Updated June 9, 2023
Overview of Implementation of Neural Networks
Artificial Neural Networks are inspired by biological neural networks. Neural Networks help to solve the problems without being programmed with the problem-specific rules and conditions. They are generic models with most of the complex mathematical computations as BlackBox. The different types of neural networks are like Convolution Neural Network, Recurrent Neural Network, Feedforward Neural Network, Multilayer perceptron, and many others. In this topic, we are ogin to learn about the Implementation of Neural Networks.
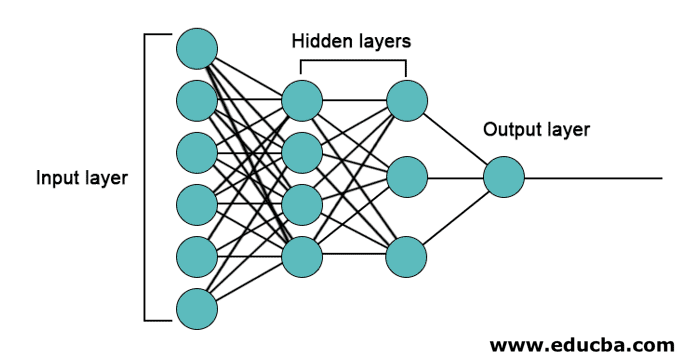
The Architecture of Neural Networks
There are 3 layers mainly in neural networks.
- Input Layer
- Hidden Layers
- Output Layer
1. Input Layer: The input layer contains the neurons for the input of features. There is also one bias added to the input layer in addition to the features. So if there are n features, then the input layer contains n+1 neurons.
2. Hidden Layer: The hidden layers are the intermediate layers between the input and output layers. There can be any number of hidden layers. The network with more than one hidden layer is called deep neural networks. The neurons in the hidden layer get input from the input layer, and they give output to the output layer.
3. Output Layer: The output layer contains the number of neurons based on the number of output classes. If it is a multi-class classification problem, then it contains the number of neurons equal to the number of classes. For binary classification, it contains one neuron.
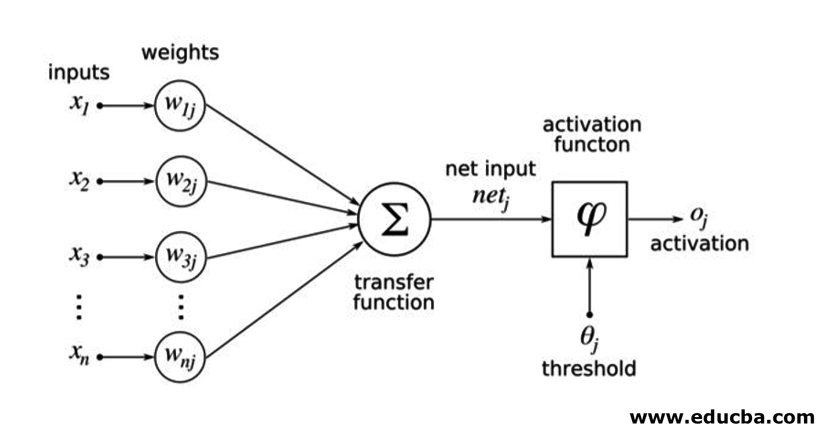
The inputs are multiplied with weights and then fed into the next hidden layer. Bias is also given as input along with weighted inputs. The weighted sum is passed through a nonlinear function called the activation function.
Implementation Example
Here is the implementation example mention below
Libraries Installation
There are many built-in libraries for the implementation of artificial neural networks in different programming languages. Here we will talk about two of the famous libraries TensorFlow and Keras using python as the programming language for the implementation of neural networks. Keras is a higher-level API build on TensorFlow or theano as backend. It is much easier for implementation. You can choose any of the libraries for your model. There are some others also available like PyTorch, theano, Caffe and many more.
To install the TensorFlow / Keras using pip, run the following command:
pip install tensorflow
pip install Keras
Alternatively, it can be installed using conda command,
conda install -c conda-forge tensorflow
conda install -c conda-forge keras
Implementation
Here we will talk about Keras for the generation of the deep learning models. It is an open-source Python deep learning library.
- Import the available MNIST dataset. MNIST is the dataset of handwritten numerals of English digits.
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
train_images = mnist.train.images.reshape(mnist.train.images.shape[0], image_rows, image_cols, 1)
test_images = mnist.test.images.reshape(mnist.test.images.shape[0], image_rows, image_cols, 1)
- Initialize the parameters and hyperparameters necessary for the model.
- Then initialize the deep learning model.
model = Sequential()
- Add convolution layer, activation layer and max-pooling layer for each of the convolution layers that we add between input and output layer (hidden layers). Here we are adding two convolution layers.
model.add(Convolution2D(num_filters, conv_kernel_size[0], conv_kernel_size[1], border_mode='valid', input_shape=imag_shape))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=max_pool_size))
- Different activation function can be used as per the problem. Some common activation functions are relu activation, tanh activation leaky relu, and many others.
- Then comes a fully connected layer before the dense layer. They compile the data extracted by previous layers to form the final output.
- The output layer dimension depends on the number of classes. The activation functions used for the output layer are generally sigmoid activation for binary classification and softmax activation for multi-class classification.
model.add(Dense(num_classes))
model.add(Activation('softmax'))
The complete code for the deep convolutional neural network for the classification of MNIST data is as below.
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Activation, Flatten from keras.layers import Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D
# we use TF helper function to pull down the data from the MNIST site mnist_data = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
img_rows = 28
img_cols = 28
# Reshape training and test images to 28x28x1
train_images = mnist_data.train.images.reshape(mnist_data.train.images.shape[0], img_rows, img_cols, 1)
test_images = mnist_data.test.images.reshape(mnist_data.test.images.shape[0], img_rows, img_cols, 1)
num_of_filters = 32 # No. of conv filters maxPoolSize = (2,2) # shape of max_pool convKrnSize = (3,3) # conv kernel shape imgShape = (28, 28, 1) num_of_classes = 10
dropProb = 0.5
model = Sequential()
# define layers in NN
# Define 1st convolution layer.
model.add(Convolution2D(num_of_filters, convKrnSize[0], convKrnSize[1], border_mode='valid', input_shape=imgShape))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=maxPoolSize))
# 2nd Convolution Layer
model.add(Convolution2D(num_of_filters, convKrnSize[0], convKrnSize[1])) model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=maxPoolSize))
#Fully Connected Layer model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(128)) #Fully connected layer in Keras model.add(Activation('relu'))
# Dropout some neurons to reduce overfitting model.add(Dropout(dropProb))
#Readout Layer model.add(Dense(num_of_classes))
model.add(Activation('softmax'))
# Compile the model
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
# Training settings batch_size = 128
num_of_epoch = 2
# fit the training data to the model.
model.fit(train_images, mnist_data.train.labels, batch_size=batch_size,
nb_epoch=num_of_epoch, verbose=1, validation_data=(test_images, mnist_data.test.labels))
# predict the test_data using the model
test_labels_predicted = model.predict_classes(test_images)
# To get the predicted labels of all test images for i in range(len(test_images)):
print ("Image {} -> Label {}".format(i+1, test_labels_predicted[0]))
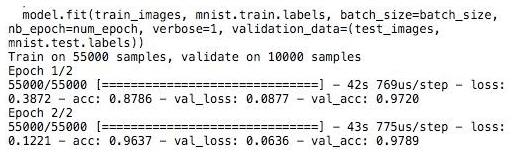
Training
The Training of the model looks like,
Conclusion – Implementation of Neural Networks
Neural Networks provide an easy way for classification or regression problems in machine learning when the samples’ feature space is very large, mainly for large images or other multimedia or signals.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Implementation of Neural Networks. Here we discuss the architecture and implementation of Neural Networks with a training model and sample code. You may also look at the following article to learn more –