat2));
}
}Output:

Explanations: In the above program, a variable called dat1 is defined to store one date. Then a variable called dat2 is defined to store another date. Then boolean after(Date date) method is used to check if dat1 comes after the dat2 date and the output returned is either true or false. Then boolean before(Date date) method is used to check if dat1 comes before the dat2 date and the output returned is either true or false.
3. Object clone(): The object clone() method is used to return the present date’s clone object.
Below are the examples of java.util.Date:
Code:
import java.util.Date;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//an instance of the date class is created
Date dat=new Date(2020,6,01);
//clone method is called on the instance of the date class to create a clone of the given date
System.out.println("The clone of the given date is : "+dat.clone());
}
}Output:
![]()
Explanations: In the above program, an instance of the date class is created. Then the clone method is called on the date class instance to create a clone of the given date.
4. intcompareTo(Date date): int compareTo(Date date) method is used to compare the present date with the date specified as a parameter. The output is returned as zero if the present date is the same as the date specified as the parameter. The output is returned is less than zero if the present date is before the date specified as the parameter. The output is returned is greater than zero if the present date is after the date specified as the parameter.
5. booleanequals(Date date): boolean equals(Date date) method is used to compare the present date with the date specified as the parameter for equality. The output is returned as true if the present date is the same as the date specified as the parameter otherwise the output is returned as false.
Below are the examples of java.util.Date:
Code:
import java.util.Date;
public class Example
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//an instance of the date class is created to store one date
Date dat1=new Date(2020,6,01);
//an instance of the date class is created to store another date
Date dat2=new Date(2021,6,01);
//compareTo method is used to compare the two dates stored using the two variables defined before
int comp=dat1.compareTo(dat2);
//the result is displayed after comparing the two dates
System.out.println("The result after comparing the two values is : "+comp);
//Equals() method of date class is used to check if the two dates specified are equal
System.out.println("The dates stored in the two variables are equal : "+dat1.equals(dat2));
}
}Output:
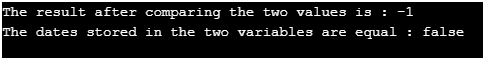
Explanations: In the above program, an instance of the date class is created to store one date. Then an instance of the date class is created to store another date. Then compareTo method is used to compare the two dates stored using the two variables defined before. Then the result is displayed after comparing the two dates. Then equals method is used to check if the two dates stored using the two variables defined before are equal.
6. static Date from(Instant instant): static Date from(Instant instant) method is used to return the date object’s instance from the instant date.
7. long getTime(): long getTime() method is used to return the time represented by the date object.
8. inthashCode(): int the hashCode() method is used to return the hash code value represented by the date object.
9. Instant toInstant(): Instant toInstant() method is used to convert the present date into an instant object.
10. String toString(): The string toString() method is used to convert the given date into an instant object.
Below are the examples of java.util.Date:
Code:
import java.time.Instant;
import java.util.Date;
public class Example
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//an instance of the date class is created which stores the present date
Date dat=new Date();
//instant date and time is obtained using instant.now() method
Instant inst= Instant.now();
//the instant date and time is displayed by using from() method
System.out.println("The instant date is : "+dat.from(inst));
//getTime() method is used to obtain the number of milliseconds since January 1st 1970
System.out.println("The number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 GTM : "+dat.getTime());
//hashcode() method is used to obtain the hash code of the given date
System.out.println("The hash code for the given date is : "+dat.hashCode());
//toInstant() method is called to convert the present date to the instant object
System.out.println("The instant object after converting the present date : "+dat.toInstant());
//toString() method is used to convert the date to string
System.out.println("The date after conversion to string is : "+dat.toString());
}
}Output:
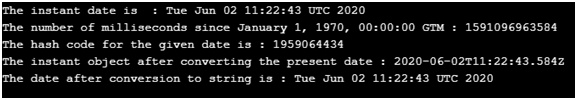
Explanations: In the above program, an instance of the date class is created to store the present date. Then instant date and time are obtained using instant.now() method. Then the instant date and time are displayed by using from the () method. Then getTime() method is used to obtain the number of milliseconds since January 1st, 1970. Then hashcode() method is used to obtain the hash code of the given date. Then toInstant() method is called to convert the present date to the instant object. Then toString() method is used to convert the date to string.
11. void setTime(long time): void setTime(long time) method is used to set the present date and time to the time specified as a parameter.
Below are the examples of java.util.Date:
Code:
import java.util.Date;
public class Example
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//an instance of the date class is created to store one date
Date dat=new Date(2020,6,01);
long lil=2000;
//settime() method is used to set the time to the given time specified
dat.setTime(lil);
System.out.println("The time after setting the time to given time is : "+dat.toString());
}
}Output:
![]()
Explanations: In the above program, an instance of the date class is created to store one date. Then setTime() method id used to set the present time to the given date.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we understand the concept of java.util.Date in Java through definition, its constructors and methods through programming examples and their outputs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to java.util.Date. Here we discuss the concept of java.util.Date through definition and their methods along with programming examples and their outputs. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


