What is Homomorphic Encryption?
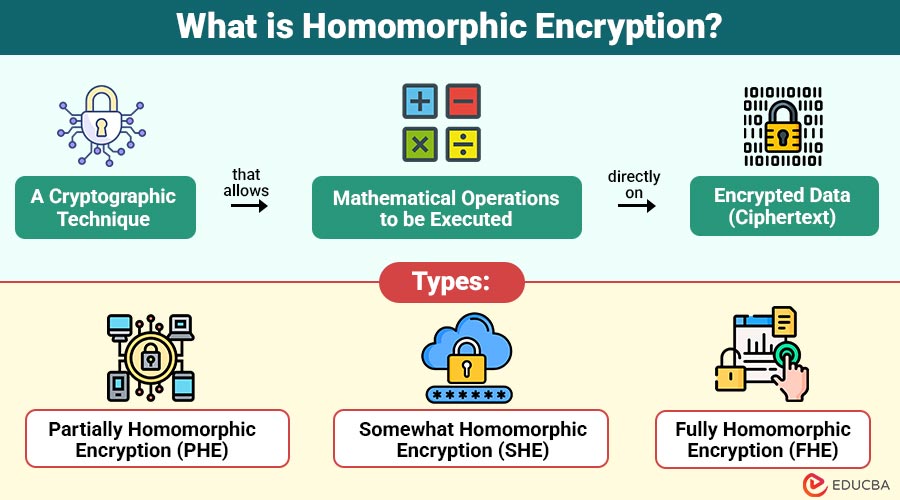
Homomorphic Encryption is cryptographic technique that allows mathematical operations to be executed directly on encrypted data (ciphertext). When the processed data is decrypted, the output is identical to the result that would have been obtained if the same operations were applied to the original plaintext.
For example:
- Suppose you encrypt two numbers, 5 and 7.
- A homomorphic encryption scheme allows you to add these encrypted numbers without decrypting them.
- After decryption, you will get 12—the same result as if you had added the plaintext values.
This unique ability makes homomorphic encryption different from traditional methods, which require decryption before computation.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data, ensuring privacy without exposing sensitive underlying information.
- It supports industries like healthcare, finance, AI, and government by enabling secure, privacy-preserving data processing.
- Its complexity, high computation, and scalability challenges slow its adoption across industries today.
- Ongoing research promises efficiency improvements, making it more practical for secure future applications.
Why is Homomorphic Encryption Important?
The importance can be summarized in three main points:
1. Data Privacy
It allows organizations to process sensitive data like healthcare or financial records securely without exposing the underlying information.
2. Cloud Security
It lets organizations do calculations on encrypted data in the cloud while keeping it completely secure and private.
3. Regulatory Compliance
It enables businesses to meet global regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA by safeguarding personal data throughout processing stages.
How does Homomorphic Encryption Work?
The foundation of it lies in advanced mathematics, particularly number theory and algebra. While the mathematics can get complex, we can break the working principle into simple steps.
1. Encryption
Plain text is turned into encrypted data using homomorphic encryption, keeping it safe while still letting calculations be done on it
2. Computation on Encrypted Data
The system can do math like adding or multiplying directly on encrypted data, keeping the original information completely safe.
3. Decryption
You decrypt the encrypted outcome to plaintext, producing results identical to calculations performed directly on the original data.
Types of Homomorphic Encryption
It can be parted into three primary types:
1. Partially Homomorphic Encryption (PHE)
Support only one kind of action on the ciphertext, either multiplication or addition. Ideal for simple tasks but insufficient for intricate ones.
2. Somewhat Homomorphic Encryption (SHE)
Allows for addition and multiplication, but only up to a limited number of operations before the system starts to malfunction or become inefficient. Acts as a precondition for fully homomorphic encryption.
3. Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE)
Supports unlimited addition and multiplication operations on ciphertext. It is regarded as the “holy grail” of encryption since it permits arbitrary calculations to be made on encrypted data.
Applications of Homomorphic Encryption
Here are some practical applications where it is transforming industries through secure and privacy-preserving data processing:
1. Healthcare Data Security
Hospitals and researchers can securely analyze patient records on encrypted datasets, enabling collaborative studies while ensuring privacy and compliance with healthcare regulations.
2. Banking and Finance
Banks utilize it to perform fraud detection and risk analysis on encrypted customer data, maintaining confidentiality even during external computational processes.
3. Cloud Computing
Organizations can safely work with encrypted data in the cloud, keeping it private while using cloud resources for heavy computing or large-scale analysis.
4. Government and Defense
It supports secure sharing, processing, and analysis of classified defense or intelligence data between agencies without risking leaks or compromising national security.
5. Machine Learning and AI
Privacy-preserving machine learning enables secure model training on encrypted datasets, allowing organizations to gain insights without revealing sensitive or proprietary information.
Benefits of Homomorphic Encryption
Here are the key benefits that make it a powerful approach to secure and privacy-preserving data processing:
1. Enhanced Privacy
Sensitive data stays encrypted while being processed, avoiding extra decryption and keeping it more secure
2. Secure Outsourcing
Organizations can safely use cloud services for computing while keeping their sensitive data private and secure.
3. Regulatory Alignment
By reducing the need for decryption and protecting critical company or personal data, it guarantees adherence to international data protection laws.
4. Innovation in AI and ML
Allows AI and machine learning to work with encrypted data safely, helping develop smarter systems while keeping information private.
Challenges of Homomorphic Encryption
Here are the major challenges that hinder the widespread adoption and practical implementation today:
1. Performance Overhead
It requires heavy computation, making it slower than traditional methods, demanding significant processing power and resources.
2. Complexity
Implementing it involves advanced mathematics and cryptographic expertise, making integration with existing systems difficult without specialized technical knowledge.
3. Scalability Issues
Using homomorphic encryption for big data or many transactions is slow and inefficient, making it hard to use at an industrial scale.
4. Limited Standardization
Despite ongoing efforts from global consortiums, homomorphic encryption lacks universal standards, slowing adoption and interoperability across different industries.
Real-World Examples
Here are some notable real-world examples of homomorphic encryption in action:
1. Google’s Encrypted Search Experiments
Google researchers have tried using homomorphic encryption to handle search queries while they are still encrypted. This means searches can be processed without seeing the user’s private data, keeping information safe while using cloud services.
2. NVIDIA & Private AI Research
NVIDIA has leveraged homomorphic encryption to allow AI models to be trained on encrypted datasets. This ensures sensitive data, such as medical images or financial records, remains private while still enabling AI-driven insights.
Future of Homomorphic Encryption
Here are some key developments shaping the future of homomorphic encryption and its potential impact across industries:
1. Improved Efficiency
Ongoing research focuses on reducing computational overhead, making it faster, practical, and accessible for widespread real-world applications.
2. Integration with Blockchain
Using homomorphic encryption with blockchain lets people build apps where data stays private, and transactions are safe in a shared digital network
3. Wider Adoption in Cloud Platforms
As cloud providers implement support for homomorphic encryption, businesses will increasingly outsource sensitive computations securely and efficiently.
4. Healthcare Breakthroughs
It lets researchers around the world work together on genomics and medical AI, using data safely without risking patient privacy.
Final Thoughts
Homomorphic encryption is a groundbreaking cryptographic technology that enables computations on encrypted data while maintaining full privacy. Its adoption in healthcare, finance, cloud computing, and government allows secure, privacy-preserving analytics, transforming data management and setting new standards for protecting sensitive information in the digital era.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Who invented homomorphic encryption?
Answer: Craig Gentry introduced the first fully homomorphic encryption scheme in 2009.
Q2. Is homomorphic encryption practical today?
Answer: Yes, but with limitations. While some real-world applications exist, performance and scalability challenges remain.
Q3. What industries benefit the most from Homomorphic Encryption?
Answer: Healthcare, finance, government, and cloud computing benefit notably due to their reliance on sensitive data.
Q4. Is homomorphic encryption the same as end-to-end encryption?
Answer: No. End-to-end encryption guarantees data is protected during transmission, while homomorphic encryption allows encrypted data to be processed without decryption.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Homomorphic Encryption” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.