Updated March 6, 2023

Introduction to DB2 trim
IBM provides a function called as trim in DB2 which helps to remove all the spaces from the starting, ending or both the ends or even any other character than the space one which can be specified by us depending on our requirement. It is a scalar function in DB2 that is most often used with strings. We cannot use the name of the function in place of qualified names if we are using the keywords inside the signature of the function. In this article, we will study the usage, syntax, and rules to be followed while using the trim scalar function in DB2 along with implementation with the help of some examples.
Syntax
The syntax of the DB2 function is as shown below –
TRIM ([ BOTH |TRAILING | LEADING] name of character to be removed FROM string value )
Where the usage of the name of the character to be removed is optional and is a character constant that we wish to remove from the ends of the string. When not specified the strip character that is the character that is to be removed from either end is considered as blank value. Also, the specification of BOTH, LEADING, or TRAILING keywords is optional as by default when not mentioned the character to be stripped is removed from both the ends of the provided string.
The string value is an expression that evaluates to string from which the final result is derived. The output of the function is a string whose length is less than or equal to the original string value mentioned while using the TRIM function.
The character to be stripped from either of the ends can be any value which when encoded in UTF-32 format gives a single character or numeric value of the single digit. When the function is used at that time the binary representation of that character is matched with the string characters from both ends. If we do not mention the character to be removed and the specified source string is specified in DBCS graphic string format the default value of the character to be removed is DBCS blank with a code point. The code point of this default space character depends on the code page.
In case of the source string expression is in UCS-2 graphic string format then the default character to be removed has the value of UCS-2 blank which is equivalent to (X’0020’). If the source string is a binary string expression then the function takes hexadecimal zero with X’20’ value as the default value of the character to be striped. In all other cases of source string expression specification, the SBCS blank value is treated as the default value of the strip character.
The source string can have any expression from which we extract the final output and which should return whose datatype is built-in one from the list –
- GRAPHIC
- VARGRAPHIC
- CHAR
- VARCHAR
- BINARY
- VARBINARY
- Numeric
- Datetime
In case if the specified value of the source string does not belong to any of the above-mentioned datatypes then it is cast to VARCHAR implicitly by the function before the trimmed value of the source string is evaluated.
It is necessary that both the datatypes of the source string and the character to be removed are compatible with each other while using the function. The data type of the output string from the function depends upon the data type of the source string expression and the dependency followed over there is as specified below –
- The resultant string is in VARCHAR if the source string has the data type of VARCHAR or CHAR.
- The data type of the output string is a VARGRAPHIC if the datatype of source string expression is GRAPHIC or VARGRAPHIC.
- It is in the VARBINARY datatype output value if the source string has VARBINARY or BINARY datatype.
Examples of DB2 trim
Let us have a look at the implementation of the TRIM() function to understand its usage completely. Firstly, let us take one example where we will remove all the blank values at the beginning of the string by explicitly specifying LEADING in the TRIM function’s parameter as shown below. Consider a string “ DB2 comes with great features and functionalities ” which has the leading as well as trailing spaces in it. The following statement is used to remove all the blank spaces in the beginning –
SELECT
TRIM(LEADING FROM ' DB2 comes with great features and functionalities ') outputString
FROM
sysibm.sysdummy1;
The output of the above example is as shown in the below image with no spaces in the beginning –
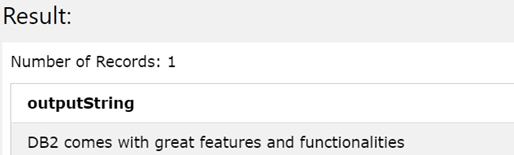
Let us take one more example, where we will remove all the spaces at the end of the source string. Let us consider the same source statement ‘ DB2 comes with great features and functionalities, our query statement will now have TRAILING mentioned in the TRIM function’s parameter and it will look like the following –
SELECT
TRIM(TRAILING FROM ' DB2 comes with great features and functionalities ') outputString
FROM
sysibm.sysdummy1;
The output of the above query statement gives out the following resultant value –
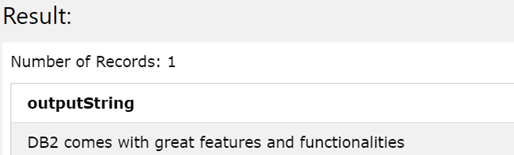
Let us use the TRIM() function to remove all the leading and trailing blank spaces that are present in our source string – ‘ DB2 comes with great features and functionalities, our query statement will now have BOTH mentioned in the TRIM function’s parameter or we can even skip the specification of BOTH as by default internally TRIM() function removes the strip character from both the ends. Our query statement will look like following –
SELECT
TRIM(BOTH FROM ' DB2 comes with great features and functionalities ') outputString
FROM
sysibm.sysdummy1;
The output of the above query statement gives out the following resultant value –
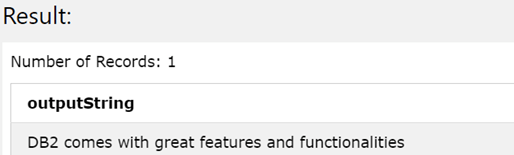
Conclusion
We can make the use of the TRIM() scalar function in DB2 DBMS provided by IBM to remove a particular character or blank space from the start or end of a string. By default, if we don’t mention LEADING or TRAILING while using the function the character is stripped from both sides. Also, if the character to be removed that is strip character is not mentioned, it is considered to be blank space.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 trim. Here we discuss the usage, syntax, and rules to be followed while using the trim scalar function in DB2. You may also look at the following article to learn more –


