Updated March 23, 2023
Difference Between Forward Chaining and Backward Chaining
Forward Chaining vs Backward Chaining is two important strategies in the field of Artificial Intelligence. Its origin lies in the Expert System Domain of AI. One of the most prominent research domains of AI, Expert System was introduced to emulate the decision-making ability of human experts. It has 3 components:
- Knowledge Base: To Store domain-specific and high-quality knowledge.
- Inference Engine: Use the knowledge from Knowledgebase to arrive at a decision.
- User Interface: Provides Interaction between the user of the ES and the expert system.
Forward and Backward chaining is the strategies used by the Inference Engine in making the deductions.
Forward Chaining
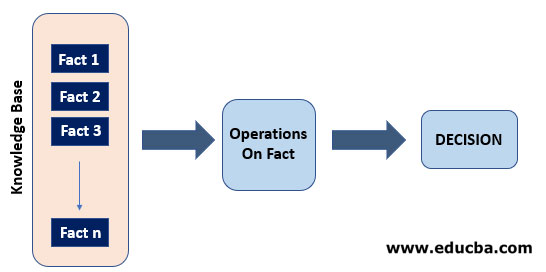
Forward Chaining the Inference Engine goes through all the facts, conditions, and derivations before deducing the outcome i.e. it starts with a set of rules to perform a chain of operations to conclude the final decision. This Strategy is used to get the conclusion by manipulating the knowledge from the knowledge base.
This strategy is used to answer the question “WHAT CAN HAPPEN NEXT ?”
Properties:
- Since it moves from top to bottom it’s called a top-down approach.
- It makes a conclusion by making deductions from data and moving from initial state to the goal state.
Backward Chaining
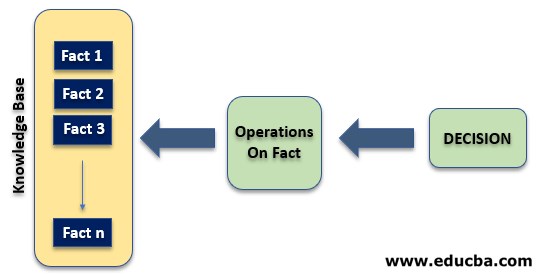
In this, the inference system knows the final decision, it tries to figure out the conditions that would have resulted in that decision. It is mostly used in finding the cause of a problem.
This strategy is used to answer the question “WHY THIS HAPPEN?”
Properties:
- In this, the goals are broken into sub-goals to prove a fact.
- It’s a goal-driven approach
- It used the depth-first strategy for proof.
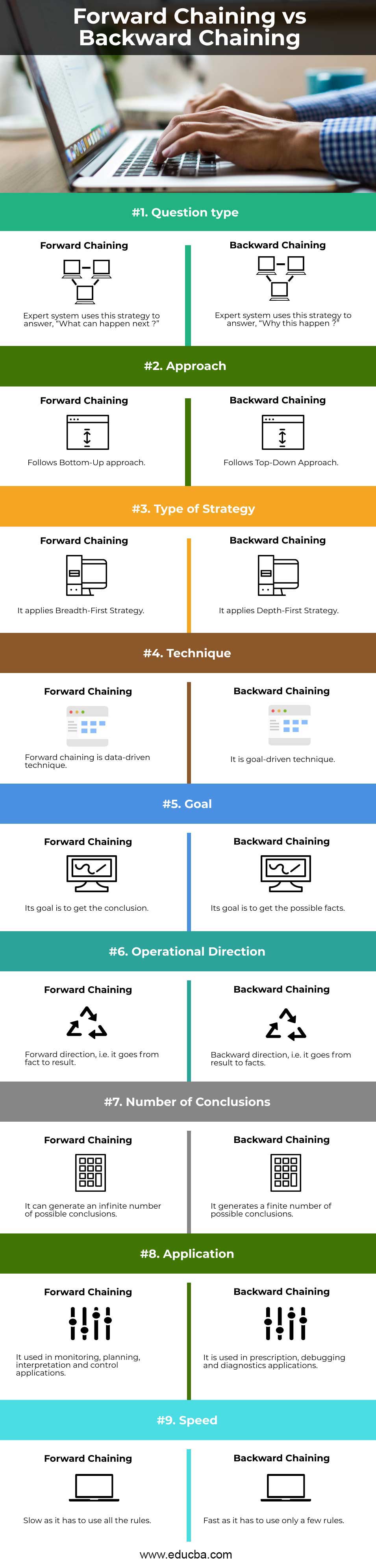
Head to Head Comparison between the Forward Chaining and Backward Chaining (Infographics)
Below is the top 9 Comparison between the Forward Chaining vs Backward Chaining:
Key Differences Between the Forward Chaining and Backward Chaining
Let us discuss some of the major key differences:
- Forward chaining is used to deduce the conclusion by taking the facts and move in forward direction by applying the inference rule to get more data, till the time it reaches the goal while in backward chaining it takes the goal and moves backward by using the inference rule to determine the fact which could be the reason for the goal.
- Forward chaining uses the breadth-first strategy to deduce conclusion while backward chaining uses the depth-first strategy to get the facts.
- Due to the reason of taking the facts and deducing the result forward chaining is termed as bottom-up approach while backward chaining is also known as a top-down approach.
- Forward chaining is used to get the goal from data hence it is called a data-driven inference technique while the Backward chaining is used to get the data from the goal it is called goal-driven inference techniques.
- Forward chaining will search all the possible ways for getting the goal while Backward chaining avoids unnecessary paths.
- Since Forward Chaining checks all rules it is slow, whereas backward chaining is fast as checks only required rules.
- Forward chaining can be used in the share market to detect the price of shares using the available data while Backward chaining can be used to know the reason for a cause like cancer.
- Forward chaining is used in tasks like planning, monitoring, interpretations and control application while backward chaining is used in debugging and diagnostic tasks.
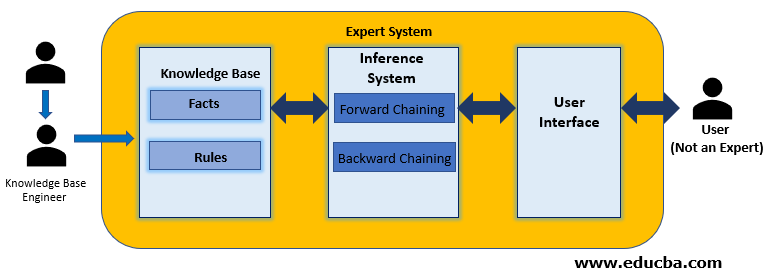
- Now you might be having a clear understanding of these two strategies of Inference System and how they are related to the Expert System. Look at the figure below to understand their relation:
- Expert and Knowledge Base Engineer creates the Knowledgebase of Expert System, which is then used by the strategies of Inference system to deduce the result in case of forward chaining using the facts and rule available In the knowledge base or getting the reason for the goal by taking the input as a goal from the user and fact and rules from the knowledge base.
Forward Chaining vs Backward Chaining Comparison Table
The table below summarizes the comparisons:
| Basis of comparison | Forward Chaining | Backward Chaining |
| Question Type | Expert System uses this strategy to answer, “What can happen next ?” | Expert System uses this strategy to answer, “Why this happen ?” |
| Approach | Follows Bottom-Up approach | Follows Top-Down Approach |
| Type of Strategy | It applies the Breadth-First Strategy | It applies the Depth-First Strategy |
| Technique | Forward chaining is a data-driven technique | It is a goal-driven technique. |
| Goal | Its goal is to get a conclusion. | Its goal is to get the possible facts |
| Operational Direction | Forward direction, i.e. it goes from fact to result | Backward direction, i.e. it goes from result to facts. |
| Number of Conclusions | It can generate an infinite number of possible conclusions | It generates a finite number of possible conclusions |
| Application | It used in monitoring, planning, interpretation and control applications. | It is used in prescription, debugging and diagnostics applications. |
| Speed | Slow as it has to use all the rules | Fast as it has to use only a few rules. |
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen differences between the Forward Chaining vs Backward Chaining with their key differences. I hope you will find this article helpful.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the difference between the Forward Chaining vs Backward Chaining. Here we also discuss the Forward Chaining vs Backward Chaining key differences with infographics, and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –