Updated March 21, 2023
Introduction to Filter Function in Matlab
This function filters the data sequence by using a digital filter, the output of filtering is basically smoothening or sharpening of signal (eliminating specific frequency range). It is direct from II implementation of signal (standard difference equation). There are four ways to represent filters in Matlab as follows:
- Output = filter ( coeff b ,coeff a , x )
- Output = filter ( ( b , a , x , z )
- Filter (b, a, x, z, dim )
- F , zf = filter ( )
Syntax and Examples of Filter Function in Matlab
Below are the Syntax and Examples of Filter Function in Matlab:
1. Output = filter (coeff b , coeff a , x )
- This modeling used rational transfer function on input signal ‘ x ’. In the above equation, a and b are the numerator and denominator coefficients of signal.
- In this case, it is mandatory to have a ( 1 ) is 1 so, we normalize the coefficient to 1 to satisfy this condition a ( 1 ) should be not equal to zero then only we can normalize the coefficient.
- The output of the filter depends on the type of input ‘x’.
- If input ‘x’ is vector then we get output ‘z’ as a vector.
- If the input signal ‘x’ is matrix then we get an output signal ‘z’ with respect to each column.
- And if it is a multidimensional signal then we get output with respect to the first array.
Code:
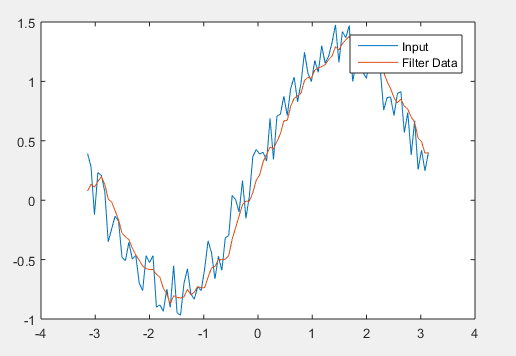
T = linspace(-pi , pi , 100 );
X = sin( t ) + 0.50 * rand ( size( t )) ;
w_size = 5;
b = ( 1 /w_size ) * ones( 1 , w_size ) ;
a = 1 ;
f = filter ( coeff b , coeff a ,x ) ;
plot ( t , x )
hold on
plot ( t ,f )
legend ( 'Input ' ,'Filter Data')
Output:
2. F = filter ( ( b , a , x , z )
- If there are memory limitations in designing then some filters consider the initial condition and final condition.
- These filters create large data and divide input into two segments.
Code:
x = randn( 110000 ,1 ); - - - creation of input sequence x (1 to 110000)
x1 = x ( 1 : 51000 ) ; - - - splitting the seq. x1= 1 to 51000
x2 = x ( 51001 : end ) ; - - - second seg is x2 = 51000 to 110000
b = [ 4 , 3 ] ; - - - numerator coefficient
a = [ 1 , 0.4 ] ; - - - denominator coefficient
[ f1 , zf ] = filter ( b , a , x1 ) ; - - - filter function
f2 = filter ( b , a , x2 , zf ) ; - - - filter function
f = filter ( b , a ,x ) ; - - - filter function
isequal( f ,[ f1 ; f2 ] ) - - - filter function matching
Output:
The output of the above code is 1 that means logical 1, logical 1 is a true condition.
3. Filter (b, a, x, z, dim)
This type of filter is used for matrix input and output designing.
Code:
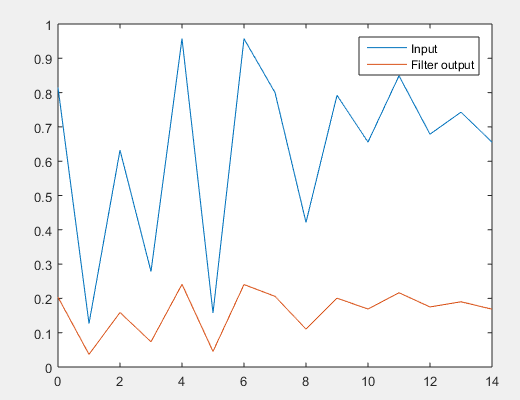
rng default
x = rand ( 3 , 10 ) ; - - - creation of input sequence 3 by 10
b = 1 ; - - - coefficient of numerator
a = [ 4 -0 .1 ] ; - - - coefficient of numerator
f = filter ( b , a , x,[ ] ,2 ) ; - - - filter function
t = 0 : length (input seq. )-1 ;
plot ( t , x ( 1 , : ) ) - - - input signal
hold on
plot ( t , f ( 1 , : ) ) - - - output signal
legend('Input ','Filter output')
Output:
4. F , zf = filter ( )
If there is memory limitation then this type of filter is used, it used initial and final conditions and it divides the input signal into two segments.
Code:
x = randn ( 110000 , 1 ) ; - - - create random signal
x1 = x ( 1 : 51000 ) ; - - - splits signal from 1 to 51000
x2 = x ( 51001 : end ) ; - - - second input signal 51001 to 110000
b = [ 6 , 3 ]; . - - -numerator coefficient
a = [ 1 , 0.9 ] ; - - - denominator coefficient
[ f1 , zf ] = filter ( b , a , x1 ) ; - - - filter function
f2 = filter ( b , a , x2 , zf ) ; . - - - filter function
f = filter ( b , a , x) ; - - - .filter function
isequal ( f , [ f1 ; f2 ] ) - - - output signal matching
Output:
The output of the above signal is logical 1 that means the condition is true.
Conclusion
The filter function mainly used to implement Moving average filter. Moving average filtering is the simplest and common method of smoothening. filtering is also used to remove noise.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Filter Function in Matlab. Here we discuss the introduction and different examples of filter function in Matlab along with its syntax. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –