Updated July 31, 2023
Debt Service Coverage Ratio Formula
As its name suggests, the debt service coverage ratio is the amount of cash a company has to service/pay its current debt obligations (interest on a debt, principal payment, lease payment, etc.). It is calculated by dividing the company’s net operating income by its debt obligations for that particular year.
Here’s the Debt Service Coverage Ratio Formula:
Net operating income is the income left when all the operating expenses are paid. The Income statement is under the head EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes). Total debt service is all the debt-related payments that a company needs to pay. For example, interest payments, principal payments, and other obligations.
A DSCR greater than 1 is preferable and indicates that the company has enough cash to service its debt. Generally speaking, the higher the DSCR, the better it is for the business.
Examples of Debt Service Coverage Ratio Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Debt Service Coverage Ratio formula in a better manner.
Example #1: Debt Service Coverage Ratio Formula
Suppose that company A is selling TVs, and they have 2 stores as of now. They want to expand and open a new store, but they do not have much cash to invest now. So they want to explore the debit option and want to take a loan for that. The company already has a loan in its books, so they are worried that it might not be able to get another loan.
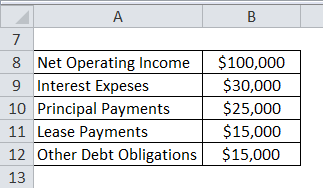
Following are the details of their financials:
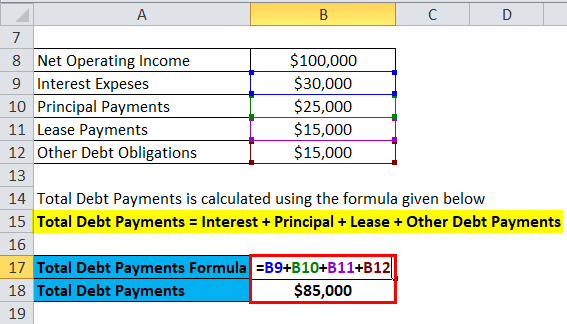
Formula to calculate Total Debt Payments is as below:
Total Debt Payments = Interest + Principal + Lease + Other Debt Payments
- Total Debt Payments = $30,000 + $25,000 + $15,000 + $15,000
- Total Debt Payments = $85,000
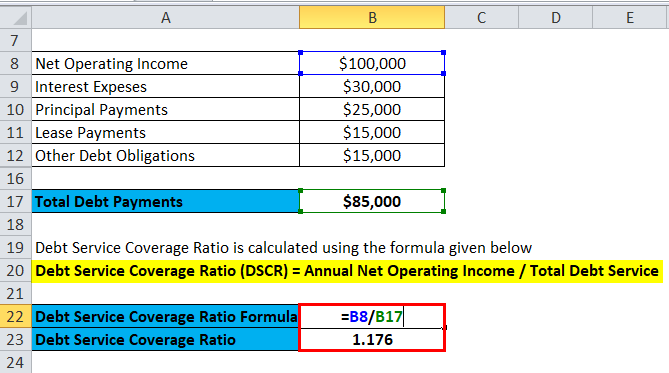
Debt Service Coverage Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR) = Annual Net Operating Income / Total Debt Service
- DSCR = $100,000 / $85,000
- DSCR = 1.176
So it means they have enough operating profit to service their current debt and will not face many difficulties in getting another loan.
Example #2: Debt Service Coverage Ratio Formula
Let’s see some practical examples and take some well know stocks from the market. Let’s take Ford, for example.
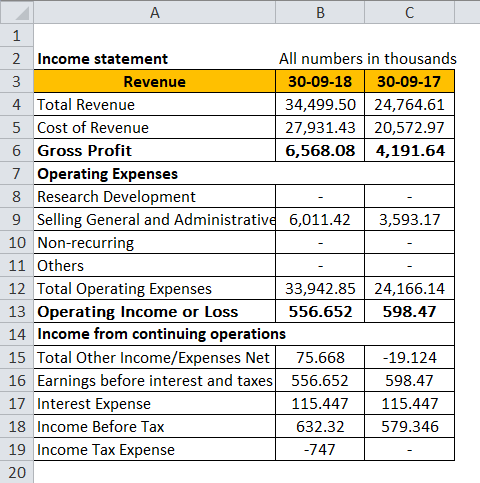
Following is its Income statement snippet:
If you see the income statement of Ford:
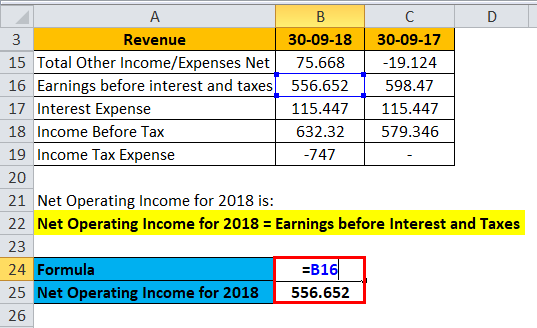
Net Operating Income for 2018 is:
Net Operating Income for 2018 = Earnings before Interest and Taxes
Net Operating Income for 2018 = 556.652k
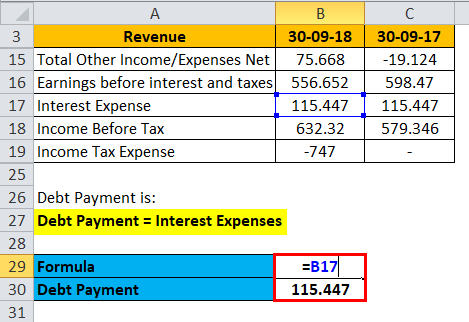
Debt Payment is:
Debt Payment = Interest Expenses
Debt Payment= 115.447k
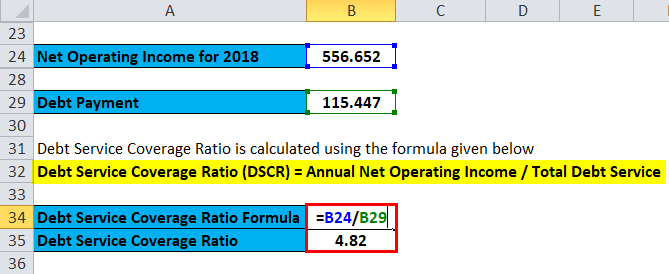
Formula to calculate Debt Service Coverage Ratio is as below:
Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR) = Annual Net Operating Income / Total Debt Service
- DSCR = 556.652 / 115.447
- DSCR = 4.82
Explanation:
- If you are giving a loan to someone, you would not like that person to default on that, and you lose your money. That is where Debt Service Coverage Ratio Formula helps the lender understand how risky the borrower is and how likely he will default. As explained above, the debt service coverage ratio measures a company’s ability to serve its debt obligation through its operating income. A higher ratio is always good and shows enough operating income to cater to debt. If your debt coverage ratio is very low, the best way to improve it is to reduce the loan amount in your books. This will make your principal and interest lower, which in turn, increases the ratio.
- But the lower ratio does not mean the company has some problems. Companies should always be benchmarked against their sector or industry. It is very common in some industries that huge debt is involved, for example, the aviation industry. So we should not compare their DCSR with companies such as IBM and Accenture, where there is very little debt. It is also one of the most critical ratios to analyze in the case of leveraged buyout transactions because this will evaluate the debt capacity of the target company.
Relevance and Uses
- As stated multiple times above, this ratio is important to sense the level of financial flexibility the business has, particularly in a growth situation. If the ratio is high, it means there is a higher ability for the business to invest and grow in the future. Similarly, if DSCR is low (less than 1 or slightly above 1), businesses need to improve this ratio; otherwise, they will face difficulty procuring a loan from lenders.
- All lenders have different risk appetites and strategies; some give more importance to DSCR than others. So they use DSCR differently while entering into loan agreements with a borrower. Lenders, who only get paid back through the company’s Cash flow (like mezzanine lenders), focus more on DSCR, and they generally put a covenant in the agreement with an escalating ratio to ensure that money is coming. In a nutshell, lenders have greater control over this ratio because they are the ones who will dictate the repayment of the principal.
Debt Service Coverage Ratio Formula Calculator
You can use the following Debt Service Coverage Ratio Calculator.
| Annual Net Operating Income | |
| Total Debt Service | |
| Debt Service Coverage Ratio Formula | |
| Debt Service Coverage Ratio Formula | = |
|
|
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Debt Service Coverage Ratio formula. Here we discuss calculating the debt service coverage ratio along with practical examples. We also provide a debt service coverage ratio calculator with a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –