Updated February 10, 2023
Definition
Java 8 method reference is used to refer to the functional method interface. It’s a very easy and compact form of the lambda expression. When we use the lambda expression for referring the method, we can replace our lambda expression by using method reference. Lambda function and functional interfaces are required to grasp the references in java. As we know, the method is statements collection, which performs periodical tasks.
Introduction to Java 8 Method Reference
It performs some specified task; while performing the task, it will not return anything. Java 8 method allows us to use the code without retyping the same. We are using the method as it will contain the primitive values or objects and treat them as a variable. We are using lambda expression for creating the method, which was anonymous.
The lambda expression will call the existing method. Method reference is a new feature that was introduced in java 8; it will contain the short and easily readable syntax of the lambda expression. We are using the method reference to refer to the method of a functional interface. We can also replace the reference of the method for our lambda expression at the time we are referring the lambda expression with the method.
Key Takeaways
- Java 8 method reference implements the functional interface, which contains less code as compared to the lambda expressions.
- By using it, we do not provide the functional interface implementation. Instead of that, we are providing the reference of a method that already exists.
Syntax of Java 8 Method Reference
The syntax will be different for every method. We are providing it by using three ways. Below is the syntax as per the types of reference methods as follows:
1. Reference to static method
Below is the syntax of reference to static method as follows. This syntax will contain the class name and name of the static method.
Syntax:
ContainingClass::StaticMethodName2. Reference to instance method
Below is the syntax of reference to instance method as follows. This syntax contains the object name and the name of the instance method.
Syntax:
ContainingObject::InstanceMethodName3. Reference to a constructor
Below is the syntax of reference to a constructor as follows. This syntax will contain the class name and name of the new keyword.
Syntax:
ContainingClass::newTypes of Java 8 Method Reference with Example
Below are the types, it contains four types as follows:
1. Static Method Reference
We can refer to the static method, which defines a class. By using static method reference, it is presented in the class will refer to the specified class.
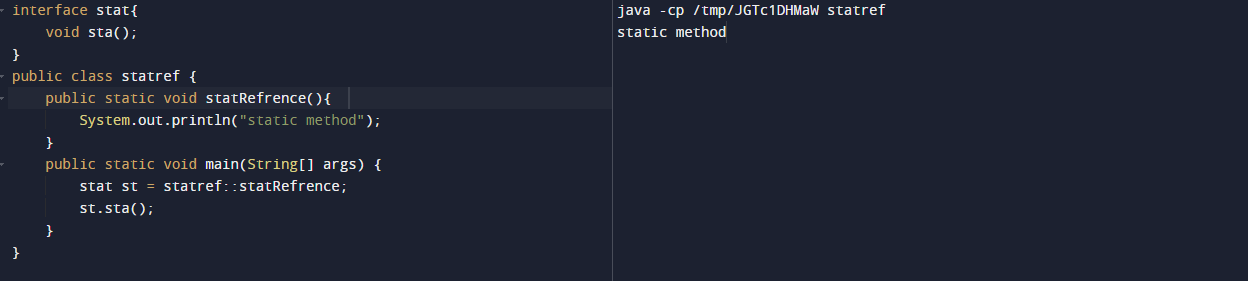
In the below example, we are defining the interface name as functional and referring to the method as static as follows.
Code:
interface stat {
void sta ();
}
public class statref {
public static void statRefrence (){
System.out.println ("static method");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
stat st = statref::statRefrence;
st.sta ();
}
}Output:
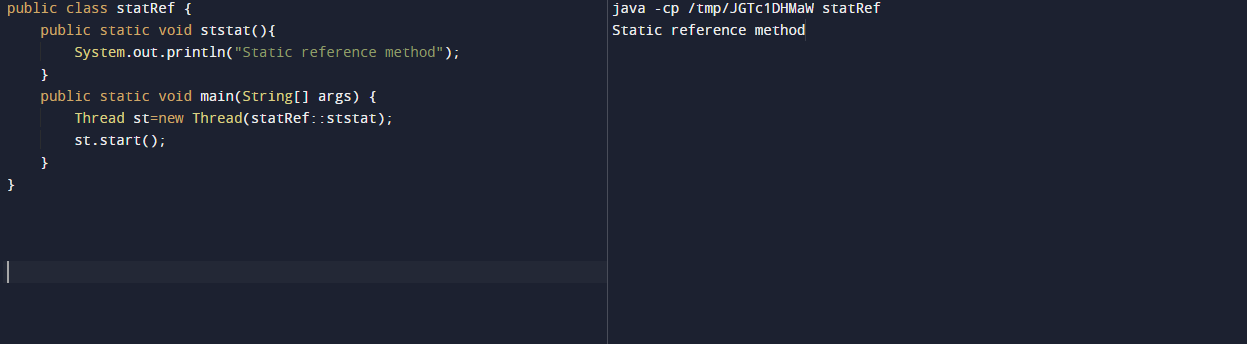
In the below example, we are using a runnable interface, which was predefined and was used for referring to the static method.
Code:
public class statRef {
public static void ststat () {
System.out.println ("Static reference method");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread st=new Thread (statRef::ststat);
st.start ();
}
}Output:
2. Instance Method Reference
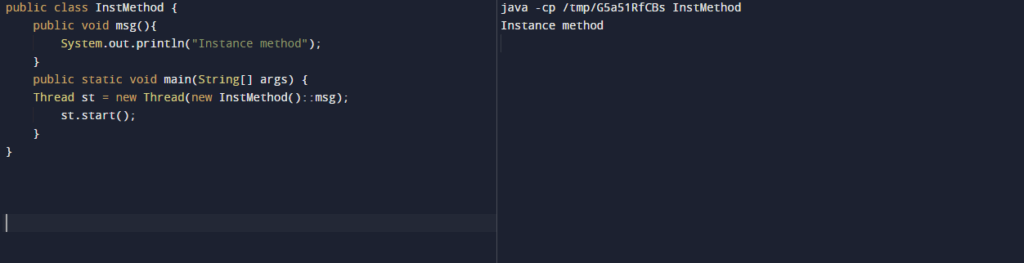
In reference to methods like the static method, we are also referring to the instance method. The below example shows the instant method reference as follows. In the below example, we are referring to the instance method.
Code:
public class InstMethod {
public void msg () {
System.out.println ("Instance method");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread st = new Thread (new InstMethod ()::msg);
st.start ();
}
}Output:
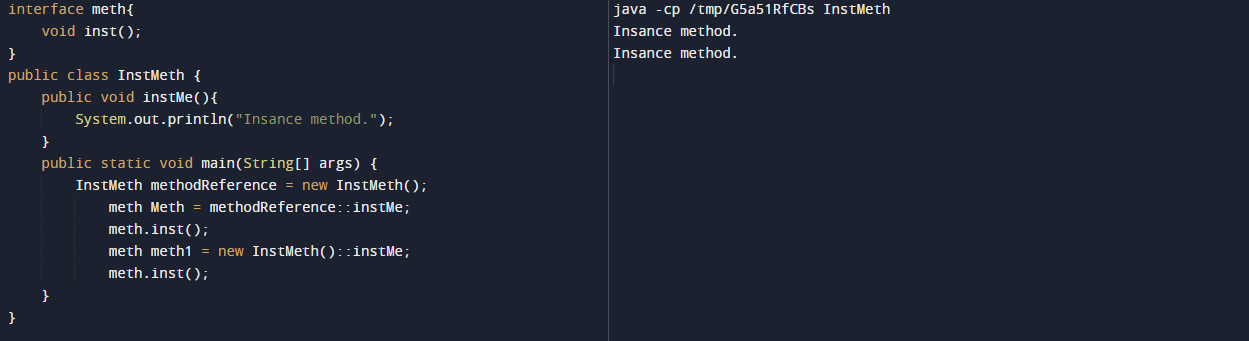
In the below example, we refer to the instance method. We are referring to using class and anonymous objects.
Code:
interface meth {
void inst ();
}
public class InstMeth {
public void instMe (){
System.out.println ("Insance method.");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
InstMeth methodReference = new InstMeth ();
meth Meth = methodReference::instMe;
meth.inst ();
meth meth1 = new InstMeth()::instMe;
meth.inst ();
}
}Output:
3. Reference to a Constructor
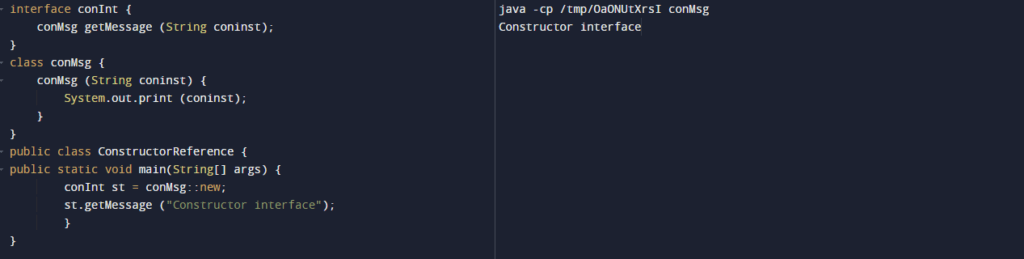
We are referring to the constructor by using a new keyword. In the below example, we refer to the constructor by using the help of the functional interface.
Code:
interface conInt {
conMsg getMessage (String coninst);
}
class conMsg {
conMsg (String coninst) {
System.out.print (coninst);
}
}
public class ConstructorReference {
public static void main(String[] args){
conInt st = conMsg::new;
st.getMessage ("Constructor interface");
}
}Output:
4. Instance Method for an Arbitrary Object of Particular Type
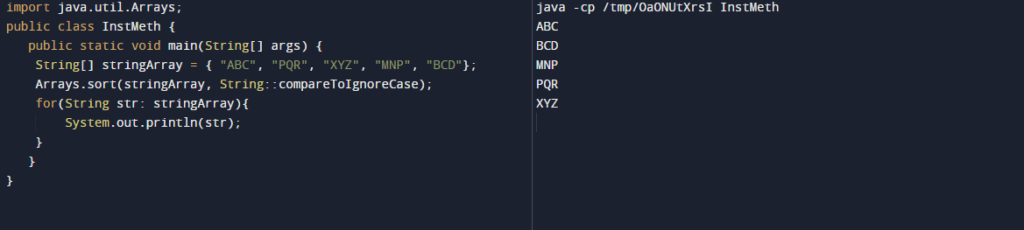
We can also define the method reference by using a particular type of arbitrary object of an instance method. Below is the example of a particular type of arbitrary object of instance method as follows.
Code:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class InstMeth {
public static void main(String[] args){
String[] stringArray = { "ABC", "PQR", "XYZ", "MNP", "BCD"};
Arrays.sort (stringArray, String::compareToIgnoreCase);
for (String str: stringArray) {
System.out.println (str);
}
}
}Output:
FAQs
Given below are the FAQs mentioned:
Q1. What is the use of the method reference?
Answer: Basically, it is used to refer to the method of a particular functional interface. We can also use the method reference in the lambda expression.
Q2. How many types of Java 8 method references are available?
Answer: There are four types available.
- Static reference method
- Instance reference method
- Reference to constructor
- Instance method for an arbitrary object of the particular type
Q3. What is the syntax of the Java 8 static reference method?
Answer: Below is the syntax of the Java 8 static reference method. It contains the class name and static method name as follows.
ContainingClass::StaticMethodNameQ4. What is the main difference between java 8 static and instance method reference?
Answer: Static method contains the class name, while the instance reference method contains the object name.
Conclusion
The java 8 method reference performs some specified task; while performing the task, it will not return anything. Java 8 method allows us to use the code without retyping the same. Java 8 method reference is used to refer to the functional method interface. It’s a very easy and compact form of the lambda expression.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java 8 Method Reference. Here we discuss the introduction and types of java 8 method references with examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –