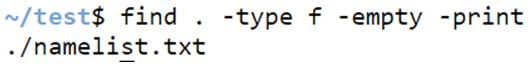Updated May 30, 2023
Introduction to Find Command in Unix
The Find Command in Unix Shell Scripting is a command-line utility for maintaining a file hierarchy system. The find command is used to find out the files and directories in the system and execute the following operations on the files. This command helps to support to search a file, name, folder, modification date, permissions of a file, and owner of a file.
The Find Command is the most frequent and useful command for searching and locating the file list and directories based on the requirement for a file matching the argument passed as the input. It is also used in many conditions to help find files by their user names, permissions, groups, date, file type, and many available possibilities.
What can we do from Find Command?
Below are the options that are used in Unix with Find Command:
The tabular structure shows the option and its function:
| -inum N | Used to search the files with an inode number. |
| -links N | Used to search files with links. |
| -name demo | Searches the files with the name ‘demo’. |
| -newer file | Checks for the files based on creation or modification date. |
| -perm octal | Checks the permission of the file to see if it is octal or not. |
| Used to print the filenames that are given in the input criteria. | |
| -empty | Searches for empty files or directories. |
| -user name | It is used to search the files owned by a user’s ID. |
| ! expr | It returns false if ‘expr’is true. |
| \(expr \) | This option is used for grouping criteria along with OR or AND. It returns true if the ‘expr’value is true. |
Syntax:
Find Command Syntax in Unix Shell Scripting is given below:
find [from where to start the search] [what to find] [options] [what to find]Examples of Find Command in Unix
Let us consider there are a few files under the test directory.
Below is the file name list that is listed under the current directory.
Code:
llOutput:
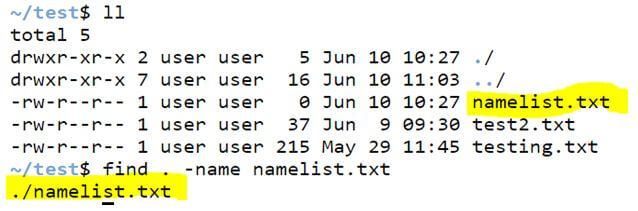
Example #1 – Finding files using the name option in the current directory.
We can search for files in the current directory using the option ‘name’ as shown below.
Syntax:
find . -name filename.txtCode:
ll
-name namelist.txtOutput:
Example #2 – Finding files using the name option in the home directory.
We can search for files in the home directory using the option ‘name’ as shown below.
Syntax:
find /home -name filename.txtCode:
find /home -name namelist.txtOutput:
Example #3 – Finding files ignoring case.
We can search for the files in the system by ignoring the case using -iname.
Syntax:
find . -iname filename.txtCode:
find . -iname Namelist.txtOutput:
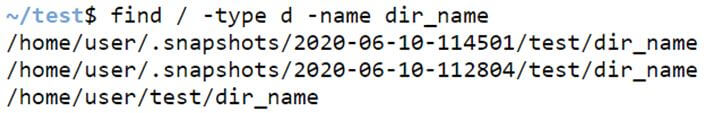
Example #4 – Finding directories using the name option.
We can find the directories using the option ‘name’ in the / directory.
Syntax:
find / -type d -name directory_nameCode:
find / -type d -name dir_nameOutput:
Example #5 – Option -perm.
We can find the files with permissions as 777 and print them.
Syntax:
find . -type d -perm 0777 -printCode:
find . -type d -prem 0777 -printOutput:
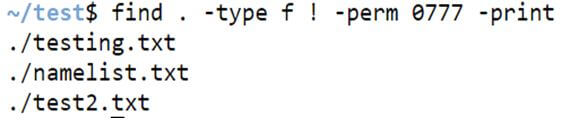
Example #6 – Option! Perm.
We can find the files with no permissions as 777 and print them as well.
Syntax:
find . -type f ! -perm 0777 -printCode:
find . -type f ! -prem 0777 -printOutput:
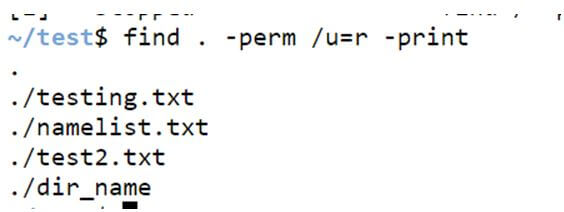
Example #7 – Finding read-only files.
We can find the files with read-only options in current directories, as shown below.
Syntax:
find . -perm /u=r -printCode:
find . -prem /u=r -printOutput:
Example #8 – Option -empty.
We can also find all empty files in the system and whichever folder you want.
Syntax:
find . -type f -empty -printCode:
find . -type f -empty -printOutput:
Example #9 – Option -empty.
We can also find all empty directories in the system and whichever folder you want.
Syntax:
find . -type d -empty -printCode:
find . -type d -empty -printOutput:
Example #10 – Finding hidden files.
We can also find hidden files or directories using Unix’s find command by the syntax below.
Syntax:
find . -type f -name “.*”Code:
find . -type f -name ".*"Output:
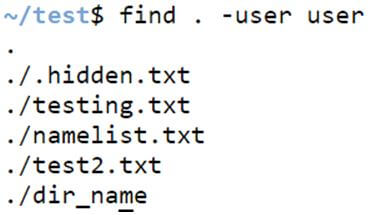
Example #11 – Finding files based on user.
We can find the users based on the user it belongs to, either under the current directory or home directory, as shown below.
Syntax:
find . -user user_nameCode:
find . -user userOutput:
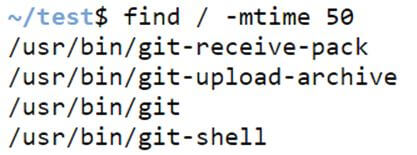
Example #12 – Finding files modified in the last 50 days.
Finding files modified in the last 50 days can be shown below.
Syntax:
find / -mtime 50Code:
find / -mtime 50Output:
Example #13 – Finding files accessed in the last 50 days.
Finding files accessed in the last 50 days can be shown below.
Syntax:
find / -atime 50Code:
find / -atime 50Output:
Example #14 – Finding changed files in the last 15 mins.
We can find files that have been changed in the last 15 minutes, as shown in the syntax below.
Syntax:
find . /cmin 15Code:
find . -cmin -15Output:
Example #15 – Finding modified files in the last 1 hour.
We can find files modified in the last 15 min as shown in the syntax below.
Syntax:
find / -mmin -60Code:
find . -mmin -60Output:
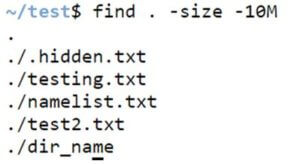
Example #16 – Option -size.
We can use option -size for various criteria like less than size or more than size by the given syntax below. In this case, we check for files with sizes less than 10MB.
Syntax:
find . -size -sizeCode:
find . -size -10MOutput:
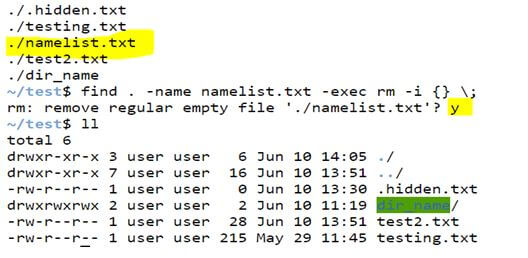
Example #17 – Find and delete a file.
We can find and delete a file using the find command in Unix. When we enter the below syntax, it will ask you for confirmation if we want to delete the file or not; type ‘Y or y’ to confirm.
Syntax:
find . -name filename -exec rm -i {} \;Code:
find . -name namelist.txt -exec rm -i {} \;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Find Command in Unix” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.