Updated June 9, 2023
Introduction to Footer in CSS
Footer in CSS is used when the user wants to fix the elements at the bottom position to separate the logic of the top elements from the bottom elements logic. There are two types of footers fixed footers and Movable footers. Fixed footer means the footer is fixed at the bottom; even the page scrolls down to the bottom or up to the top. It means the footer is always fixed on the bottom. Nowadays, the fixed footer feature has almost all websites because it is very difficult to select the different options from the footer when we scroll down the entire page. If we want to access footer elements, then we must go to the bottom again and select the option. It will kill user time; therefore, developers come up with sticky footer concepts in Bootstrap. So, most people prefer a fixed footer over a movable footer because a movable footer always scrolls with the page.
Advantage:
- Easily access bottom elements with the fixed footer.
- The footer separates the logic from header elements.
Why CSS over HTML?
In HTML, developers must write styles separately for every class, id, link, button, etc. Whereas in CSS, even if we have 1000’s of html pages, we can write the common logic in a single CSS file, which can be included in the HTML file with <link> tag.
How does Footer work in CSS?
The footer in CSS is nothing but a navigation bar-like structure at the bottom; we can fix the navigation bar (sticky footer) or movable at the bottom and then use the syntax below.
Syntax for the Fixed footer:
<style>
.footer {
position: fixed;
}
</style>
<div class="footer">
<p>Footer</p>
</div>Syntax for the Movable footer:
<style>
footer {
display: block;
}
</style>
<div class="footer">
<p>Footer</p>
</div>Examples of Footer in CSS
Here are some different examples:
Example #1 – Movable footer
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style type="text/css">
h2 {
text-align: center;
color: green;
}
.footer {
position: block;
width: 100%;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
color: maroon;
text-align: center;
background-color: green;
}
.p1 {
border-style: solid;
border-color: red;
border-width: 1px;
font-size: 20px;
color: blue;
}
.p2 {
border-style: solid;
border-color: blue;
border-width: 1px;
font-size: 20px;
color: fuchsia;
}
.p3 {
border-style: solid;
border-color: brown;
border-width: 1px;
font-size: 20px;
color: red;
}
.p4 {
border-style: solid;
border-color: red;
border-width: 1px;
font-size: 20px;
color: lime;
}
div {
width: 600px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h2>Movable Footer Demo</h2>
<p class="p1">Footer in CSS used when user wants to fix the elements at the bottom position to separate the top elements logic with bottom elements logic. There are 2 types of footer 1.fixed footer and 2. Movable footer. Fixed footer means footer fixed at the bottom even page scroll down to the bottom or scroll up to the top. It means footer always fixed on the bottom. </p>
<br>
<p class="p2">Footer in CSS used when user wants to fix the elements at the bottom position to separate the top elements logic with bottom elements logic. There are 2 types of footer 1.fixed footer and 2. Movable footer. Fixed footer means footer fixed at the bottom even page scroll down to the bottom or scroll up to the top. It means footer always fixed on the bottom.</p>
<br>
<p class="p3">Footer in CSS used when user wants to fix the elements at the bottom position to separate the top elements logic with bottom elements logic. There are 2 types of footer 1.fixed footer and 2. Movable footer. Fixed footer means footer fixed at the bottom even page scroll down to the bottom or scroll up to the top. It means footer always fixed on the bottom.</p>
<br>
<p class="p4">Footer in CSS used when user wants to fix the elements at the bottom position to separate the top elements logic with bottom elements logic. There are 2 types of footer 1.fixed footer and 2. Movable footer. Fixed footer means footer fixed at the bottom even page scroll down to the bottom or scroll up to the top. It means footer always fixed on the bottom.</p>
</div>
<div class="footer">
<p>I am block(movable) footer portion</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:
Explanation: In the above example, you can see the footer moved with scroll up and down.
Example #2 – Fixed Footer
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style type="text/css">
h2 {
text-align: center;
color: brown;
}
.footer {
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
color: maroon;
text-align: center;
background-color: green;
}
.p2 {
border-style: solid;
border-color: red;
border-width: 1px;
font-size: 20px;
color: blue;
}
.p4 {
border-style: solid;
border-color: blue;
border-width: 1px;
font-size: 20px;
color: fuchsia;
}
.p3 {
border-style: solid;
border-color: brown;
border-width: 1px;
font-size: 20px;
color: red;
}
.p1 {
border-style: solid;
border-color: red;
border-width: 1px;
font-size: 20px;
color: lime;
}
div {
width: 600px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h2>Fixed Footer Demo</h2>
<p class="p1">Footer in CSS used when user wants to fix the elements at the bottom position to separate the top elements logic with bottom elements logic. There are 2 types of footer 1.fixed footer and 2. Movable footer. Fixed footer means footer fixed at the bottom even page scroll down to the bottom or scroll up to the top. It means footer always fixed on the bottom. </p>
<br>
<p class="p2">Footer in CSS used when user wants to fix the elements at the bottom position to separate the top elements logic with bottom elements logic. There are 2 types of footer 1.fixed footer and 2. Movable footer. Fixed footer means footer fixed at the bottom even page scroll down to the bottom or scroll up to the top. It means footer always fixed on the bottom.</p>
<br>
<p class="p3">Footer in CSS used when user wants to fix the elements at the bottom position to separate the top elements logic with bottom elements logic. There are 2 types of footer 1.fixed footer and 2. Movable footer. Fixed footer means footer fixed at the bottom even page scroll down to the bottom or scroll up to the top. It means footer always fixed on the bottom.</p>
<br>
<p class="p4">Footer in CSS used when user wants to fix the elements at the bottom position to separate the top elements logic with bottom elements logic. There are 2 types of footer 1.fixed footer and 2. Movable footer. Fixed footer means footer fixed at the bottom even page scroll down to the bottom or scroll up to the top. It means footer always fixed on the bottom.</p>
</div>
<div class="footer">
<p>I am block(movable) footer portion</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:
Explanation: You can see the footer fixed in the above example even if we scroll up or down.
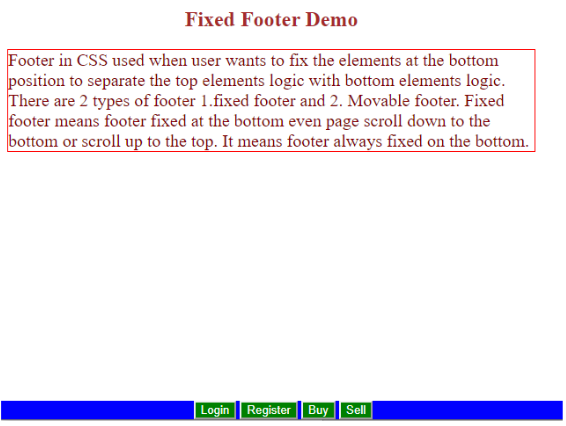
Example #3 – Fixed Footer with Buttons
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style type="text/css">
h2 {
text-align: center;
color: brown;
}
.footer {
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
color: maroon;
text-align: center;
background-color: blue;
}
button
{
color: white;
background: green;
}
.p1 {
border-style: solid;
border-color: red;
border-width: 1px;
font-size: 20px;
color: maroon;
}
div {
width: 600px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h2>Fixed Footer Demo</h2>
<p class="p1">Footer in CSS used when user wants to fix the elements at the bottom position to separate the top elements logic with bottom elements logic. There are 2 types of footer 1.fixed footer and 2. Movable footer. Fixed footer means footer fixed at the bottom even page scroll down to the bottom or scroll up to the top. It means footer always fixed on the bottom. </p>
</div>
<div class="footer">
<button class="b1">Login</button>
<button class="b2">Register</button>
<button class="b3">Buy</button>
<button class="b4">Sell</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:
Conclusion
You can create a footer in CSS using two methods: the fixed footer and the movable footer. First, the footer separates the header logic with the footer logic and accesses the bottom elements faster using a fixed footer.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Footer in CSS” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.