Updated April 17, 2023
Introduction to Factorial in Python
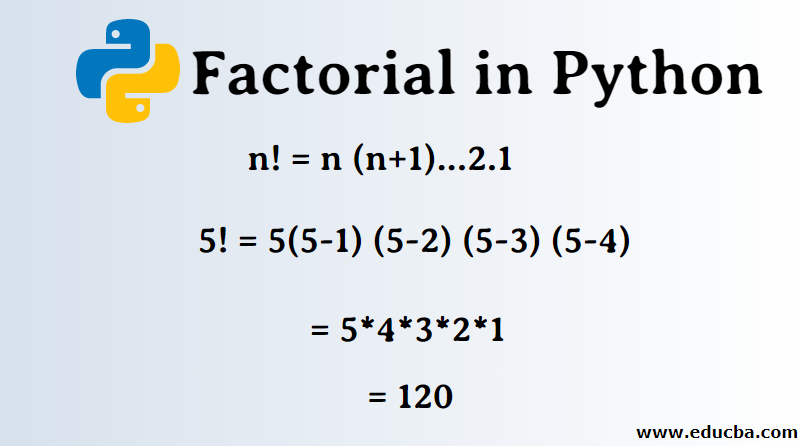
Factorial, in general, is represented as n!, which is equal to n*(n-1)*(n-2)*(n-3)*….*1, where n can be any finite number. In Python, Factorial can be achieved by a loop function, defining a value for n or passing an argument to create a value for n or creating a prompt to get the user’s desired input.
Types of Programming Technique used in Python
They can be created with the incremental loops like ‘factorial=factorial*I’ and n*factorial(n-1)
n! = n * (n-1) * (n-2) * (n-3) * (n-4) * (n-5) * (n-6) * (n-7) * . . . . . . .* 1
Example:
20! = 20 * 19 * 18 * 17 * 16 * 15 * 14 * 13 * 12 * 11 * 10 * 9 * 8 * 7 * 6 * 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1 = 2432902008176640000
| n | n! |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 6 |
| 4 | 24 |
| 5 | 120 |
| 6 | 720 |
| 7 | 5 040 |
| 8 | 40 320 |
| 9 | 362 880 |
| 10 | 3 628 800 |
| 11 | 39 916 800 |
| 12 | 479 001 600 |
| 13 | 6 227 020 800 |
| 14 | 87 178 291 200 |
| 15 | 1.30767E+12 |
| 16 | 2.09228E+13 |
| 17 | 3.55687E+14 |
| 18 | 6.40237E+15 |
| 19 | 1.21645E+17 |
| 20 | 2.4329E+18 |
Techniques of Factorial in Python
Following are some techniques:
Technique #1 – Factorial Program
Code:
# Python program to determine the value of factorial for a given number
# modifying the value keyed in will produce a different result
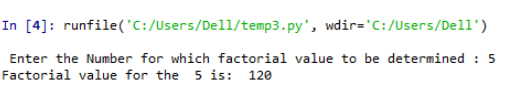
Number = int(input(" Enter the number for which factorial value to be determined : "))
factorial = 1
# to verify that the given number is greater than zero incase it is less than zero then the
# message stated below will be printed
if Number < 0:
print(" ! ! ! ! ! Factorial value cannot be intended for negative integers ! ! ! ! ! ")
# The default factorial value for zero is one and this is printed here
elif Number == 0:
print(" ! ! ! ! 1 is the factorial value 0 ! ! ! ! ")
else:
# For loop to handle the factorial calculation
for i in range(1,Number + 1):
factorial = factorial*i
print("The factorial value for the " , Number , "is" , factorial)
Output:
Explanation: The program calculates the factorial of a number using the looping technique; here, the specific integer value for which the factorial value has to be calculated is keyed in into the ‘Number’ variable. Alongside, the variable ‘Factorial’ is initialized with a value of 1. The first check carried out is to settle on whether the key value is a positive integer. this is because the factorial value for a negative integer cannot be calculated. so the check is implied such that the keyed in value is greater than zero. also, if the value keyed is equal to zero, then the factorial value for zero, which is one, is printed. In the next instance, the factorial for a given value is determined by the formula below being executed in a loop with the iterator value incremented by one.
factorial = factorial*iThis loop’s range is maintained between 1 and one value greater than the number being keyed in. At the end of the last execution, the value of the factorial is printed.
Technique #2 – Factorial Program
Code:
# Python program to determine the value of factorial for a given Number
# modifying the value keyed in will produce a different result
# Function through which factorial is achieved
def factorial(Number):
"""Factorial of a number is calculated through the below mentioned recursive function"""
if Number == 1:
return Number
else:
return Number * factorial(Number - 1)
# Number for which the factorial has to be determined
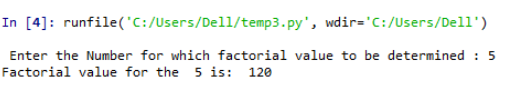
Number = int(input(" Enter the Number for which factorial value to be determined : "))
# to verify that the given Number is greater than zero in case it is less than zero then the
# message stated below will be printed
# An error message will be returned if the keyed in input is negative.
# elif an error message will be returned if the keyed in input is zero.
# else user defined function is used for calculating the factorial
if Number < 0:
print( " ! ! ! ! ! Factorial value cannot be intended for negative integers ! ! ! ! !" )
elif Number == 0:
print( " ! ! ! ! 1 is the factorial value 0 ! ! ! ! " )
else:
print("Factorial value for the ", Number , " is: " , factorial(Number))
Output:
Explanation: The program calculates the factorial of a number using a recursive function calling technique; here, the value for which the factorial needs to be determined is keyed into the ‘Number’ variable. Value 1 is initialized to the factorial variable. The first check carried out is to settle on whether the keyed value is a positive integer. this is because the factorial value for a negative integer cannot be calculated. so the check is implied such that the keyed in value is greater than zero. also if the value keyed is equal to zero, then the factorial value for zero, which is one, is printed. In the next instance, the factorial for a given value is determined by the below formula being recursively executed,
Number * factorial(Number - 1)Recursive execution by process means a technique through which looping of a given coding instance is achieved manually. this technique involves calling a given function within the same function, and this call is encapsulated inside a given if condition. So this encapsulation allows the function to be called until the given condition is satisfied.
Conclusion
These programs are implied to check whether the given palindrome of a given integer value. Thus, using the above programs, any given numeric value can be successfully evaluated for its factorial value. the programs are implied using two widely different techniques such as recursive function call and usual looping process. from a standard perspective, both these techniques don’t largely differ, and they are very much accepted methods of programming.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Factorial in Python” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.