Updated March 18, 2023

Introduction to Function Overloading in C++
C++ programming has amazing features and one of the most important features is function overloading. It means a code having more than one function with the same name but with the different argument lists. The argument list means the sequence of the arguments and data types of arguments. Function overloading is used to perform similar operations. It is used to enhance the readability of the code. Redefined the function because there is no point in creating two different functions for performing the same work again and again.
Syntax
void add(int a, int b);
void add(float a, float b);Both are the same function but arguments are different. So in case you want to perform addition on different data types using the same function then function overloading feature can be used in programming with C++.
Here is the C++ code to demonstrate function overloading in C++ programming:
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void print(int x) {
cout << " Here is the integer " << x << endl;
}
void print(double y) {
cout << " Here is the float " << y << endl;
}
void print(char const *v) {
cout << " Here is the character* " << v << endl;
}
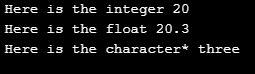
int main() {
print(20);
print(20.30);
print("three");
return 0;
}
Different Ways to Overload Function in C++
There are several ways to overload a function in the C++ programming language. Let’s see how can we do that:
1. Function Overloading
Use to increase code readability in programming. It can be defined as overloading 2 or more functions with the same name but different parameters are known as Function overloading.
Syntax:
DataType Functionname (parameter list)
{
Function body
}Example #1
Here is the C++ code to demonstrate function overloading by changing the number of arguments in C++ programming:
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Calculate {
public:
static int addition(int a,int b){
return a + b;
}
static int addition(int a, int b, int c)
{
return a + b + c;
}
};
int main(void) {
// Declaration class object to call function
Calculate S;
cout<<S.addition(50, 50)<<endl;
cout<<S.addition(25, 26, 27);
return 0;
}
Example #2
Here is the C++ code to demonstrate function overloading by having different types of arguments in C++ programming:
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Calculate {
public:
int addition(int a,int b){
return a + b;
}
float addition(float a, float b, float c)
{
return a + b + c;
}
};
int main(void) {
// Declaration class object to call function
Calculate S;
cout<<S.addition(50, 50)<<endl;
cout<<S.addition(25.20, 26.30, 27.60);
return 0;
}![]()
2. Operator Overloading
There are several built-in operators in the C++ programming language. A coder can use these operators to overload or redefine these built-in operators. It’s a compile-time polymorphism in which an overloaded operator is used to performing tasks on user-defined data types. Almost many operators can be overloaded in C++ programming language.
Syntax:
ReturnType Classname :: operator OperatorSymbol (parameter list)
{
Function body
}Example #1
Here is the C++ code to demonstrate Operator overloading in C++ programming:
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Demo
{
private:
int count;
public:
Demo(): count(5){}
void operator ++()
{
count = count+1;
}
void DisplayCount() { cout<<"The Count is : "<<count; }
};
int main()
{
Demo d;
// this calls void operator ++()" function
++d;
d.DisplayCount();
return 0;
}![]()
Example #2
Let’s see How function overloading actually works? in programming through C++ coding examples:
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void show(int);
void show(float);
void show(int, float);
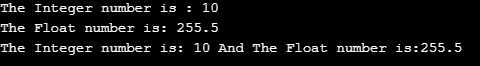
int main() {
int x = 10;
float y = 255.5;
show(x);
show(y);
show(x, y);
return 0;
}
void show(int variable) {
cout << "The Integer number is : " << variable << endl;
}
void show(float variable) {
cout << "The Float number is: " << variable << endl;
}
void show(int variable1, float variable2) {
cout << "The Integer number is: " << variable1;
cout << " And The Float number is:" << variable2;
}
Code Explanation:
In the above code, we have created a function to show the output of different data types but if you notice functions name is same and arguments are different. Then we initialized a variable called x and assigned it a value and some value assigned to float variable y also. After assigning values to x and y variables we called the function shown to display input value on the output screen.
As you can see the function names but argument is different in all three cases. First, we called the function only show integer variable after that we called show function to display output only for float variable. Finally, we called the show function which has both integer and float variables to show output on the display screen as output.
This is how actually function overloading feature works in the C++ programming language. Depending on different data types the same function can be used to perform a similar set of operations.
Example #3
Here is the C++ code to demonstrate Function overloading in C++ programming:
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class X
{ int x;
public:
X(){}
X(int j)
{
x=j;
}
void operator+(X);
void display();
};
void X :: operator+(X a)
{
int n = x+a.x;
cout<<"The addition of two objects is : "<<n;
}
int main()
{
X a1(505);
X a2(409);
a1+a2;
return 0;
}![]()
Code Explanation:
In the above code, we created a class X and created an integer variable x, and then declared two constructors so that we don’t have to create objects for calling the function as constructor automatically initializes a newly created class object just after a memory is allocated. Two functions are created operator and display to show the addition of two objects using function overloading concepts in our code.
Conclusion
In Conclusion, function overloading feature in C++ can be used in multiple ways to increase code readability. It helps in saving memory space as well as compilation time while programming with the C++ language. The compile-time polymorphism concept is also introduced through operator overloading concepts where almost every operator can be overloaded.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Function Overloading in C++. Here we discuss the various ways to overload function in C++ along with different examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following article to learn more –


