Updated May 3, 2023

Introduction to Indexes in PostgreSQL
Indexes are handy in PostgreSQL to fast retrieval of data; we can create an index on a column of the table which used in select operation for retrieving fast data; PostgreSQL index is the same as a pointer on a table; for example, If one book and we want a reference of all pages for discussion of topic later, then we have first referred index page, which has all points or topics list serially or alphabetically. Then we refer to specific page number and topics that we want to search; the same thing happens in the PostgreSQL index.
Syntax:
The index is used to increase database performance.
Create [UNIQUE] INDEX [CONCURRENTLY] [index_name] ON table_name [Using
Method (Type of index)] ( { column_name | ( expression ) } [ COLLATE collation ] [ opclass (name of operator class) ] [ ASC | DESC ] [ NULLS { FIRST | LAST (Specify the sort order of index)}] [, ...] )
[WITH (name of storage parameter)]
[TABLESPACE tablespace_name]
[WHERE predicate]Below is the description of the above syntax:
- Unique: It causes the system to check the duplicate value in tables.
- Concurrently: After using this parameter, PostgreSQL will create an index without locking other sessions like (Insert, Update or Delete) on tables. Without using this parameter, PostgreSQL locks the table on write operation.
- Index name: Any name given to the index.
- Table name: Table name, which is indexed.
- Method: Method or type of index like Btree, Hash, etc.
- Column: Name of the column on which we are creating the index.
- Expression: Expression will be written in parenthesis.
- Collation: The name of collation which is used in the index; if we have not declared, then the index will automatically take as default.
- Opclass: This is the name of the operator class.
- ASC: It will specify ascending sort order.
- DESC: It will specify descending sort order.
- Nulls first: This specifies that nulls sort before non-nulls.
- Nulls last: This specifies that nulls sort after non-nulls.
- Storage parameter: This is the name of the storage parameter.
- Tablespace: Tablespace name in which we have created an index.
- Predicate: This is a constraint expression.
How to Create Indexes in PostgreSQL?
- PostgreSQL index is used to increase database performance. Using the index, we improve our database performance.
- We have used the customer table for describing the index in PostgreSQL.
- Please find below details of the creation of a new index in PostgreSQL.
1. Create a customer table and insert data into it.
testing=#CREATE TABLE customer ( cust_id INT NOT NULL, cust_name character(10) NOT NULL, cust_address character(20) NOT NULL, cust_phone character(14), PRIMARY KEY (cust_id));testing=#INSERT INTO customer (cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_phone) VALUES (1, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890');testing=#INSERT INTO customer (cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_phone) VALUES (2, 'PQR', 'Pune', '1234567890');Output:

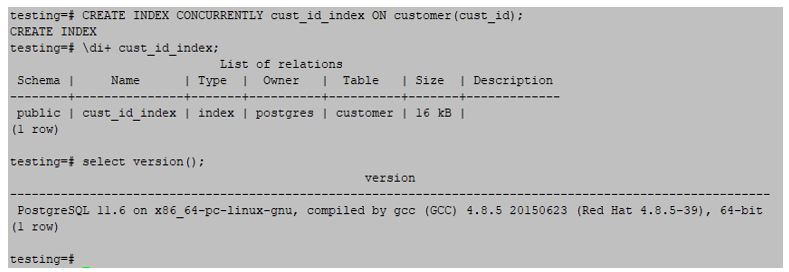
2. Create an index on the cust_id column in the customer table.
testing=#CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY cust_id_index ON customer (cust_id);Output:
Types of Indexes in PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL supports different types of indexes. Please find below PostgreSQL index types:
- B-Tree
- Hash
- GIN (Generalized Inverted Index )
- GiST (Generalized Inverted Search Tree)
- SP-GiST(Space partitioned Generalized Inverted Search Tree)
- BRIN (Block Range Indexes)
Let us discuss each of them in detail.
1. B-Tree
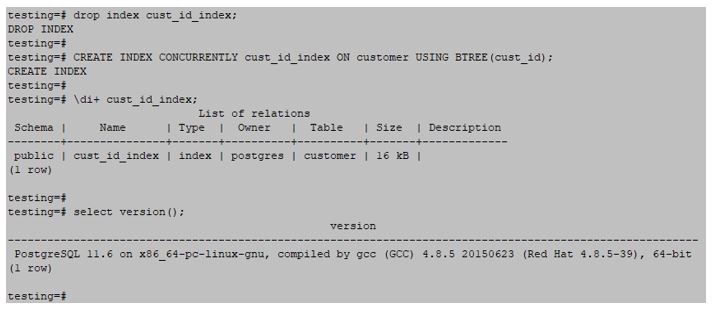
Btree index is most popular and fairly used in PostgreSQL while creating an index. Btree index will create a tree and stores data in a node; the node can be a variable number. The below example shows the Btree index are as follows:
Example:
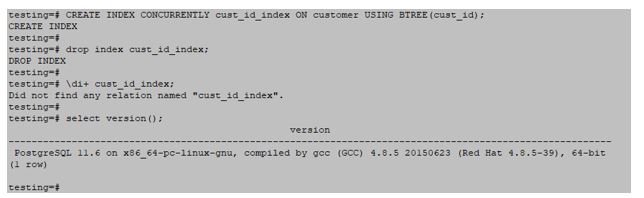
testing=#CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY cust_id_index ON customer USING BTREE(cust_id);Output:
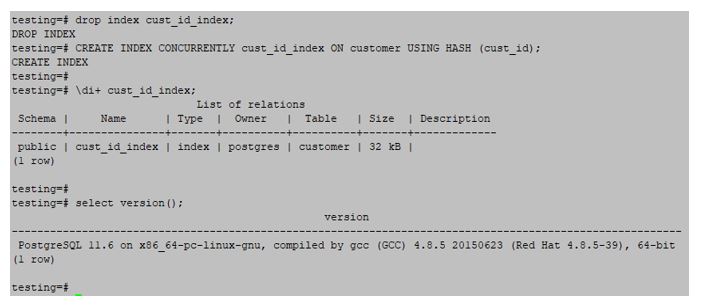
2. Hash Index
The Hash index is faster than the Btree index, but the hash index was limited to equality operations. The below example shows the HASH index is as follows:
Example:
testing=#CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY cust_id_index ON customer USING HASH (cust_id);Output:
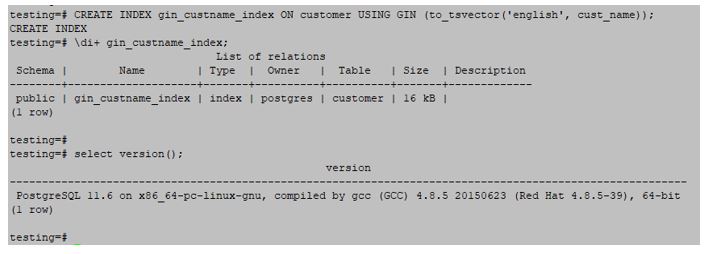
3. GIN (Generalized Inverted Index )
When we have data types with many values in a single column, the gin index is most helpful. A generalised inverted index was another name for the GIN index.The below example shows the GIN index are as follows.
Example:
testing=#CREATE INDEX gin_custname_index ON customer USING GIN (to_tsvector('English', cust_name));Output:
4. GiST (Generalized Inverted Search Tree)
GiST index is useful when our data is in geometrical format. It is also known as the generalized search tree. The below example shows the GiST index is as follows.
Example:
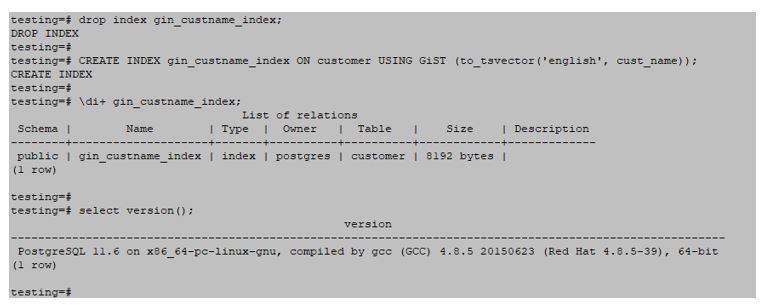
testing=#CREATE INDEX gin_custname_index ON customer USING GiST (to_tsvector('English', cust_name));Output:
5. SP-GiST(Space partitioned Generalized Inverted Search Tree)
SP-GiST index referred to as space partitioned generalized inverted search tree. An SP-Gist index is most useful when our data is a clustering element or in clustered format. The best example is the phone number. The below example shows the SP-GiST index as follows.
Example:
Create a table for the creation of the SP-GiST index.
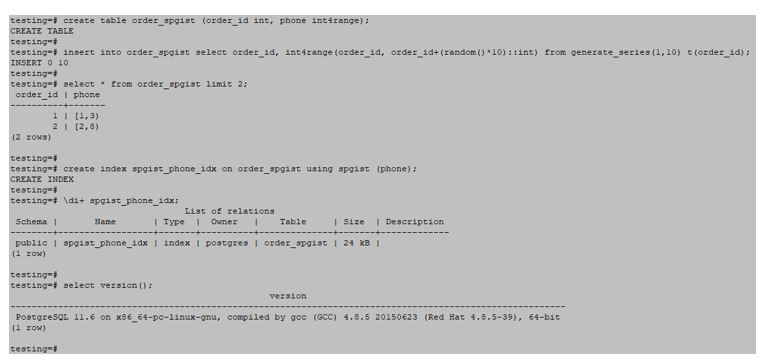
testing=#create table order_spgist (order_id int, phone int4range);testing=#insert into order_spgist select order_id, int4range(order_id, order_id+(random()*10)::int) from generate_series(1,10) t(order_id);Create an SP-GiST index.
testing=#CREATE INDEX gin_custphone_index ON customer USING SPGiST (to_tsvector('English', cust_phone));Output:
6. BRIN (Block Range Indexes)
When there are lots of naturally grouped data, BRIN index is helpful. Block range indexes are another name for BRIN indexes. The below example shows the BRIN index as follows.
Example:
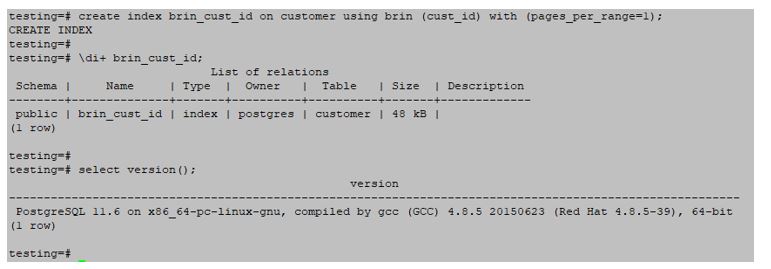
testing=#create index brin_cust_id on customer using brin (cust_id) with (pages_per_range=1);Output:
How to Drop Indexes in PostgreSQL?
The index is dropped in PostgreSQL using the drop command below is the syntax and example for the same.
Syntax:
DROP INDEX index_name;Example:
testing=#drop index cust_id_index;Output:
Examples:
Below is an example of creating an index in PostgreSQL.
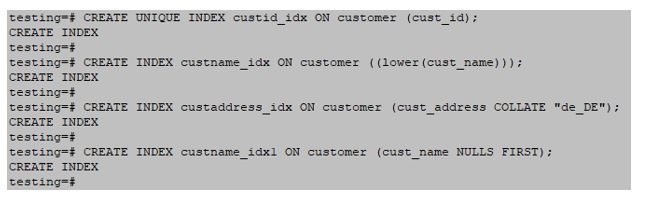
testing=#CREATE UNIQUE INDEX custid_idx ON customer (cust_id);testing=#CREATE INDEX custname_idx ON customer ((lower(cust_name)));testing=#CREATE INDEX custaddress_idx ON customer (cust_address COLLATE "de_DE");testing=#CREATE INDEX custname_idx1 ON customer (cust_name NULLS FIRST);testing=#CREATE INDEX custid_idx1 ON customer (cust_id) TABLESPACE pg_default;Output:
Conclusion
PostgreSQL uses a specific index structure to speed up data retrieval, and it is known as the Btree index, which is used by default if no index type is specified at the time of creation. The Btree index fastens the operation of data retrieval in PostgreSQL
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Indexes in PostgreSQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

