Updated March 20, 2023
Introduction to Fact Table and Dimension Table
Fact tables comprises of the facts of the system as its data content, and Dimension tables comprises of all the properties or objects of the fact tables that can help to connect fact tables to the respective dimension tables. The data in both the tables can be in normal text format, while fact tables can have numbers along with the texts. In the process of creating the database, dimension tables are created before fact tables due to their own properties.
Fact table
It is a table that has values of the attributes of the dimension table. It contains quantitative information in a denormalized form. It basically contains the data that needs to be analyzed. Fact tables mostly have two columns, one for foreign keys that helps to join them with a dimension table and others that contains the value or data that need to be analyzed. It mostly contains numeric data. It grows vertically and it contains more records and fewer attributes.
Characteristics of Fact Table
- Keys: Fact table consists of a key that is the combination or concatenation of all primary keys of various dimension tables associated with that fact table. Such key is called a concatenated key which uniquely identifies the row of the fact table.
- Fact Table Grain: Grain of the table means the level of the detail or the deepness of the information that is stored in the fact table. The level must be the highest for designing an efficient fact table.
- Additive Measures: Attributes in the fact table can be fully additive, semi-additive or non- additive. Fully additive or additive measures are those that are added to all dimensions. In semi-additive, measures are added to some dimensions and not to all and non-additive measures are those which stores basic unit of measurement of any business process.
- Sparse Data: Some records present in the fact table contain attributes with null values or measures i.e. these records do not give or provide any information.
- Degenerated Dimensions: The dimensions or attributes present in the fact table which cannot be added or which are not additive are called a degenerated dimension.
- Outrigger Dimensions: The dimensions that have reference to any other dimension table are called as outrigger dimensions.
- Shrunken Rollup Dimensions: The dimensions which are the subdivision of columns and rows of the base dimension are called Shrunken Rollup dimensions.
Dimension Table
A dimension table contains the dimensions along which the values of the attributes are taken in the fact table. Dimension tables are small in size, contains only several thousand rows but the size can be increased occasionally. These tables are associated with a fact table through foreign keys. These tables are de-normalized. The dimension table contains hierarchical relationships and grows horizontally.
Characteristics of Dimension Table
- Keys: Every dimension table needs to have a primary key that helps to uniquely identify each record of the dimension table.
- Attributes: Dimension table contains many attributes and therefore the dimension table appears to grow horizontally.
- Attribute Values: The values in the dimension table are mostly in textual format and not in numeric format.
- Relation Between Attributes: Attributes present in the dimension table are generally not directly related to each other but still are a part of the same dimension table.
- Normalization: Dimension table is not normalized because normalization splits the data and creates additional tables which decrease the efficiency of the query execution as it must pass through these additional tables when it wants to recover measurements from the fact table for any corresponding attribute in the dimension table.
- Drilling Down, Rolling Up: Attributes present in dimension table permits to derive details through traversing from the higher level to lower level or it also allows rolling up from lower level to the higher level of the attributes.
- Records: Dimension table has less number of records and more number of attributes.
Head to Head Comparison Between Fact Table and Dimension Table (Infographics)
Below are the Top 12 differences between Fact Table vs Dimension Table
Key Differences Between Fact Table and Dimension Table
Let us discuss some of the major differences between Fact Table vs Dimension Table.
- Fact Table contains the values or measurements of the attributes of the dimension table.
- Fact table comprises of fewer attributes and more records whereas the dimension table comprises of lesser records and more attributes.
- The fact table grows vertically while the dimension table grows horizontally.
- Fact Table contains a concatenated key while the dimension table contains a primary key.
- Dimension tables must be created before the fact table is created.
- Any schema contains more dimension tables and less fact tables.
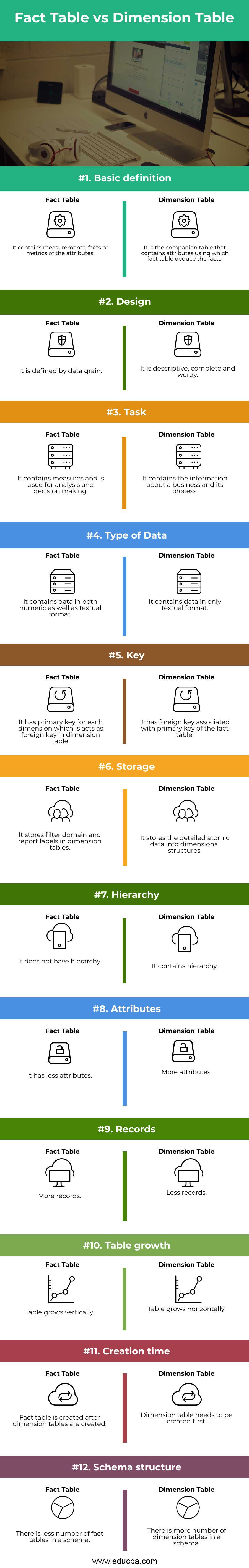
Fact Table vs Dimension Table Comparison Table
Let us discuss the topmost differences between Fact Table vs Dimension Table.
| Characteristics | Fact Table | Dimension Table |
| Basic Definition | It contains measurements, facts or metrics of the attributes. | It is the companion table that contains attributes using which fact table deduce the facts. |
| Design | It is defined by data grain. | It is descriptive, complete and wordy. |
| Task | It contains measures and is used for analysis and decision making. | It contains information about a business and its process. |
| Type of Data | It contains data in both numeric as well as textual format. | It contains data in only textual format. |
| Key | It has a primary key for each dimension which is acts as a foreign key in the dimension table. | It has a foreign key associated with the primary key of the fact table. |
| Storage | It stores the filter domain and reports labels in dimension tables. | It stores the detailed atomic data into dimensional structures. |
| Hierarchy | It does not have a hierarchy. | It contains a hierarchy. |
| Attributes | It has less attributes | More attributes |
| Records | More records | Less records. |
| Table Growth | The table grows vertically. | The table grows horizontally. |
| Creation Time | A fact table is created after dimension tables are created. | The dimension table needs to be created first. |
| Schema Structure | There is less number of fact tables in a schema. | There is a number of dimension tables in a schema. |
Conclusion
In this article, we read about the fact table vs dimension table and the differences between them in detail. These tables are important for developing a schema. Dimension table is a companion of the fact table and both are necessary for each other.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Fact Table vs Dimension Table. Here we also discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –