Updated June 15, 2023
Difference Between Java Heap and Stack
Java virtual machine (JVM) allocates some memory from the operating system; JVM uses this memory to create objects and instances called Java heap. Java uses the heap for dynamic memory allocation, where it creates objects and manages memory. The heap is typically located at the bottom of the address space, and when it becomes full, Java performs garbage collection to reclaim unused memory. Stack memory follows the rule of Last-In-First-Out (LIFO). A stack is referred to as static memory allocation. The size of the memory stack is less as compared to the heap memory size.
Let us study much more about Java Heap and Stack in detail:
- In Java Heap, garbage collection is the process of clearing the objects which are dead or that are not in use, which helps to free the space from the heap and make space for new things or instances.
- When a method is invoked, its stack frame is placed on top of a call stack. The stack frame contains the state of the method, including the currently executing lines of code and all the local variables. The Stack’s current running method is always the method that is at the top of a stack.
- When a method is invoked, a block is created on the stack to hold the method’s values and object reference. After the execution of a technique, the block is not in use anymore and becomes free, which can be available for the following method.
- The Stack is used for executing the threads. Each thread has Java virtual machine stack, and the JVM stack stores frames. The methods are allocated to stack memory, and memory access is fast. We cannot alter the Java virtual machine stack; it can be done only through push and pop on the Java stack. Java stack becomes larger and reduced as push and pop have done with local variables. JVM plays its part in method invocation and return. In simple terms, Java Stack is to store methods and variables.
Head to Head Comparisons Between Java Heap and Stack (Infographics)
Below are the Top 7 Comparisons Between Java Heap vs Stack:
Key Difference Between Java Heap and Stack
- In Java, the Java Heap stores and deallocates objects in any order, while the Stack stores and removes elements based on the Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) principle.
- When Java Heap is fully occupied, it throws out a memory error or Java heap space error. When the stack memory is exhausted, it throws a stack overflow error.
- For Java Heap, Xms, and Xmx, the Java virtual machine option can define the start and maximum sizes.
- In a heap, there is no dependency on any element to access other details. In Stack, there is a particular order to access the feature.
- Heap is more complex as sometimes it cannot know whether memory gets occupied or free. In a stack, it is simple and easy.
Java Heap vs Stack Comparisons Table
Following is the comparison table between Java heap vs stack:
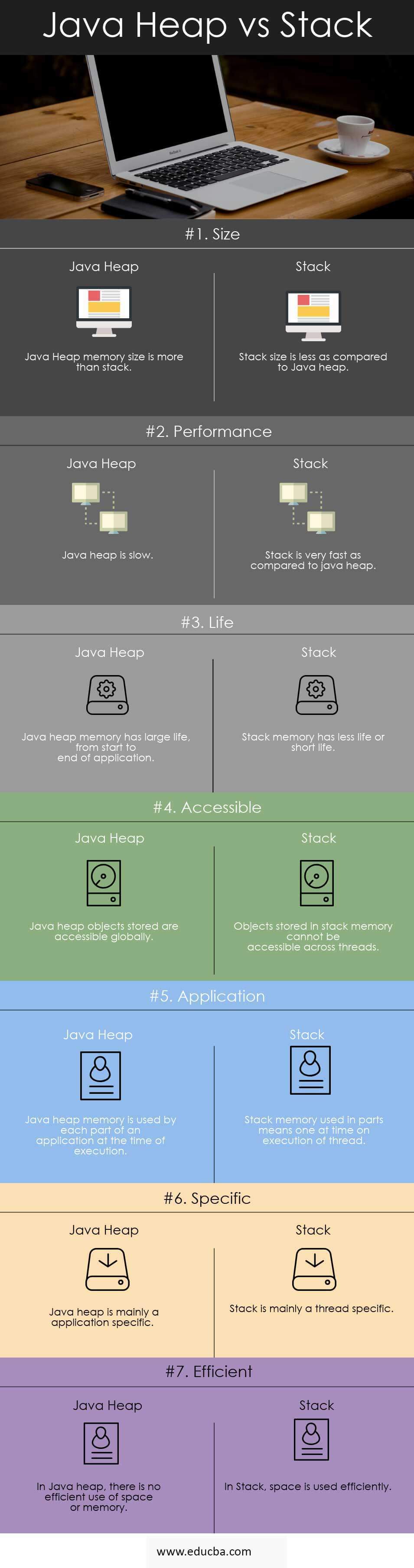
| Basis of Comparison | Java Heap | Stack |
| Size | Java Heap memory size is more than a stack. | Stack size is less as compared to Java heap. |
| Performance | Java heap is slow. | A stack is very fast compared to a Java heap. |
| Life | Java heap memory has a large life, from the start to an end of an application. | Stack memory has less life or a short life. |
| Accessible | Java heap objects stored are accessible globally. | Objects stored in stack memory cannot be accessible across threads. |
| Application | Each part of an application uses the Java heap memory during execution. | Stack memory used in parts means one at a time on execution of a thread. |
| Specific | Java heap is mainly an application-specific | The stack is mainly thread-specific. |
| Efficient | In Java heap, there is no efficient use of space or memory. | In Stack, space is used efficiently. |
Conclusion
Java Heap and Stack both are parts of memory management for the system. It plays a crucial role while designing and implementing the application. The knowledge of memory management is necessary for an individual before working on live projects. This makes your application faster and easily managed.
The stack is really important in exception handling and execution of threads. Java only stores local variable primitives on the stack.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Java Heap vs Stack” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.