Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to IoT Boards
The Internet of Things has a never-ending scope in real-world applications and has been widely considered by organizations and governments worldwide. The number of design boards available for IoT is also overwhelming, with large industrial involvement. Many microcontroller panels, daughter boards, chipboard devices, and application-specific ICs are available with onboard Wi-Fi routers, infrared, other communication protocols, and many General-Purpose Input/output pins for sensor interface. IoT boards are essentially hardware structures used to build models of the inventions of the designer. There’s a wide range of IoT boards available in the market today.
Classification of IoT Boards
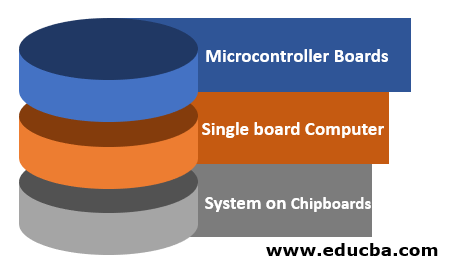
In today’s market, one can find many boards with different specifications. IoT boards can be broadly classified into three segments:
- Microcontroller Boards
- Single board Computer
- System on Chipboards
1. Microcontroller Boards
Some of the popular open-source hardware used for development and for providing software programming are mentioned below:
a. Arduino Uno Rev
It is an ATmega328P microchip-based open-source microcontroller board produced by Arduino, a tech company. The board has arrays of digital and analog input/output pins that can be interfaced with different boards for expansion and other circuits.
Arduino Uno Rev consists of 6 analog inputs, 15 Input/output connectors, 15MHz quartz crystal, a reset option, and an ICSP header. Since this board fully supports the microcontroller, it can simply be connected to a device with a USB cable or power to start with an AC-to-DC converter or battery.
Advantages:
- Arduino Uno is very simple to learn and implement.
- Low-cost IoT board with high standards.
- A wide range of third-party libraries and sensors are available for Arduino Uno.
- A huge community of users, along with readily available resources.
Disadvantages:
- The board’s processing and task performance speeds are lower than other competitors.
- Arduino Uno has a big structure requiring a large-sized PCB; competitors like ATmega work well for IoT development.
b. ESP8266
ESP8266 is a low-cost IoT board with an embedded WIFI system that allows for rapid prototyping of IoT applications. This comes with multiple variants and specific features such as memory capacity and number pins. The Arduino IDE can be utilized for developing alternative IoT IDEs or IoT applications.
Advantages:
- ESP8266 IoT board is cost-friendly. IoT solution in real-time implementation.
- This segment is very reliable and readily available in the market.
Disadvantages:
- Most of the document is available in Mandarin, making it inaccessible to the rest of the world.
2. Single Board Computer
Mostly used in industrial situations for process control, single-board computers provide command and interfacing within several devices.
Some of the widely used computers are:
a. Beagle Board
The BeagleBoard, developed by Texas Instruments, is a low-power open-source single-board computer that is commonly associated with Digi-Key. It ran on Linux distribution and was designed as an instructional board by a small team of engineers to teach open-source hardware and software skills in colleges worldwide. This board is very similar to Raspberry Pi.
Advantages:
- The beagle board is very convenient and reliable in usage.
- When compared to its competitors, the board is inexpensive.
- The board doesn’t require additional cooling equipment and has low power consumption.
Disadvantages:
- It has a basic structure suitable for beginners in electronic programming.
- Lacks audio and graphical capabilities.
b. Raspberry Pi3
The development of the Raspberry Pi 3 took place in the United Kingdom to promote basic computer science education in schools. Raspberry Pi includes a series of small single-board computers which run on Raspbian operating system created for Raspberry Pi. A quad-core 64-bit ARM v8 processor powers Raspberry Pi3 and runs at 1.2 GHz. It comprises a power unit, 4 USB ports, and an extendable board.
Advantages:
- Cost friendly, and the board category is largely available in the market.
- Consists of General-purpose Input-Output pins.
Disadvantages:
- Raspberry Pi 3 isn’t as fast as CPU processing speed and has less memory than a Mac or a laptop.
- If pins are inserted incorrectly, the board’s low fault tolerance makes it prone to damage.
3. System on Chipboards
System on Chipboards consists of various functional units such as:
a. Tessel 2
Tessel 2, an open-source development board, runs on JavaScript and is specifically designed to generate scripts using Node. It is a platform designed for the Internet of Things (IoT) to play, tinker, design, and create integrated hardware. Tessel has a collection of Command Line Interface devices to set up the Tessel 2 panel and work with it. One must download these tools and use the terminal command line to execute the script.
Advantages:
- The javascript development environment makes Tessel 2 a worthy choice.
- Low maintenance and optimum speed.
Disadvantages:
- The Tessel 2 is decent but not as cost-effective as Raspberry Pi, nor does it provide much extra value over the latter.
b. Particle Photon
A particle Photon is a tiny IoT board with an integrated WIFI module. This IoT-ready board has a range of expansion kits to make the design process quicker.
Advantages:
- The Particle Photon is a handy tool for IoT prototyping that facilitates remote coding, quick application migration, and fast project turnaround.
- With the platform’s built-in factory models, you can be certain that bricking the Photon is impossible, and charging the device from a standard phone charger is easy with the micro USB cable.
c. Intel Edison Board
The Intel Edison is a tiny computer, about the size of a memory card at 35 x 25 x 3.8 mm. But this little chip boasts some great power despite its tiny size. The Intel Edison has no problem running Linux 1.6 with a dual-core, multi-threaded Intel Atom CPU operating at 600mhz and 2 GB of RAM.
Advantages:
- Small yet powerful board for IoT integration.
- Widely used across the industry with full support provided by Microsoft.
Disadvantages:
- Limited potential when compared to present-day boards.
- Expensive when compared to its competitors.
Conclusion – IoT Boards
In this article, we have seen different IoT boards; most boards have huge support communities and groups to support any project. With the advancement in IoT, boards of multiple sizes and specifications are now available in the market. An organization or individual needs to select the boards to implement IoT projects based on the project requirement.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to IoT Boards. Here we have discussed the introduction and classification of IoT boards in 3 segments with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –