Difference Between Hadoop vs MapReduce
The roots of Hadoop date way back to 2002 when Dough Cutting was working on an open-source project named Nutch (used to index the web pages and use the indexed web pages for searching, the same thing Google does). He was facing scalability issues both in terms of storage and computing. In 2003, Google published GFS (google file system); in 2004, Nutch created NDFS (Nutch distributed file system). After Google announced MapReduce as the computational brain behind their sorting algorithms, Dough was able to run Nutch on NDFS and used MapReduce in 2005, and in 2006, Hadoop was born.
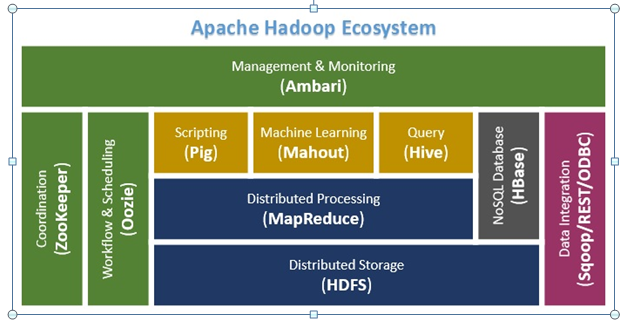
Hadoop and MapReduce! Hadoop is an Eco-system of open-source projects such as Hadoop Common, Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS), Hadoop YARN, and Hadoop MapReduce. Hadoop, as such, is an open-source framework for storing and processing massive datasets. HDFS carries out the storing, and MapReduce takes care of the processing. On the other hand, MapReduce is a programming model that allows you to process vast amounts of data stored in Hadoop. Let us understand Hadoop and MapReduce in detail in this post.
Head to Head Comparison between Hadoop vs MapReduce (Infographics)
Below is the Top 5 comparison between Hadoop vs MapReduce:
Key Differences between Hadoop and MapReduce
The following is the difference between Hadoop and MapReduce
- If we want to differentiate Hadoop and MapReduce in layman’s terms, we can say that Hadoop is like the car wherein you have everything that is needed to travel distances, but MapReduce is like the engine of the car, so without the car an engine can’t exist, but the exterior of the car may change (other DFS (distributed file systems)).
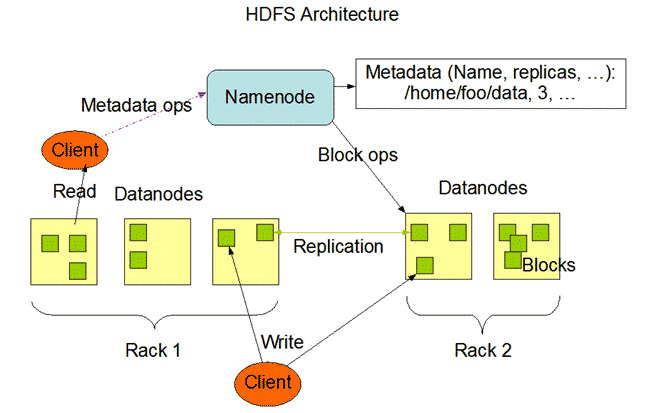
- The basic idea behind Hadoop is that the data must be reliable and scalable, reliable as in case of a disaster or network failure, the data must be available all the time, and this is achieved by Hadoop’s framework using Name Nodes and Data Nodes.
- Some basic ideas of Data Nodes and Name Nodes
The basic idea behind the architecture of the Data Node and Name Node is the enslaver/enslaved person architecture, where one stores the location of the data (Name Node), and the other stores the data itself (Data Node). The data is split into chunks of 64 MB and saved in the data blocks, and the registry is maintained at the Name Node. The data is replicated thrice by default for reliability. Talking about scalability, the hardware can be increased on the go, and this helps to increase the storage and make the system scalable.
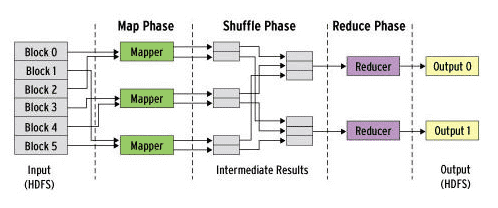
Now coming to MapReduce, there are three phases.
- Map Phase
- Shuffle Phase
- Reduce Phase
Let’s take an example to understand it better.
The Word Count program gives us the key-value pairs of the word and its frequency in a paragraph/article or any data source. To understand it easily, let’s take the below as example data.
In the dataset, as we can see, we have three words bus, car, and train. The column named Input has the data as we have in the dataset, and the column Output has the data in the intermediate stage, wherein the shuffling will take place.
Here we are taking the splitter as a comma (,) to split the words. The splitter can be a comma or space or a new line etc.
| Input | Set of data | caR, CAR, car, BUS, TRAIN,bus, train, bus, TRAIN,BUS, buS, Car, bus, car, train, car, bus, car |
| Output | Convert into another set of data
(Key,Value) |
(Bus,1), (Car,1), (bus,1), (car,1), (train,1),
(car,1), (bus,1), (car,1), (train,1), (bus,1), (TRAIN,1),(BUS,1), (buS,1), (caR,1), (CAR,1), (car,1), (BUS,1), (TRAIN,1) |
And the output of the above intermediate stage is given to the reducer and below is the final output of the program.
| Input
(output of Map function) |
Set of Tuples | (Bus,1), (Car,1), (bus,1), (car,1), (train,1),
(car,1), (bus,1), (car,1), (train,1), (bus,1), (TRAIN,1),(BUS,1), (buS,1), (caR,1), (CAR,1), (car,1), (BUS,1), (TRAIN,1) |
| Output | Converts into a smaller set of tuples | (BUS,7),
(CAR,7), (TRAIN,4) |
- One of the key differences between Hadoop with other big data processing frameworks is that Hadoop sends the code (MapReduce code) to the clusters where the data is stored rather than sending the data to code, as the data sets will in TBs or sometimes in PB’s it will be a tedious task to do.
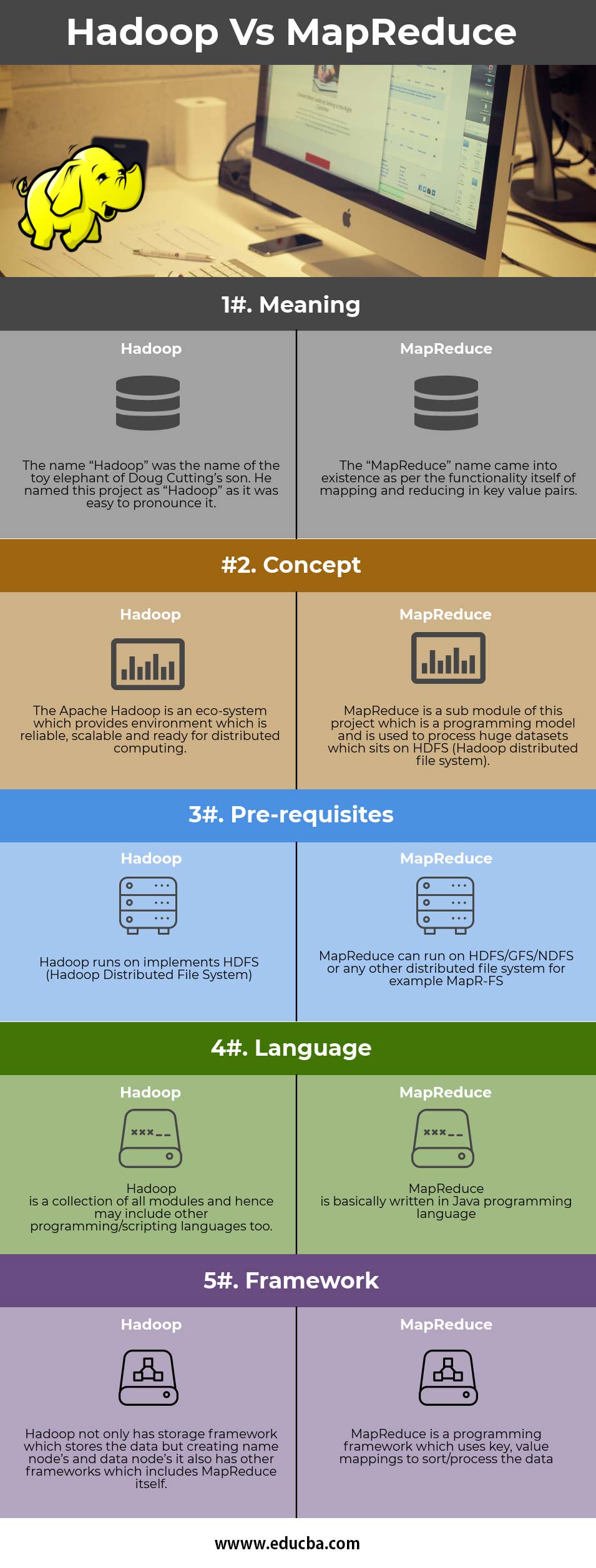
Hadoop vs MapReduce Comparision Table
Below are the primary comparison
| Basis of Comparison | Hadoop | MapReduce |
|
Meaning |
The name “Hadoop” was the name of the toy elephant of Doug Cutting’s son. He named this project “Hadoop” as it was easy to pronounce it. | The “MapReduce” name came into existence as per the functionality itself of mapping and reducing in key-value pairs. |
|
Concept |
The Apache Hadoop is an ecosystem that provides an environment that is reliable, scalable, and ready for distributed computing. | MapReduce is a submodule of this project which is a programming model and is used to process huge datasets which sit on HDFS (Hadoop distributed file system). |
|
Pre-requisites |
Hadoop runs on implements HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) | MapReduce can run on HDFS/GFS/NDFS or any other distributed file system; for example MapR-FS |
|
Language |
Hadoop is a collection of all modules and hence may include other programming/scripting languages too. | MapReduce is basically written in Java programming language. |
|
Framework |
Hadoop not only has a storage framework that stores the data but creates name nodes and data nodes it also has other frameworks, which include MapReduce itself. | MapReduce is a programming framework that uses a key and value mappings to sort/process the data. |
The below figure will help in differentiating MapReduce from Hadoop.
MapReduce Framework
As we can see from the above picture that MapReduce is a distributed processing framework, whereas Hadoop is a collection of all the frameworks.
Conclusion
Hadoop being open source, gained popularity as it was free to use, and the programmers could change the code as per their needs. The Hadoop Eco-system was developed continuously over the past years to make the Eco-system as bug-free as possible. With the ever-changing needs of the world, technology changes rapidly, and it becomes difficult to keep track of the changes.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Hadoop vs MapReduce” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.