Updated May 31, 2023

Introduction to egrep command in Unix
The egrep command in Unix shell scripting is owned by the family of the grep command that is used for searching and matching a specific pattern in Unix. egrep works similarly to grep -E (grep Extended regex’) do. egrep generally searches a specific file or even line to line or prints the line in the input file, which has the scanned regular expression. It takes the selected pattern as a regular expression and will finally print the output out the lines, which is the same as the specified pattern. For any case, if there are a number of files with the same matching pattern, it will give the output showing the file names matching the pattern for each line.
What can we do from egrep command?
There are many options to search and match a specific pattern in Unix with the help of egrep command. We can perform n number of search patterns and get the output as the egrep command requires.
Below are a few options that can be used to search and match the pattern:
PATTERN Selection and Interpretation:
| -E, –extended-regexp | PATTERN is an extended regular expression. |
| -F, –fixed-strings | PATTERN is a set of newline-separated strings. |
| -G, –basic-regexp | PATTERN is a basic regular expression (default). |
| -P, –perl-regexp | PATTERN is a Perl regular expression. |
| -e, –regexp=PATTERN | Use PATTERN for matching. |
| -f, –file=FILE | Obtain PATTERN from FILE. |
| -i, –ignore-case | Ignore case distinctions. |
| -w, –word-regexp | Force PATTERN to match only whole words. |
| -x, –line-regexp | Force PATTERN to match only whole lines. |
| -z, –null-data | A data line ends in 0 byte, not a newline. |
Output Control:
| -m, –max-count=NUM | Stop after NUM selected lines. |
| -b, –byte-offset | Print the byte offset with output lines. |
| -n, –line-number –line-buffered |
Print line number with output lines.
Flush output on every line. |
| -H, –with-filename | Print file name with output lines. |
| -h, –no-filename –label=LABEL |
Suppress the file name prefix on output.
Use LABEL as the standard input file name prefix. |
| -o, –only-matching | Show only the part of a line matching PATTERN. |
| -q, –quiet, –silent | Suppress all normal output. |
| -a, –text | Equivalent to –binary-files=text. |
| -d, –directories=ACTION | How to handle directories;
ACTION is ‘read’, ‘recurse’, or ‘skip’. |
| -r, –recursive | Like –directories=recurse. |
| -R, –dereference-recursive –include=FILE_PATTERN–exclude=FILE_PATTERN–exclude-from=FILE–exclude-dir=PATTERN |
Likewise, but follow all symlinks.
Search only files that match FILE_PATTERN. Skip files and directories matching FILE_PATTERN. Skip files matching any file pattern from FILE. Directories that match PATTERN will be skipped. |
| -L, –files-without-match | Print only names of FILEs with no selected lines. |
| -l, –files-with-matches | Print only names of FILEs with selected lines. |
| -c, –count | Print only a count of selected lines per FILE. |
| -T, –initial-tab | Make tabs line up (if needed). |
| -Z, –null | Print 0 byte after the FILE name. |
Context control:
| -B, –before-context – NUM | Print NUM lines of leading context. |
| -A, –after-context – NUM | Print NUM lines of trailing context. |
| -C, –context – NUM | Print NUM lines of output context. |
| -NUM | Same as –context=NUM. |
| –color[=WHEN], | Use markers to highlight the matching strings; |
| –colour[=WHEN] | WHEN is ‘always’, ‘never’, or ‘auto’ |
| -U, –binary | do not strip CR characters at EOL (MSDOS/Windows). |
Syntax of egrep:
egrep command would need the option to mention the matching pattern and the filename to search and match the way in the file.
Below is the syntax for egrep command:
egrep [options] [pattern] [files..]Examples of using egrep commands in Shell Scripting
Let us consider there is a file named ‘testing.txt’ which contains the below data, and we will be taking this file and show examples below:
Code:
cat testing.txtOutput:
Example #1: Option -c
It counts the number of lines in the files that match the pattern.
Syntax:
egrep -c [pattern] file_nameCode:
egrep -c student testing.txtOutput:
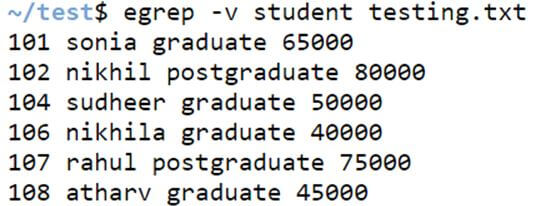
Example #2 Option -v
This option helps print the lines that do not match the pattern specified in the input parameter.
Syntax:
egrep -v [pattern] filenameCode:
egrep -v student testing.txtOutput:
Example #3: Option -i
It displays the lines in the file that match the input pattern while ignoring the case of alphabets.
Syntax:
egrep -i [pattern] filenameCode:
egrep -i student testing.txtOutput:
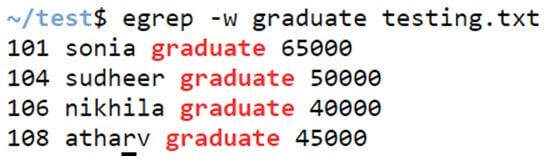
Example #4: Option -w
It displays only the lines which have the complete word in it.
Syntax:
egrep -w [pattern] filenameCode:
egrep -w graduate testing.txtOutput:
Example #5: Option -x
With this option, we can only print the entire line if it is given in the input file.
Syntax:
egrep -x [line] filenameCode:
egrep -x '101 sonia graduate 65000' testing.txtOutput:
Example #6: Option -m
With this option, it will continue to search the pattern until the number of counts mentioned in the input reaches the number mentioned in the parameter.
Syntax:
egrep -m [number] [pattern] filenameCode:
egrep -m 3 graduate testing.txtOutput:
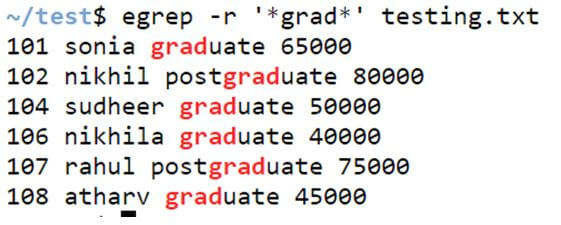
Example #7: Option -r
It recursively scans for the matched pattern given in the input parameter. It will give you the information in the file that matches the input pattern.
Syntax:
egrep -r [pattern] filenameCode:
egrep -r '*grad*' testing.txtOutput:
Example #8: Option ‘OR’
We can have an option for ‘OR’ using a pipe ‘|’ symbol. When choosing between two options, ‘OR’ is used.
Syntax:
egrep 'option1|option2' filenameCode:
egrep 'sonia|teja' testing.txtOutput:
Example #9: Option -l
This option will help print only the filenames with the matched pattern or string inside it. It will only give you the filename that has the matched string.
Syntax:
egrep -l 'string' filename_patternCode:
egrep -l sonia *.txtOutput:
Example #10: Option -o
Instead of printing the entire line in a file, we can print the specified pattern from the file. The output will display the number of times the word appeared in the specified file.
Syntax:
egrep -o [pattern] filenameCode:
egrep -o student testing.txtOutput:
Conclusion
The egrep command in Unix shell scripting is owned by the family of the grep command that is used for searching and matching a specific pattern in Unix. egrep works similar to grep -E (grep Extended regex’) do. egrep generally search a specific file or even line to line or prints the line in the input file, which has the scanned regular expression.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “egrep command in Unix” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.