What is Endpoint Security?
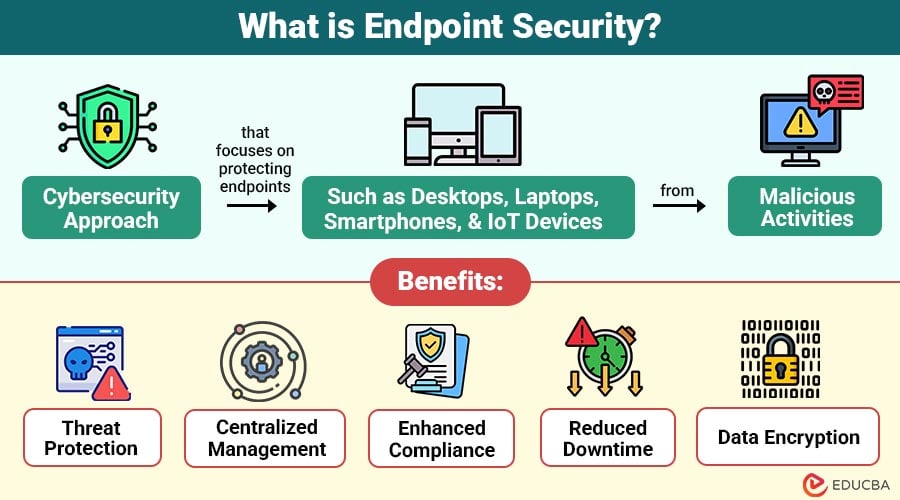
The Endpoint Security is a cybersecurity approach that focuses on protecting endpoints such as desktops, laptops, smartphones, and IoT devices from malicious activities. It entails monitoring, identifying, and reacting to threats directed at these devices using software tools and tactics.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Importance
- Key Components
- Working
- Benefits
- Challenges
- Best Practices
- Real World Examples
- Future Trends
Key Takeaways:
- Endpoint security protects all devices, safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining business continuity.
- Multi-layered defenses, including antivirus software, EDR, firewalls, and encryption, reduce risks from cyber threats.
- Keep software up-to-date, fix security issues quickly, and use strong passwords to stop hackers and protect your data.
- Continuous monitoring and employee awareness help detect threats early and respond effectively to incidents.
Importance of Endpoint Security
With the growing number of endpoints connecting to corporate networks, attackers have more opportunities to exploit vulnerabilities. Endpoint security is crucial because:
1. Protects Sensitive Data
Protects sensitive information from theft or unauthorized access, keeping the organization secure and maintaining customer trust.
2. Prevents Malware Infections
Blocks harmful software from entering systems, keeping operations running smoothly and protecting important business data.
3. Supports Compliance
Helps organizations meet strict legal requirements under GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, avoiding penalties and ensuring proper handling of sensitive data.
4. Mitigates Remote Work Risks
Ensures strong security measures for employees working remotely, protecting corporate resources from cyber threats targeting external or unsecured network connections.
5. Reduces Financial Losses
Helps prevent cyberattacks, avoiding expensive downtime, penalties, and harm to the company’s reputation.
Key Components of Endpoint Security
Effective endpoint security relies on a combination of technologies, policies, and processes. The main components include:
1. Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Protects devices against viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, spyware, and emerging threats by scanning, detecting, and removing malicious code before it causes harm.
2. Endpoint Detection and Response
Monitors endpoints in real-time, detects unusual behavior, and provides immediate incident response to contain and remediate threats before they escalate.
3. Firewall Protection
Stops unauthorized access, monitors network traffic, and blocks harmful connections from reaching or leaving the device
4. Data Encryption
Secures sensitive data stored locally or transmitted over networks using cryptographic methods, ensuring unauthorized parties cannot access or misuse the information.
5. Application Control
Restricts execution of unapproved or potentially dangerous applications, preventing malware installation and ensuring only trusted software runs on endpoint devices.
6. Patch and Vulnerability Management
Regularly applies software updates and security patches to fix vulnerabilities and reduce the likelihood that hackers would exploit outdated systems.
7. Device Access Control
Verifies identities, enforces authentication, and limits network access to authorized devices and users, safeguarding against unauthorized entry into corporate systems.
How Endpoint Security Works?
The working of endpoint security can be summarized in a systematic approach:
1. Agent Deployment
A security agent or client software is installed on every endpoint device, enabling activity monitoring and enforcing organizational security policies effectively.
2. Continuous Monitoring
The agent constantly monitors devices, network activity, files, and system events to detect threats early.
3. Threat Detection
To find questionable patterns or departures from typical activity, collected data is examined using behavioral analytics, machine learning algorithms, and predetermined criteria.
4. Incident Response
Upon detecting a threat, the system automatically isolates the compromised endpoint, blocks harmful processes, and promptly notifies security teams for further investigation.
5. Reporting and Analytics
Centralized security dashboards provide comprehensive insights, enabling teams to analyze incidents, identify trends, and enhance defenses to prevent future cybersecurity breaches effectively.
Benefits of Endpoint Security
Implementing a robust endpoint security strategy offers several benefits:
1. Threat Protection
Protects devices from many cyber threats—like viruses, ransomware, phishing, and new attacks—keeping them safe from evolving dangers.
2. Centralized Management
Provides IT teams with a unified dashboard to efficiently monitor, control, and secure all connected endpoints from a single centralized console.
3. Enhanced Compliance
Ensures adherence to regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, safeguarding sensitive data and avoiding costly legal consequences effectively.
4. Reduced Downtime
Reduces downtime by preventing and quickly handling cyber incidents, keeping business operations running smoothly.
5. Data Encryption
Protects sensitive business data by encrypting it, whether stored or sent online, so unauthorized people cannot access or misuse it.
Challenges of Endpoint Security
While endpoint security is vital, organizations face several challenges:
1. Increasing Endpoint Diversity
Managing security for numerous devices, operating systems, and platforms poses complexity, requiring adaptable solutions capable of handling varied configurations and usage environments.
2. Remote Workforce Expansion
Maintaining consistent security controls for employees working remotely outside corporate networks requires strong policies, secure connections, and reliable endpoint protection tools.
3. Evolving Cyber Threats
Keeping pace with increasingly sophisticated and constantly evolving cyberattack techniques demands continuous updates, proactive monitoring, and adaptive defensive measures across all endpoints.
4. Shadow IT
Employees using unauthorized applications or devices without IT oversight create hidden vulnerabilities, making network monitoring and policy enforcement more difficult.
5. Resource Constraints
Organizations with limited staff or budget face challenges in deploying, managing, and maintaining comprehensive endpoint protection across diverse and distributed environments.
Best Practices for Endpoint Security
To maximize effectiveness, organizations should follow these best practices:
1. Implement Multi-Layered Security
Use several security tools—like firewalls, antivirus, and intrusion detection—to protect against all kinds of cyber threats.
2. Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Update operating systems and apps with security patches and software as soon as possible to eliminate vulnerabilities before hackers can use them to obtain unwanted access.
3. Enforce Strong Authentication
Uses multi-factor authentication (MFA) to access devices, apps, and sensitive systems, making it much harder for hackers to break in.
4. Encrypt Sensitive Data
Keep all sensitive data safe by turning it into code (encrypting it) so that nobody without permission can see, steal, or misuse it.
5. Educate Employees
Train employees regularly on security, so they can spot phishing emails, harmful links, and risky actions that may threaten devices and company data.
6. Monitor and Audit Continuously
Continuously monitor endpoint logs, alerts, and system reports to identify unusual activity early, enabling timely incident response and mitigation before serious damage occurs.
Real World Examples
Here are some real-world examples that showcase how endpoint security is implemented in practice.
1. CrowdStrike Falcon
Provides strong endpoint security across platforms by using AI-driven analytics to identify and react to sophisticated threats instantly.
2. Symantec Endpoint Protection
Provides multiple layers of protection—like firewalls, malware blockers, and intrusion prevention—managed from one place to defend against both old and new cyber threats.
3. Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Brings together threat information, reduces security weaknesses, and uses automated checks and fixes to protect devices from new cyber threats worldwide.
4. Sophos Intercept X
Uses advanced AI, anti-exploit, and ransomware protection to detect and stop complex cyberattacks before they harm devices.
Future Trends
Here are emerging trends shaping the future of endpoint security and redefining how organizations defend against evolving cyber threats.
1. AI-Powered Threat Detection
Uses advanced machine learning to improve the identification of zero-day threats, enhancing proactive defense against emerging cyberattacks.
2. Cloud-Delivered Security
Uses small software programs that connect to the cloud, allowing easy and efficient protection without needing lots of hardware on-site.
3. Zero Trust Security Models
Enforces continuous verification for all users and devices, granting access only after identity and compliance requirements are confirmed.
4. Integration with XDR
Offers a single system to detect and respond to threats on devices, networks, and the cloud, making security easier and more coordinated.
5. Automated Incident Response
Reduces the time to fix threats by automatically running preset security steps across all affected systems.
Final Thoughts
Endpoint security is no longer an optional element of cybersecurity—it is a foundational requirement for safeguarding today’s distributed IT environments. As endpoints remain a prime target for cybercriminals, organizations must adopt robust endpoint protection solutions, implement strict security policies, and continuously monitor for threats. By doing so, businesses can protect sensitive data, maintain operational continuity, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can endpoint security work on mobile devices?
Answer: Yes, modern endpoint security solutions cover smartphones and tablets, offering malware protection, encryption, and remote wipe capabilities.
Q2. Is endpoint security necessary for small businesses?
Answer: Absolutely. Due to their often weaker security measures, small firms are frequently the target of cybercriminals.
Q3. How often should endpoint security be updated?
Answer: Endpoint security systems should be updated regularly—preferably automatically—to address emerging threats.
Q4. Does endpoint security slow down devices?
Answer: Modern solutions are optimized to minimize performance impact, though older systems may experience slight slowdowns.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Endpoint Security” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.