
Introduction to Java Static Nested Class
Static inner classes is a nested class. This class is present as a static member under any class that acts as an outer class. It does not require a class object to be created to use member functions and variables. It can be instantiated with the help of the outer class. Also, it has a limitation that it can not access non-static member functions and member variables just like static variables.
Syntax:
The syntax of the JAVA static nested class is provided below. Here we need to have an outer class that will work as an umbrella class for the inner class. The inner class will lie inside the outer class loop. The inner class will have a “static” keyword before class so that the inner class can be recognized as a static inner or nested static class.
class outerclass
{
static class Innerclass
{
//Member variables
//Member functions
}
}How does Java Static Nested Class Works?
JAVA static nested classes are declared by using the “static” keyword before class at the time of class definition. The static keyword is also used with methods and variables to maintain the scope of variables and methods throughout the program without them begin overridden. The same feature can be used on the class level but with the exception that it has to be inner class. The functioning of a nested static class can be well understood via examples explained in the next section.
Although there are some important points to note regarding JAVA static nested classes:
- The static word can not be used with the outer class. That means only if any class is in the inner class, then the static word can be used before class.
- The static nested class can access static member functions and static variables of the outer class along with its own. With respect to accessibility to the outer class, it can access even the private members if they are declared static.
- Static classes can access only static variables and methods.
- There is no need to create objects for static classes. There is a direct calling to member functions and variables that are assigned with the static keyword.
Examples to Implement Java Static Nested Class
Some examples, along with their explanation, are provided below for you to review.
Example #1
These examples demonstrate the use and understanding of static keywords in data flow during program processing.
Code:
public class Test1
{
static int vnumber=25;
static class Innerclass
{
void printmsg ()
{
System.out.println ("We are running this proram to undertsand the implementation of static keyword under JAVA nested class. The value of number passed here is "+vnumber);}
}
public static void main(String args[] )
{
Test1.Innerclass object=new Test1.Innerclass();
object.printmsg();
}
}Output:
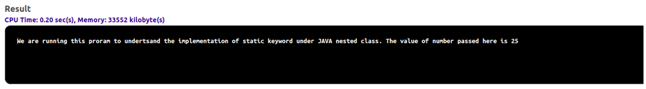
Explanation: Static classes are not instantiated directly, so in this example, the static class is instantiated with the outer class’s help. The outer class “Test1” is defined with a static variable named “vnumber” and a static class called “Innerclass”. The method is defined under the inner class named “printmsg()”. This function contains a string and a variable that is defined in the outer class.
When a program is executed, the main function is called first. The outer class, along with the inner class with a dot operator, is used for instantiation. The instance named “object” is invoked. The object is then used to call function printmsg(). The printms() function brings the string stored in it and a variable with a value of 25 coming from the outer class static variable declaration. So we have used the class instantiation method to demonstrate the usage of the static nested class. One thing to note here is that the static inner class and the static variable is used, but the printmsg() function is non-static. This is the reason we instantiated in the above example. If this function would have been static, then we would have used it another way.
Example #2
Code:
public class Test2
{
static int vnumber=30;
static class Innerclass
{
static void printmsg()
{
System.out.println("We are running this proram to undertsand the implementation of static keyword under JAVA nested class. The value of number passed here is : "+vnumber);}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Test2.Innerclass.printmsg();
}
}Output:
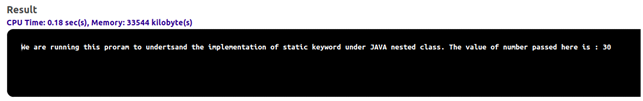
Explanation: Here, we are demonstrating an example of a static nested function where the variable, class, and method all are defined statically. This is done to demonstrate the method calling directly instead of invoking an object to call a method. Since wherever the “static” keyword is used, there is not required to create an object. One can directly use it. So here, an outer class named “test2” is created with a static variable called “vnumber” and an inner class named “innerclass”. Innerclass is attached with a static keyword to demonstrate the use of the static nested class. The inner class has a static member function with its string and a variable.
The main function is called as the program is executed. Outer class, inner class, and a method are directly called via a dot operator. Here we did not create an object as we created in the previous example since the method itself is declared static.
Conclusion
Static nested classes can be useful when we want to restrict the use of member functions of outer function in an inner class. This is possible as an inner static class can access only the outer class’s static members while other non-static members of the outer class still need an object to be created if the inner class wants to use them. This is used in case the programmer is looking for some security to be inherited in his/her code. The static keyword makes sure that data is not manipulated easily. This encourages data security and reliability on the application.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java Static Nested Class. Here we discuss the concept of Java Static Nested Class through definition along with programming examples and their outputs. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


