Updated April 18, 2023

Introduction to Haskell ByteString Function
ByteString is used to represent bytes of string in Haskell. ByteString is used when we want high performance, high-speed requirement, etc. ByteString is also known as time and space-efficient implementation. ByteString contains 8-bit character data. Byte string in Haskell is very immutable, compact with two basic varieties provided by the Byte one is for lazy and another one is strict. In short, it is used to represent a sequence of 8 bit or bytes, where the high-speed requirement is necessary. In the coming section, we will discuss more the internal working of the ByteString, its usage and implementation in detail for better understanding.
Syntax of Haskell ByteString Function
As discussed it is used where high performance is required, also we will see its syntax in detail how we can use this while programming in Haskell for beginners see below;
import qualified Data.ByteString as bs
ByteString = bs.pack "your string"
As you can see in the above line of syntax we are using one import statement to deal with the ByteString in Haskell. Also for creating ByteString in Haskell we are using the pack method of the ByteString library. Let’s take a practice syntax to better understand the syntax of ByteString in Haskell see below;
Example:
ByteString = bs.pack "hello"
In the above way you can create ByteString in Haskell, as it is very easy to create and handle in Haskell. In the coming section, we will see more about the internal working of the ByteString function in Haskell and how to use this while programming while Haskell for beginners.
How does ByteString Function Work in Haskell?
As we already know that ByteString is a library that provides a different function to deal with type in Haskell. Also, it is an in-build function so we can use it directly, we do not require to install any library for this. We need to import ByteString in our program in order to use this. Byte string comes up with the two variant see below;
Let’s discuss each of them in detail;
- Strict ByteStrings: This variant of ByteString helps us to maintain the string as a large array. This helps us to passing data between Haskell and C.
- Lazy ByteStrings: This variant of ByteString uses the lazy list of strict variant, which provide and make it suitable for I/O streaming.
Below see the import statement which needs to be included for using ByteString in the Haskell program;
import qualified Data.ByteString as BS
If we want high performance and handle quality list or data then we should go for ByteString in Haskell. It provides us various library to convert the data into ByteString, that a string can easily be converted into ByteString. For this, we have a pack function in the ByteString library, which helps us to convert string to ByteString vice versa we have another one called as unpack which is used to convert again a ByteString to string and so on. ByteString library has not been designed for Unicode, so if you want Unicode string you can use type as Text from the Text package.
Methods of ByteString Library
Some of the methods defined by the ByteString library are decided as below;
1. fromListN
Below you can see the method signature for this,
signature:
fromListN :: Int -> [Item ByteString] -> ByteString
2. fromList
Below you can see the method signature for this,
signature:
fromList :: [Item ByteString] -> ByteString
3. toList:
Below you can see the method signature for this,
signature:
toList :: ByteString -> [Item ByteString]
Let’s take a sample example in Haskell using byte string, this will help beginners to start with using ByteString while programming in Haskell see below;
e.g. :
import qualified Data.ByteString as B
import qualified Data.ByteString.Char8 as Bytechar
demo = Bytechar.pack "sample in bytestring"
main = do
Bytechar.putStrLn demo
As you can see in the above lines of code we are trying to use the ByteString library in Haskell, the first step that we need to do here is import, at the first statement of the program. We have imported two packs one is ByteString and another one is ByteString char after this we can assign them any name thought which we want to access this in our program. In the second step we have used pack() method from the Bytechar which is the part of ByteString only, this will give us ByteString representation of string, and in the main block we have just print the value of the ByteString using putStrLn function of Haskell.
Points to remember and keep in mind while using ByteString see below;
1. This is an in built library in Haskell, which provide us various function to convert the string into ByteString.
2. If you want speed requirement, high performance then ByteString is a good choice.
3. This library is very easy to handle we have to include only one package in our program before using it.
4. In short ByteString is a representation of the bytes or sequence of string in Haskell.
Example of Haskell ByteString
1) In the below example we are trying to use ByteString and converting existing string to ByteString using the Bytechar provided by ByteString in Haskell, remember ByteString is not a function it is a library in Haskell. This is a sample example for beginners to start using ByteString for it good features.
Code:
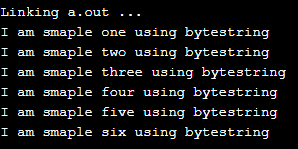
import qualified Data.ByteString as B
import qualified Data.ByteString.Char8 as Bytechar
demo1 = Bytechar.pack "I am smaple one using bytestring"
demo2 = Bytechar.pack "I am smaple two using bytestring"
demo3 = Bytechar.pack "I am smaple three using bytestring"
demo4 = Bytechar.pack "I am smaple four using bytestring"
demo5 = Bytechar.pack "I am smaple five using bytestring"
demo6 = Bytechar.pack "I am smaple six using bytestring"
main = do
Bytechar.putStrLn demo1
Bytechar.putStrLn demo2
Bytechar.putStrLn demo3
Bytechar.putStrLn demo4
Bytechar.putStrLn demo5
Bytechar.putStrLn demo6
Output:
Conclusion
By using ByteString we can easily convert our existing string to ByteString it provide various function, internally it used Bytechar to convert it. Apart from it, it has many more functions as well. ByteString is not a function rather it is a library that offers compact, high performance, speed performance, and so many other things as well.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Haskell ByteString. Here we discuss the basic concept of Haskell ByteString, various methods of ByteString library along with an example and code Implementation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –

