Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to DB2 with
DB2 with clause is used to do the subquery refactoring in complex queries that involve usage of the same result set of a particular query repeatedly. It is similar to the subqueries that are used in SQL but using the with a clause in the query reduces the complexity of debugging and execution of your query when it is very complex. The usage of with clause is also being done when we need a certain temporary table that will hold the data to be used by our query once or multiple times even without having any of the view or temporary table. In this article, we will study the syntax of the with clause, the usage, tips while using them with clause, and the implementation with the help of certain examples.
Syntax
With clause can be used which any of the sql statement of SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE. The syntax of with clause is as shown below –
WITH new temp table (list of new columns) as
(statement for filling temp table),
statement(s) which use the temp table;
In the above syntax, the new temp table is the temporary table that can be referenced for retrieving the temporary result acquired by executing the statement for filling the temp table. The list of the columns that are specified is the names of the columns of the temporary table, which should be the same as that of the number column values retrieved from the statement for filling the temp table. The as keyword is used to alter mentioning the list of columns inside the brackets for the temporary table. The other statements using the result of the new temp table should be specified after giving a comma after filling the query.
Execution of statement containing with clause
The execution of the query statement containing the with clause gives the preference for calculating the result set of the clause, which holds the within it and retrieves the temporary result set in the new temp table. After this, the statement or statements which are specified other than the with clause are executed. These statements can make the use of the new temp table in it as many times as required. They will be executed after retrieving the result in the new temp table. The temporary table that is the new temp table is also called CTE which is a common table expression.
Usage of with clause
There are many scenarios in which the usage of with clause may prove helpful in query execution and data management. Here are some of the key cases where it can be used most probably to make efficient usage of executing and debugging the complex queries that are listed below –
- When it is not possible to create a view in the database for using it in query statements.
- When we have to make use of the same result set multiple times inside the query statement.
- When we have to use the recursion while retrieving the result set.
Examples of DB2 with
Let us now study how we can implement them with a clause in our query statements with the help of certain examples.
Example #1
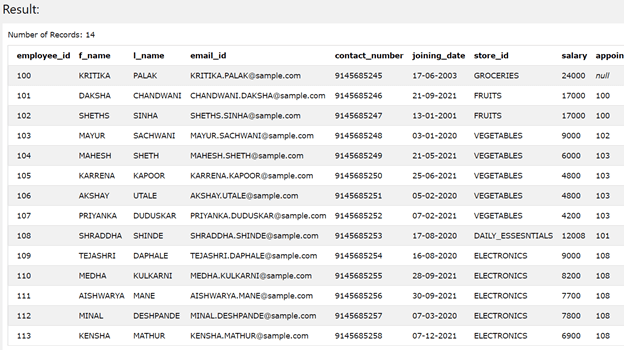
Suppose we have a table named employee_details which contains the records as shown in the output of the below query statement –
SELECT * FROM [employee_details]
The execution of the above query statement gives the following output –
Now suppose that we have to find out how much salary the owner of the fruits and vegetable stores does to all the employees working in that particular store. In that case, the total salary for each store can be calculated as follows by using the with a clause for storing temporary results. Our query statement will become as shown below –
WITH temp_table AS (
SELECT
store_id as "store",
SUM(salary) salary
FROM
employee_details
WHERE
store_id IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY
store_id
)
SELECT
store, salary as "storewise salary"
FROM
temp_table
WHERE
store IN ("VEGETABLES","FRUITS");
The execution of the above query statement will be done firstly for the with statement query to store the details of all the stores and their total salaries I the table temp_table. After this, the execution of the other statement of retrieving the results for only those stores whose store id column will contain vegetables and fruits will be done. The output of the execution of the above query statement is as shown below, showing the two stores and the total salary to be given by the owner for each of the stores, respectively.
Example #2
Using the temporary result of with clause multiple times –
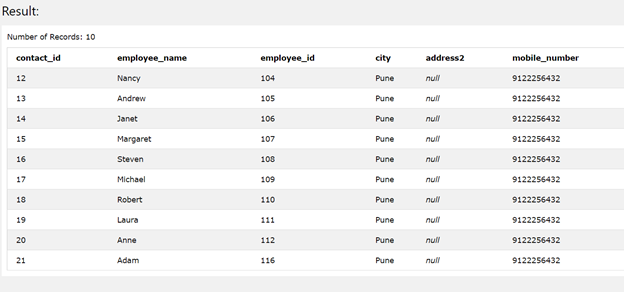
Let’s take one more example to understand the usage of with clause. There is one more table containing alternative contact mobile numbers of the employees named contact_details. The contents of this table can be retrieved by using the following query statement –
SELECT * FROM [contact_details]
The execution of the above query statement gives out the following output –
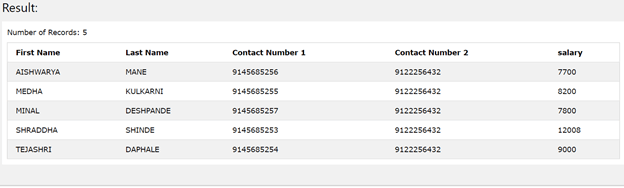
Now, consider that we need to retrieve the records from the employee_details table that have a salary greater than the average salary. Along with that, we also have to retrieve the mobile number present in the contact details table for that corresponding employee. In this case, we have to make use of the temporary table created by the with clause twice. One will be while calculating the average salary and the other one while retrieving the result set of it for getting the column details of those employees. Hence, our query statement will become as shown below –
WITH temp_table AS(
SELECT
f_name, l_name, contact_number, mobile_number, salary
FROM
employee_details
INNER JOIN contact_details
ON employee_details.employee_id = contact_details.employee_id
ORDER BY
f_name
)
SELECT
f_name as "First Name",
l_name as "Last Name",
contact_number as "Contact Number 1",
mobile_number as "Contact Number 2",
salary
FROM
temp_table
WHERE
salary > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM temp_table);
The execution of the above query statement gives out the following output –
Conclusion
We can make use of them with a clause to get the result so that it can be used inside the particular query statement as a temporary table. The result set of the with clause can be referenced single or multiple times inside the same query statement. The with clause is most often used in complex query statements for efficient and easy execution and debugging of the query statement.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 with. Here we discuss the syntax of the with clause, the usage, tips while using them with clause, and the implementation with the help of certain examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –