Updated October 5, 2023
What is Equity Value?
Equity value represents a company’s worth based on its shareholder’s equity. In other words, it is the total price equivalent to all shareholders’ equity.
It is a measure in economics to determine the value of a company’s equity. It helps investors understand a company’s worth and make business decisions. To calculate, multiply the number of shares by the price per share.
Key Takeaways
- It computes a company’s equity and share price to determine its worth. There are various metrics to calculate this, but all those measures use the company’s share price to calculate the value.
- To calculate it, one can multiply the outstanding shares by their current price in the market.
- Economists can use it to assess a company’s financial health and help investors make investments.
- Both equity and enterprise value offer the value of a company, but they provide slightly different perspectives.
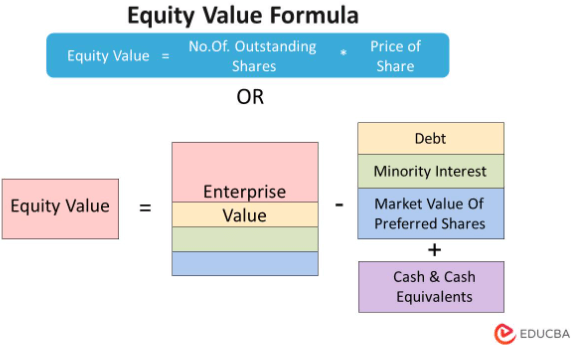
Equity Value Formula
The value of the company can be computed in two ways. For one, we can multiply all shares by the market share value. The second way is subtracting the debt from enterprise value (EV).
Examples
Excel Template
Example 1
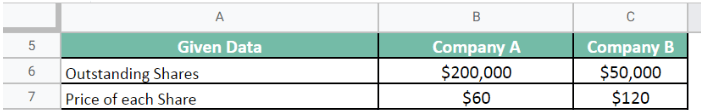
Suppose investors want to invest in equity. They are evaluating two companies, A and B. Company A has 200,000 outstanding shares at a share price of $60 each. While Company B has 50,000 outstanding shares with a share price of $120 each. Let us calculate which company has a higher value.
Given.
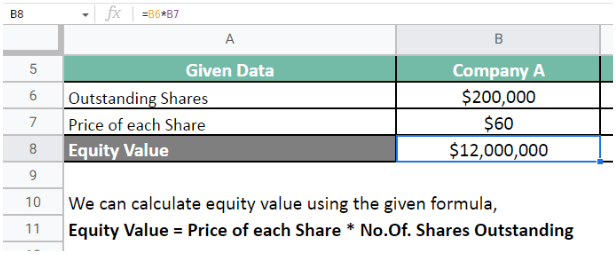
Let us first calculate the value for Company A.
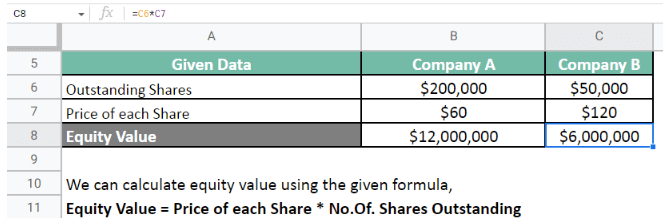
Next, we calculate the value for Company B.
Thus, values for both companies are,
Company A = $12,000,000
Company B = $6,000,000
As the value derived for Company A is higher than for Company B, investing in Company A will be more beneficial for the investor.
Example 2
In this example, let us derive the required value from the enterprise value.
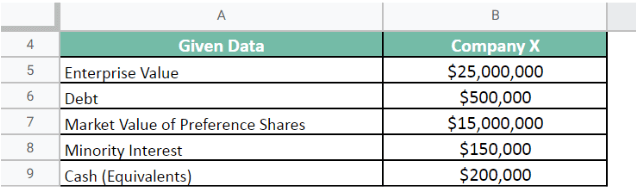
The enterprise value for Company X is $25,000,000. It has a debt of $500,000 and a minority interest of $150,000. It has 300,000 preference shares with a market value of $15,000,000. All its cash equivalents, including investments, sum up to $200,000.
Let us calculate the value for Company X.
Given.
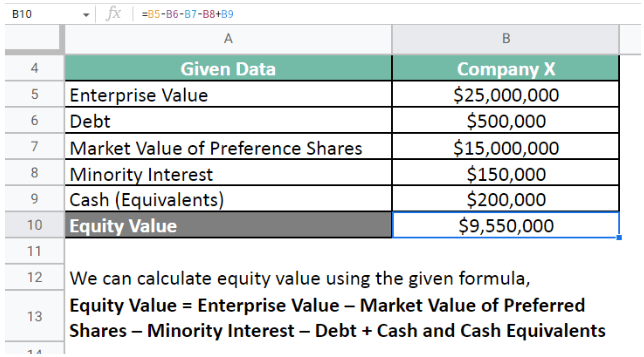
By using the formula, we get the following:
Hence, the value for Company X is $9,550,000.
Relationship with Enterprise Value
Both determine the value of businesses. The formula to calculate the value of equity is,
The formula to calculate enterprise value is,
In general, the enterprise value is a better measure of the company’s worth than the value of its equity. It is because it considers all of the company’s assets and liabilities. It values only the company’s equity and is the sum of all shares multiplied by their price. Enterprise value is the total value of a company’s equity, debt, and capital.
- It is the value an individual investor would have to purchase company shares. They can calculate the worth of the company’s equity using this measure and then invest.
- Enterprise Value is the determination of a company’s worth as a whole. Investors use this value when they want to acquire a firm or have controlling power. It is more important than the other measures because it includes all aspects of a company.
Relation to Market Capitalization
The market value of equity, also known as market capitalization, is the value that determines the worth of a company’s shares. Many economists believe that the value of equity and market cap are unrelated. However, it is not any different from market capitalization. They both are informally interchangeable terms.
It determines the size of a firm and assists investors in diversifying their assets across companies of varying sizes and risk levels. The worth of a firm is computed by multiplying the current share price by the total number of outstanding shares. As a result, the market value of a company’s shares changes as these two input factors change.
Conclusion
Equity value is an economic measure that can also be known as market capitalization. It defines the total value of the securities available to the business. Moreover, it is a financial measure similar to enterprise value but less substantial, and it calculates the worth of a company’s equity.
To calculate it, we multiply the market value per share by the total number of shares outstanding. Whereas enterprise value also includes debt and cash in its formula.
Investors use this method to make investment decisions. This measure is also critical to business owners, especially when planning to sell their businesses. It provides a good indication of what a seller would receive after clearing all debt payments.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. Is equity value the same as a market cap? What is the difference between it and enterprise value?
Answer: Although most people believe the equity value differ from the market cap, they both determine the same values. However, there is a difference between equity value and enterprise value. While the former calculates the equity market values, enterprise value also includes debt, investments, and cash equivalents.
Q2. What does equity value in DCF mean?
Answer: The DCF model calculates it by discounting a company’s levered free cash flow. The DCF valuation method determines a company’s intrinsic value, given its future cash flows and current capital structure.
Q3. How to calculate? Why is it important?
Answer: The calculation comprises multiplying available outstanding shares by their market value. It is an essential economic measure for long-term investors. It is important because it gives a comprehensive representation of the interests of equity investors. Therefore, investors can use this to understand and analyze the company.
Q4. What is the risk?
Answer: It is the risk investors who invest in shares may face. As the share market is very volatile, share prices fluctuate unusually. Investors are always prone to losing their investment or receiving a reduced amount.
Q5. What is an equity value bridge?
Answer: An equity value bridge is a financial instrument that connects the company’s value with its debt. It describes the enterprise value and market value of equity relationships. It is also known as EV to equity bridge.
Recommended articles
This article explains everything about the value of equity. To know more, visit the following articles: