Updated June 20, 2023
Introduction to Docker Systemd
Systemd is responsible for managing the Docker daemon in many Linux distributions. It facilitates various actions such as starting the Docker daemon, stopping it, enabling automatic startup on boot, and checking its status. We use the ‘systemctl’ command to manage services in most Linux distributions; in the same way, we can use this to manage Docker daemon; however, we can also use the ‘service’ command if systemctl is not available. In short, we can control and manage Docker daemon with systemd.
Syntax:
sudo systemctl <command> docker
Command:
- start: It is used to start the docker service
- stop: It is used to stop the docker service
- status: It is used to check the status of the docker service
- enable: It is used to configure the docker service to start at boot time
- disable: It prevents the docker service from starting at boot time.
- restart: It is used to restart the docker service
- show: It is used to show the environment variables defined in systemd file.
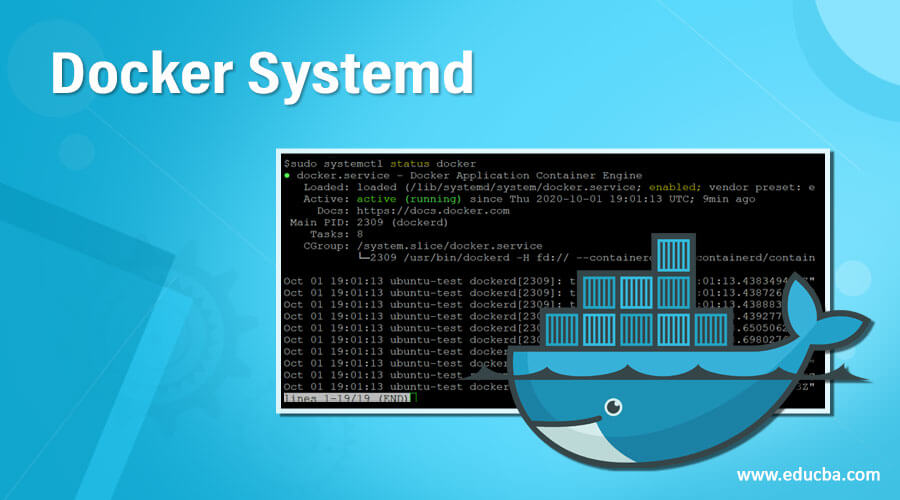
sudo systemctl status docker
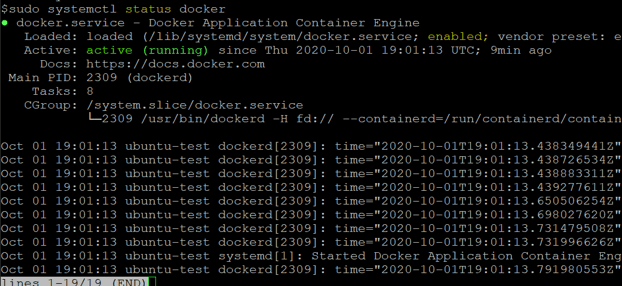
Explanation: In the above snapshot, we can see that the docker service is running and is enabled.
How does systemd Command work in Docker?
We can configure the daemon flags and environment variables for our Docker daemon in different ways; however, the recommended way to configure daemon flags and environment variables is to use the platform-independent file that is ‘daemon.json’. The default path of this file is ‘/etc/docker,’ and it does not exist when we install Docker. We have to create this file when we configure daemon flags or environment variables the first time. We must restart the Docker service after changing the ‘daemon.json’ file to enforce the changes.
Almost all daemon configuration options can be configured using ‘daemon.json’; however, we can not configure the ‘HTTP proxy’ option using ‘daemon.json’. We need to create a systemd drop-in directory for the docker service and create a configuration file inside it. It overrides the default docker. service file.
Examples
Let’s understand how we can configure Docker daemon flags or environment variables with the below examples: –
Scenario 1: Change the default logging driver to json-file and runtime directory to “/mnt/docker-data”
1. Let’s check the current configuration of the Docker daemon by running the ‘docker info’ command as below: –
docker info
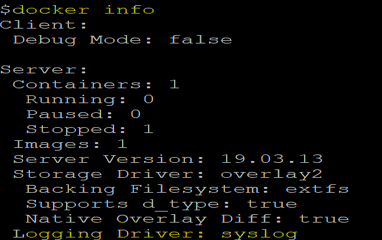
![]()
2. Now, edit the ‘daemon.json’ file or create it if it does not exist already, as shown below: –
sudo vi /etc/docker/daemon.json

3. We have to restart the Docker service using systemctl command to apply the new configuration as shown below: –
sudo systemctl restart docker
Note: You will get an error as shown below in the snapshot while restarting the docker daemon if the ‘daemon.json’ file is improper or missing something, so re-check the ‘daemon.json’ file and restart the service.
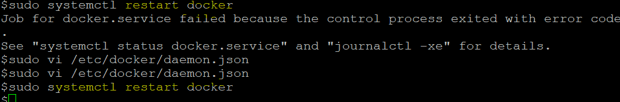
Explanation: In the above snapshot, we can see that it encountered an error in the first attempt, so recheck the ‘daemon.json’ for any error and fix it and then restart the service again without any error.
Tip: Wait for 1-2 mins after making changes to the file, and then restart the service.
4. Let’s verify the changes by running the ‘docker info’ command once again:
docker info
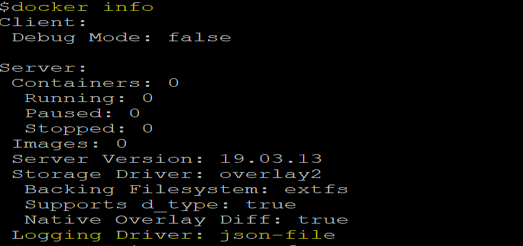
![]()
Scenario 2: Configure HTTP/HTTPS Proxy by Overriding Docker.Service File
We have two ways to configure this, one is a regular install, and another is the rootless mode. The below steps are used to configure HTTP/HTTPS proxy in regular install: –
1. First of all, we need to create a systemd drop-in directory for the docker service using the below command: –
sudo mkdir -p /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d
![]()
2. Now, create a file named http-proxy.conf inside the above directory and set the HTTP or HTTPS proxy, we can set both in the same file as shown below: –
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/http-proxy.conf
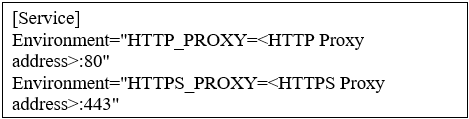
![]()

3. Save the file and exit.
4. We need to reload the daemon as we have created a new systemd file and restart the docker service to apply this new configuration as shown below: –
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
![]()
5. We can use the below command to verify the configuration has been loaded, and it is the same as expected: –
sudo systemctl show --property=Environment docker
![]()
Advantages
- It is an easy way to control the Docker service.
- We can configure daemon flags and environment variables.
- We can change the default configuration of the Docker daemon, like log driver, storage driver, etc.
Rules and Regulation
- If we have already set up daemon flags on daemon startup, then we cannot set it in the ‘daemon.json’ file.
- If Docker is running in rootless mode, we need to create the ‘docker.service.d’ folder in each user’s home directory to configure HTTP/HTTPS proxy as it uses files stored in each user’s directory. So, the folder path is ‘~/.config/systemd/user/docker.service.d’; other steps are the same as mentioned in scenario-2.
- We can use the environment variable ‘NO_PROXY’ to exclude any hosts from proxying while configuring HTTP/HTTPS proxy. For example, we can exclude internal Docker registries.
Environment="NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.1,docker-registry.example.com,.corp"

4. The ‘NO_PROXY’ option excludes all domain name that matches the option; for example, if we have mentioned ‘abc.com,’ then it will exclude ‘abc.com,’ ‘x.abc.com,’ ‘y.abc.com,’ and so on, however, if we have mentioned ‘.abc.com’ then it will exclude all ‘*.abc.com’ except ‘abc.com.’
5. We have optional field ‘features’ in ‘daemon.json’ to enable or disable specific daemon features. For example, we can enable or disable ‘buildkit’ feature to set the default docker image builder.

Conclusion – Docker Systemd
We can control and manage almost all the configuration settings of Docker daemon using systemd. If we have to install the binary without the package, we need to install two unit files, ‘service and socket’ from the Github repository to ‘/etc/systemd/system’ to integrate Docker with systemd.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Docker Systemd. Here we discuss the Introduction, How does systemd Command work in Docker with examples? respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


