Introduction to Design Pattern in Java
Design Patterns are a prevalent problem-solving technique among software developers. It contains all the solutions for common software problems while developing and designing software and has well-described solutions. The codes are a reusable form of a solution to the problem. The architect Christopher Alexander introduced these patterns to various other software developers who commonly faced problems while creating software. It is flexible and contains templates to solve while designing a system or application.
Experienced object-oriented software developers use flexible coding, reuse the codes, and add new codes to existing codes for version updates. It has solutions to all general problems faced by software engineers. These solutions are after several trials and errors by numerous developers over a period of time. Using JAVA language, we can design and develop a few applications and software along with the best practices by following the workflow of the Design Pattern.
Table of Content
- Introduction
- Types of Design Patterns Available in Java
- Understanding Design Patterns in Java
- How does the Design Pattern in Java make Working so Easy?
- Various Subsets of Design Patterns in Java
- Example of Design Patterns in Java
- Working with Design Patterns in Java
- Advantages of Design Patterns in Java
- Why Should We Use Design Patterns?
- Why do we Need a Design Pattern in Java?
Types of Design Patterns Available in Java
Given below are the types of design patterns available in java:
1. Creational Design Pattern
This type of design pattern is associated with the creation of an object. The following are sub-categories of the creation design pattern:
- Singleton Pattern
- Builder Pattern
- Factory Pattern
- Abstract Factory Pattern
- Prototype
2. Structural Design Patterns
This type of design pattern is concerned with the code structure followed while developing an application. Using a structural design pattern ensures that changing one part of an application does not affect other parts of the application.
The following are sub-categories of structural design patterns:
- Adapter Pattern
- Bridge Pattern
- Composite Pattern
- Façade Pattern
- Proxy Pattern
- Flyweight Pattern
- Decorator Pattern
3. Behavioral Design Patterns
This pattern is associated with algorithms and patterns of communication used when two or more objects need to communicate. The following are different types of behavioral design patterns:
- Chain of Responsibility Pattern
- Command Pattern
- Interpreter Pattern
- Iterator Pattern
- Mediator Pattern
- Observer Pattern
- Strategy Pattern
- Template Pattern
- Visitor Pattern
- Null Object Pattern
Understanding Design Patterns in Java
Different creative, structural, and behavioral ways exist to design patterns to provide solutions to instantiate an object in the best possible way for particular situations based on pattern structure type.
Different types of patterns are as follows:
#1 Singleton Pattern
It restricts the instantiation of a class to only one instance class that exists in Java virtual machine. Handling one instance class in the machine simultaneously is simple for designing patterns. When it comes to implementing concerns, many developers have different styles of fixing problems.
#2 Factory Pattern
It is on the inputs from clients we create or has a superclass with multiple sub-classes. This is the most widely used java design pattern because this pattern takes responsibility for instantiating a class from the client program to the functional class. This pattern is flexible in applying the Singleton pattern to the factory class or making the factory class static.
#3 Abstract Factory Pattern
It’s similar to the factory and can contain many factories in it; we can design many factories and relations with the design pattern in java. Simple factory class and many subclasses based on the input provided and switch statements to achieve as per project requirements. It helps in improving the patterns while programming.
#4 Builder Pattern
This pattern is the best one to solve some problems with factory and abstract factory design patterns when objects contain many attributions. Building pattern solves issues with many optional parameters and inconsistent ways of building the object step by step with a method that takes developers to reach the final object by the end.
#5 Prototype Pattern
This helps if the object creation is costly. Developing already existing simple objects takes a lot of time and resources. It adds codes to improve and make new objects with modifications as per needs in java cloning. The prototype design pattern has object copying, which provides the copying features. Any other class should not do it. Using the shallow or deep copy of object properties depends on requirements and design decisions.
How does the Design Pattern in Java make Working so Easy?
Design Patterns have evolved as the best problem-solving patterns provider these days. It has all the standard approaches to solve the common problem in the building phase of the software application or software. It is the IT industry’s best practice, saves time, and provides sensible patterns as required to developers. With design patterns, the developer can work and develop robust processes and maintainable codes. In addition, it has the option of reusable codes, which reduces the total development cost of the application.
It simplifies the job for testers and new learners to understand and modify the patterns as per demands. Software engineers can quickly fix problems, if any, that are noticed at any stage of the design, testing, and operations of the application or software. Fast to develop in the context of java, design patterns are creative, structural, and behavioral, which can be easily understood and applied while coding multiple objects, classes, etc. The version updates, slight changes, coding, and patterns are the reference for building new software.
Various Subsets of Design Patterns in Java
Structural design patterns are the ways to create class structures using inheritance and composition from large objects to small objects.
#1 Adopter Pattern
It helps in joining unrelated interfaces to work together with the objects. This is one of the valuable patterns used in the Java development of software design.
#2 Composite Pattern
Composite patterns are one of the structural design patterns used to represent a part-whole hierarchy. We need to create a new structure so that the objects in the structure treat the same way. A specific purpose composition patterns as per requirements operations.
#3 Proxy Pattern
It provides a placeholder or surrogate for other objects to control access to it. Proxy patterns are helpful when we want to provide controlled access to functionality. It also has implementation requirements as per needs.
#4 Flyweight Pattern
A flyweight pattern is useful when there is a demand to create many objects of a class so that every object consumes memory space which can be crucial for low-memory devices.
#5 Facade Pattern
This is useful in helping the client applications to interact with the systems efficiently. MySQL can use Oracle databases‘ interface to generate different types of logs or reports using HTML, PDF, etc. Different interfaces with different databases as per clients’ needs. It improves client application and usage with good relations with clients.
#6 Bridge Pattern
It contains both interface and implementation. A bridge pattern helps decouple the interface from implementation by hiding implementation details from the client’s program.
#7 Decorator Pattern
A decorator helps modify the object’s functionality at runtime simultaneously. Other instances of the same class will not get any effect from this. We use compositions to extend the behavior of an object with time and applicability on the instances of the class.
Example of Design Patterns in Java
Now we will see java code examples of singleton design patterns. The singleton design pattern requires creating a singleton class that returns the same instance every time someone instantiates it. The below code example shows the creation and usage of a singleton class:
Code:
package com.edubca.singleton;
class SingletonClassDemo
{
// static variable instance of type SingletonClassDemo
private static SingletonClassDemo instance = null;
// variable of type String
public String text;
// private constructor restricted to this class itself
private SingletonClassDemo()
{
text = "THIS IS SINGLETON EXAMPLE FROM EDUBCA ";
}
// static method to create instance of SingletonClassDemo class
public static SingletonClassDemo getInstance()
{
if (instance == null)
instance = new SingletonClassDemo();
return instance;
}
}
// Main Class
class SingletonTest
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// instantiating SingletonClassDemo class with variable first
SingletonClassDemo first = SingletonClassDemo.getInstance();
// instantiating SingletonClassDemo class with variable second
SingletonClassDemo second = SingletonClassDemo.getInstance();
// instantiating SingletonClassDemo class with variable third
SingletonClassDemo third = SingletonClassDemo.getInstance();
// Modifying variable of instance first
first.text = (first.text).toLowerCase();
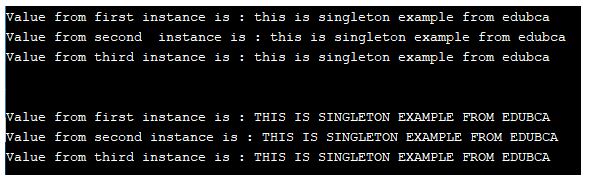
System.out.println("Value from first instance is : " + first.text);
System.out.println("Value from second instance is : " + second.text);
System.out.println("Value from third instance is : " + third.text);
System.out.println("\n");
// Modifying variable of instance third
third.text = (third.text).toLowerCase();
System.out.println("Value from first instance is : " + first.text);
System.out.println("Value from second instance is : " + second.text);
System.out.println("Value from third instance is : " + third.text);
}
}Output:
What can you do with the Design Patterns in Java?
Behavioral design patterns help create or modify existing applications per the latest market updates and benchmark with clients’ demands for smooth process flow. Software developers can well understand the design structure of an application using patterns. To make changes in a different location per version update requests by end-user, developer, and client. Easy structure for developers, testers, and other professionals.
Reusable codes that are easily maintained with quick tracking solutions using simple patterns if any problems occur in the performance of the application or system. They are solving all the problems and developing well-structured applications or software to compete in the market with industrial standards.
Working with Design Patterns in Java
Design Patterns are a prevalent problem-solving technique used by software designers when creating or modifying applications or software programs. It helps create simple and easily structured software that can be easily understood by testers, developers, and users for their use.
Maintaining and adding new attributions as per version demands can be quickly done. Finding and quick fixes of the bugs happen with good observation. Developers can use repeated codes if necessary. We can work on multiple interfaces and can bridge them. Adds professional values to experienced and junior software designing and development experts. Tool update and provide the latest codes for common mistakes in design patterns.
Advantages of Design Patterns in Java
- They facilitate modular and scalable designs, making it easier to expand and modify code.
- Patterns serve as documented best practices, aiding in communication and knowledge transfer among developers.
- Patterns often encapsulate optimized solutions, contributing to efficient and well-performing code.
- This helps design innovative and flexible codes per project requirements with suitable objects, classes, loosely coupled codes, a quick understanding of structures, and many more.
- Unwanted codes and problems can be easily identified and changed helpless work to testers and maintainers of the application.
- Client and end-users feel the interface is more user-friendly and provide a good user experience while working or using an application or software.
Why Should we use Design Patterns in Java?
The following are the main reasons why we should go for design patterns in java:
- Standard Approach: Using design patterns is considered a standard approach in java understood by all developers. This leads to the development of consistent code by different developers.
- Code Reusability: Using Design patterns increases code reusability, which results in the development of robust, maintainable, and testable code.
- Easy to Understand and Debug: Design patterns are defined and accepted practices that make our code easy to understand and debug in case of errors. Design patterns make our code easy to understand, even for beginner-level developers.
Why do we Need a Design Pattern in Java?
Design Patterns coding uses simple and repeated similar codes per the projects’ requirements, which can be handled and maintained with basic knowledge. Because of this, the application and software are designed and developed using design patterns that can maintain easily.
The design patterns help the testers, software developers, and others avoid problems or bugs while working. Even to identify the bugs in the application or system, we can quickly find them and fix them in less time. Design patterns with java also help to add new coding and features to the application or system. It is per customer feedback or internal developments for the latest or upcoming software versions.
It has all the best things for designing an application, like a user-friendly interface and experience. Software engineers can comprehend and adjust it as needed. Quick monitoring and problem-solving solutions make design patterns in java a professional software-making practice.
Conclusions
A design pattern is a reusable solution to a common software design problem. It represents best practices for solving certain types of problems and promotes code organization and maintainability. Design patterns help developers create efficient, scalable, and modular software by providing well-established templates for solving recurring design challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is MVC one of the design patterns?
Answer: MVC or Model-View-Controller is one of the design patterns supporting web application development. It designs the applications by dividing them into three components model, view, and controllers.
Q2. What is the need for a design pattern?
Answer: Design patterns are obvious in application development. It accelerates the development process by providing the paradigm, and they are the proven solutions to the problems that arise frequently. So that the developer can save time by referring them in case of any arise in problems.
Q3. How is the design pattern different from the design framework?
Answer: The design pattern is a small architecture in the design framework. In simple words, numerous design patterns combine to form a design framework. These patterns are always less specialized, and frameworks are more domain specific.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Design Pattern in Java” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.