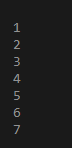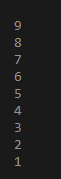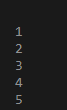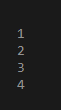Updated April 3, 2023
Introduction to For loop in PL-SQL
Since it is very simple to understand the FOR LOOP in every language. So, PL-SQL also has FOR LOOP facility. Basically for loop in PL_SQL are of two types. First is Numerical for loop and the second one is Curser for a loop. SO in this post, we will focus mainly on Numerical for a loop. So, FOR LOOP enable us to iterate any statement or statements in user-specified number of times. In this topic, we are going to learn about For Loop in PLSQL.
Syntax and its description for FOR LOOP in PLSQL
FOR lc IN [REVERSE] lower. . . . . . . .upper
LOOP
Statement_1;
Statement _2;
…
Statement_3;
END LOOP;So the first sentence enables you to initiate the loop counter variable “lc” with a lower and upper limit like every FOP LOOP in other programming languages does. So lower limit is the lower number and the upper limit is the upper limit of iteration. There is EVERSE option available in case we want to iterate the loop in a reverse manner. This keyword is optional for users. Then every bunch of statements will start with “LOOP” word and end with the “END LOOP” word. Basically in your real-time scenario, you have to specify a break statement or exit statement so we have to specify a condition at which point the loop should break so that’s this is how you specify that exit condition you can directly specify exit like this or you can just say exit when well the advantage of exit when the condition is that you can specify a condition here like on which statement it should break well that’s how simple loop works we have your loop command and in loop statement when you have exit condition well those are the two things and the design for the disadvantage of this loop statement is that suppose in case if you forgot to specify exit condition it’s going to run an infinite number of times there’s no stop to it so we have to be very careful while using a loop.
Examples to demonstrate the functioning and use of FOR LOOP in PLSQL
Now let’s try some examples which will help you understand the concepts more clearly.
Input 1:
DECLARE
BEGIN
FOR vc IN 1..7
LOOP
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(vc);
END LOOP;
END;Output:
Explanation:
This is a very simple demonstration of the PL-SQL program. So, here we have DECLARE BEGIN BLOCK. In DECLARE we can declare or/ and initialize any variable with the data type. Here since we are not using any variable except the loop variable so, we did not declare it. Then inside BEGIN block, we have started FOR LOOP. In this, FOR LOOP it is very important to have one variable which will iterate for the entire FOR LOOP cycle. So that loop has two dots with each end upper and lower limit of iteration. So every time variable VC enters the loop it gets incremented by 1 till the upper limit. So each time loop iterates the DBMS OUTPUT prints the output on the console. And lastly do not forget to end loop and put an extra loop to which will serve as a closing bracket for DECLARE block. So After executing the above code, the Value of your counter variable from each iteration is counting from 1 to7.
Input 2:
DECLARE
BEGIN
FOR vc IN REVERSE 1..9
LOOP
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(vc);
END LOOP;
END;Output:
Simply write the keyword REVERSE immediately after the keyword IN. So after executing the above command we get the below result.
Input 3:
Declare
result_var NUMBER;
BEGIN
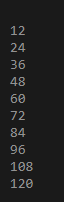
FOR vc in 1..10
LOOP
result_var:=12*vc;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(result_var)
END LOOP;
END;Output:
Explanation:
Here we wrote a full-fledged PL-SQL code to find the table of 12. So in PL-SQL, every code starts with declare command.
Then inside that, we declare var_res variable as a number to store the result. Then BEGIN statement start and inside that, we create a loop statement which will iterate 10 times multiplying with number table 12.
Input 4:
DECLARE
I number :=1;
BEGIN
LOOP
Dbms_output.put_line(i);
I:=i+1;
EXIT WHEN i>5;
END LOOP;
END;Output:
Explanation:
Here We declare I as a number equal to 1 Then our begin statement starts in the begin statement Here we have an exit statement that will exit the execution when at iteration it finds that I am greater than 5. This exit when the statement is also used to restrict the running of the loop to infinite time as we cannot use ctrl +c command to kill the job. So while the condition will be true till I am less than 5 Then the loop will iterate till I am less than 5 fros 0 to 4 and by this way iteration proceeds to increase the I number which was declared d earlier. I will be incremented every time by 1 and Dbms output will display the I each time of iteration. Then loop ends.
DECLARE
I number :=1;
BEGIN
WHILE(i<5)
LOOP
Dbms_output.put_line(i);
I:=i+1;
END LOOP;
END;
/Output:
Explanation:
Here We declare I as a number equal to 1 Then our begin statement starts in the begin statement There is a while loop now instead of exit when statement.SO while the condition will be true till I is less than 5 Then the loop will iterate till I is less than 5 from 0 to 4 and by this way, iteration proceeds to increase the I number which was declared earlier.I will be incremented every time by 1 and Dbms output will display the I each time of iteration. Then loop ends.
Conclusion
We have seen the functioning of FOR LOOP with examples. The loop is the first step of coding for any beginner. So in my next post, I will definitely explain the cursor for loop.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “For Loop in PLSQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.