Updated July 10, 2023
Definition of Flask HTTPS
Flask HTTPS is defined as a concept that allows developers to develop Flask applications and deploy them for production use through HTTPS, which is compliant with encrypted connections, thus providing extra security. HTTPS extends age-old HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) and uses an SSL (Secure Socket Layer) layer. HTTPS receives and transmits data securely and doesn’t leave room for people to eavesdrop on the data that is being transferred. Next time you look at the website address bar, keep an eye on the start of the address, and you will see HTTPS for most of the secured websites! If not, watch out for any data you share there, as it might be prone to attack.
Syntax
In the section on syntax, we will look at different syntaxes in the purview of Flask HTTPS, which are essential for us to glimpse through as this will enable us to know and map the corresponding syntax to the working so that learning the working will be more practical. So, here we go with the syntaxes in HTTPS:
Installing additional dependency for using ad-hoc certificates:
pip install pyopensslIncluding adhoc SSL certificate in the app.run() call using ssl_context:
from flask import Flask
appFlask = Flask(__name__)
<… Set of codes for endpoints>
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(ssl_context='adhoc')Including adhoc SSL certificate through the command line interface:
flask run --cert=adhocIncluding self-signed SSL certificate in the app.run() call using ssl_context:
from flask import Flask
appFlask = Flask(__name__)
<… Set of codes for endpoints>
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(ssl_context=(, ))Including adhoc SSL certificate through the command line interface
flask run --cert=<certificate file> --key=<key file>How does HTTPS work in Flask?
Before understanding HTTPS working specifically for Flask applications, it is more important to understand the working of HTTPS. For that, we would first need to understand the base system’s security functionality (HTTP), and we would do that in brief as it will ease the understanding of HTTPS. Implementing the functionality of encryption and security is done through Transport Layer Security (TLS) which is a standard way of securing any communication space and ensuring that the communication is free from any compromises.
Since this article is not an expert article on security, we will refrain from detailing HTTPS or HTTP any further and restrict our discussion of working with HTTPS to build a secure and encrypted Flask server. A Flask application establishes a connection between the server and the client. During this establishment of connection, the client requests an encrypted connection. To the request, the server replies with an SSL Certificate. This certificate comprises details that can identify the server, including the server name and domain. The certificate authority encrypts the signature on the certificate using cryptographic methods. Now to ensure that the information supplied by the server is correct, the certificate authority from the server should fall under the trusted certificates present with the client. A trusted entity verifies and confirms the signature, concluding that the server connected to the client is legitimate.
After verifying the certificate, the system generates an encryption key for communication with the server. The server certificate encrypts the key to ensure secure transfer. With the server, the private key complements the public key and is the only part that can decrypt the secure package sent from the client. With this, we can complete the full cycle of encryption, which starts as soon as the encryption key is received and all traffic packages are encrypted with the particular key, which only the client and the server knows.
Thus, we can now know that the TLS encryption implementation would require these 2 items, namely server certificate that includes the public key for encryption and the other being the private key that complements the private key for decryption. In a Flask application there are two ways through which we can build the Flask application and launch it through HTTPS. One of the methods is using ssl_context in the main() section of the code, and the other is through the command-line interface using the –cert option. Our examples will examine two different certificates: adhoc certificates created on-the-fly by PyOpenSSL. Using the self-signed certificate, we can eliminate any security warnings that might pop up, making it difficult to ascertain which certificate to trust each time a different one is generated.
It’s time to look at implementing HTTPS in a Flask application!
Examples
Now that we know of the two ways of implementing HTTPS, so here in this section, we will look at both options individually in their respective examples. Also, do not use adhoc certificates; we will learn how to use a self-signed certificate!
Example #1
Installing additional dependency for using adhoc certificates.
Syntax:
pip install pyopensslOutput:
Example #2
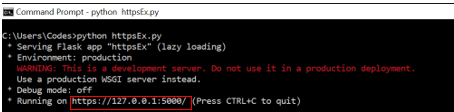
Including adhoc SSL certificate in the app.run() call using ssl_context.
Syntax:
from flask import Flask
appFlask = Flask(__name__)
@appFlask.route('/home')
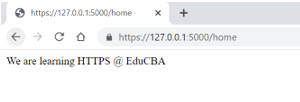
def home():
return "We are learning HTTPS @ EduCBA"
if __name__ == "__main__":
appFlask.run(ssl_context='adhoc')Output:
Example #3
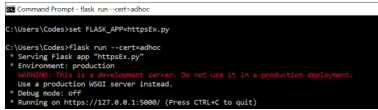
Including adhoc SSL certificate through a command-line interface
Syntax:
Code:
from flask import Flask
appFlask = Flask(__name__)
@appFlask.route('/home')
def home():
return "We are learning HTTPS @ EduCBA"
if __name__ == "__main__":
appFlask.run()Command Line:
flask run --cert=adhocOutput:
Example #4
Including self-signed SSL certificate in the app.run() call using ssl_context
Syntax:
from flask import Flask
appFlask = Flask(__name__)
@appFlask.route('/home')
def home():
return "We are learning HTTPS @ EduCBA"
if __name__ == "__main__":
appFlask.run(ssl_context=('eduCBAcert.pem', 'eduCBAkey.pem'))Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about the working of HTTPS in Flask applications and the full cycle of the process of HTTPS. Experiment and learn using the last syntax of the certificate and key through the command line!
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Flask HTTPS” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.