Updated June 16, 2023
Introduction to Java IO
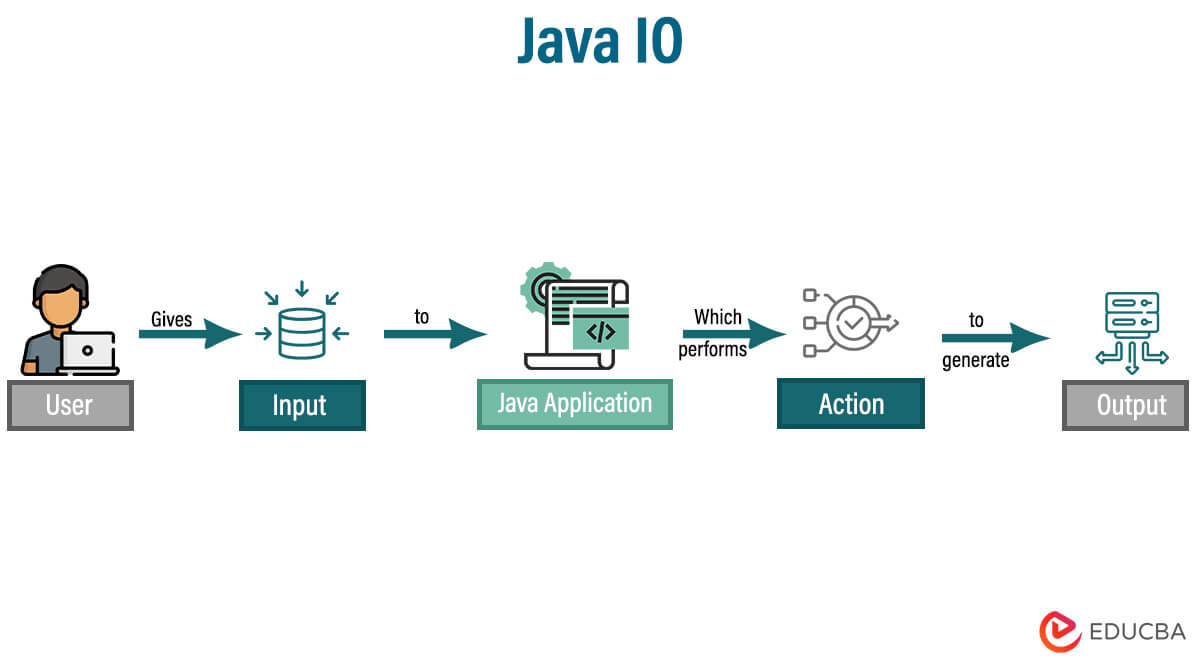
Java I/O stands for Java Input and Output. In other words, we can say that Java takes input from the user and then performs the appropriate action to generate the output. i.e., Java I/O processes the input and generates the output.
Java uses the stream concept to make the I/O operations fast; this stream in the java.io package supports all classes that need to be required to perform the input and output operations. A stream used in I/O consists of two parts: InputStream and OutputStream. The InputStream reads data from a source, while the OutputStream writes data to a destination.
Java I/O Classes
Below is a list of classes that perform I/O operations:
1. FileInputStream: In Java, FileInputStream class is used to read the data, such as audio, video, images, etc., in byte format. i.e., this class reads the bytes from the source file.
2. FileOutputStream: In Java, FileOutputStream class works opposite of FileInputStream class; it writes the data, such as audio, video, image, etc., in a byte and character format. i.e., this class writes the data to a file.
3. DataInputStream: This class allows the application to read the primitive data from the input stream in a machine-independent way.
4. DataOutputStream: This class allows an application to write the primitive data to the output stream in a machine-independent way.
5. BufferedReader: This class allows to read the text from a character-based input stream in line-by-line format by inheriting the reader class.
6. BufferedWriter: In Java, this method provides buffering to write the instances by inheriting the writer’s class.
7. BufferedInputStream: This class is used to read the data from the input stream. The BufferedInputStream automatically initializes the internal buffer array upon creation. When you read bytes from the stream, the internal buffer refills automatically from the source input stream.
8. BufferedOutputStream: This class is used to buffer the output stream. This class uses an internal buffer to store the data. i.e., this class adds a buffer in OutputStream.
9. FilePermission: This class gives the appropriate permission to a file or directory; these permissions are related to the file path.
File path can be of two types:
- D:\\IO\\: This path indicates that the permission associates with all sub-files and directories respectively.
- D:\\IO\\*: This path indicates that the permission applies to all files and directories within the specified directory, excluding subdirectories.
10. Console: This class is internally attached to the system console and used to get the console’s input by providing various methods. The console class actively reads text and passwords, displaying the text to the user while actively concealing the password (it can be shown in star format).
11. Scanner: This class in inbuilt, found in java.util package. This class reads data from the keyboard and obtains the user’s input in primitive data types (int, float, long, double, string, etc.) To get the scanner class to read the input from a user, we need to pass the input stream, i.e., System.in.
12. FilterInputStream: This class implements the InputStream and uses various subclasses, such as BufferedInputStream and DataInputStream, to provide additional functionality. It simply overrides all InputStream methods.
13. FilterOutputStream: This class works the opposite of FilterInputStream. It implements OutputStream and uses various subclasses, such as BufferedOutputStream and DataOutputStream, to provide additional functionality. It simply overrides all OutputStream methods.
14. SequenceInputStream: As the name suggests, this class reads the data in sequential format, i.e., one by one. This class starts reading the data from the first one until the end of the file reached; then, it starts reading the second one, the third, and so on.
15. RandomAccessFile: This class is used to access the random file; this random access file is a large array of bytes. People commonly use it for reading and writing to a random file. They perform read and write operations using a cursor.
16. InputStreamReader: This class acts as a bridge that joins the byte stream to the character stream. It reads bytes and decodes them into characters using a specified charset.
17. OutputStreamWriter: This class works the opposite of InputStreamReader. It converts the character stream to the byte stream. It reads the character and decodes it into a byte using a specified charset.
18. StringReader: This class is a character stream that takes an input string and converts it into a character stream using the reader class.
19. StringWriter: This class is a character stream that takes an output string that can be used to construct a string. It inherits the writer class.
20. FileReader: FileReader is a character-oriented class used to read the specified file data and return the data in byte format.
21. FileWriter: FileWriter is a character-oriented class that writes the data to a specified file.
22. ObjectStreamClass: This class acts as a serialization description of classes. It stores the name and serial version id of the class.
23. ObjectStreamField: In Java, this class is used to initialize the class’s serializable field.
24. ByteArrayInputStream: This class uses an internal buffer to read the byte array from the input stream.
25. ByteArrayOutputStream: This class writes the data into a byte array.
Conclusion – Java IO
In this article, we have seen what are Java I/O Classes to perform input-output operations in Java.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Java IO” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.