Updated March 1, 2023
Difference Between SQL vs Hadoop
Hadoop is a big data ecosystem that is used for storing, processing and mining patterns from data. Hadoop can be used for a wide range of problems. It is a full technology stack in itself. There are many additional frameworks and platforms on top of Hadoop which address one or the other technical issues like data collection, data storage, data processing, log maintenance, advanced analytics, etc. SQL is a query language that is used to store, process and extract patterns from data stored in relational databases. Data is stored in the form of tables here. It works only for structured data only.
Head to Head Comparison Of SQL vs Hadoop (Infographics)
Below is the top 17 difference between SQL and Hadoop:
Key Differences Between SQL and Hadoop
Both SQL vs Hadoop are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major Difference Between SQL and Hadoop:
- Above, we saw the key comparison between SQL and Hadoop. By those statements, we can understand that these two are two unique systems designed for specific needs and they are used for unique purposes.
- Whereas Hadoop provides a vast range of functionality and applications, SQL compliments Hadoop in more sense than compete with it. For example, HIVE which is an independent component of Hadoop is very similar to SQL. Using Hive, SQL like syntaxes can be written to do data manipulations, but the design, functioning, and intent of HIVE is different from SQL in principle.
- The most important difference to understand between the SQL vs Hadoop is that SQL can handle a very limited type of data i.e. relational data and its processing speed becomes very slow when millions of records are to be manipulated at once whereas Hadoop is specifically designed to address this problem only.
- There are massive support and research going on in Hadoop, every other day new technology stack keeps coming in this front yard, people are migrating from their traditional relational database systems to towards Hadoop based big data infrastructure. Such advances only pave a brighter path for the future for Hadoop along with which only a few are traveling now.
SQL and Hadoop Comparison Table
The primary Comparison between SQL vs Hadoop are discussed below:
|
Hadoop |
SQL |
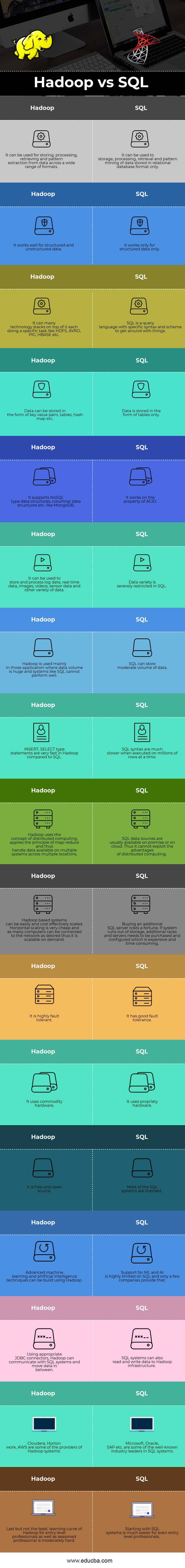
| It can be used for storing, processing, retrieving and pattern extraction from data across a wide range of formats. | It can be used for storage, processing, retrieval and pattern mining of data stored in a relational database format only. |
| It works well for structured and unstructured data. | It works only for structured data only. |
| It can many technology stacks on top of it each doing a specific task like HDFS, AVRO, Pig, HBase etc. | SQL is a query language with specific syntax and a scheme to get around with things. |
| Data can be stored in the form of key-value pairs, tables, hash map etc. | Data is stored in the form of tables only. |
| It supports NoSQL type data structures, columnar data structures etc. like MongoDB | It works on the property of ACID. |
| It can be used to store and process log data, real-time data, images, videos, sensor data and other variety of data. | Data variety is severely restricted in SQL. |
| Hadoop is used mainly in those applications where data volume is huge and systems like SQL cannot perform well. | SQL can store a moderate volume of data. |
| INSERT, SELECT type statements are very fast in Hadoop compared to SQL | SQL syntax are much slower when executed on millions of rows at a time. |
| Hadoop uses the concept of distributed computing, applies the principle of map-reduce and thus handle data available on multiple systems across multiple locations. | SQL data sources are usually available on-premise or on a cloud. Thus it cannot exploit the advantages of distributed computing. |
| Hadoop based systems can be easily and cost-effectively scaled. Horizontal scaling is very cheap and as many computers can be connected to the network as desired thus it is scalable on demand. | Buying an additional SQL server costs a fortune. If a system runs out of storage, additional racks and servers need to be purchased and configured which is expensive and time-consuming. |
| It is highly faulted tolerant. | It has good fault tolerance. |
| It uses commodity hardware. | It uses propriety hardware. |
| It is a free and open source. | Most of the SQL systems are licensed. |
| Advanced machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques can be build using Hadoop. | Support for ML and AI is highly limited on SQL and only a few companies provide that. |
| Using appropriate JDBC connectors, Hadoop can communicate with SQL systems and move data in between. | SQL systems can also read and write data to Hadoop infrastructure. |
| Cloudera, Horton work, AWS are some of the providers of Hadoop systems. | Microsoft, Oracle, SAP etc. are some of the well-known industry leaders in SQL systems. |
| Last but not the least, the learning curve of Hadoop for entry-level professionals, as well as a seasoned professional, is moderately hard. | Starting with SQL systems is much easier for even entry-level professionals. |
Conclusion
SQL is more traditional whereas Hadoop is the future. Big data is a promising future, but currently, the industry adoption and customer confidence are not that strong. It is yet to be seen how dominating it will become as time passes. AWS is certainly a force to reckon with, but still, a lot of development and support is needed to make Hadoop technology for the true future. SQL has been here for decades and is used almost everywhere. Today it is the backbone of everything that is data. In the coming future too, SQL shall be there, it will compliment Hadoop in more number of ways than complete with it. Learning and exploiting benefits of Hadoop can be very promising for individuals, both who are starting their career and those who are already established software developers, it can also be beneficial for industries and organizations who develop products and solutions in the information technology world, they should obviously consider about using Big data stack in their offerings and finally customer and partners should also implement Hadoop based solutions in their premises to make the most out of it.
Recommended Articles
This has a been a guide to the top differences between SQL vs Hadoop. Here we have discussed SQL vs Hadoop head to head comparison, key difference along with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more