Updated July 26, 2023
Definition of Cost of Goods Sold Example
Cost of Goods Sold refers to the costs incurred to produce goods or services. While calculating the Cost of Goods Sold example (COGS), the cost to produce goods and services that are not sold is excluded. The cost of Goods Sold also excludes indirect expenses.
Examples of Cost of Goods Sold (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Cost of Goods Sold in a better manner.
Cost of Goods Sold – Example #1
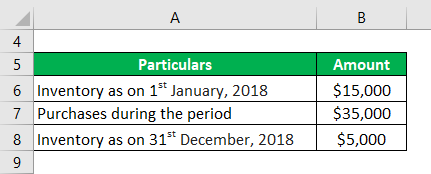
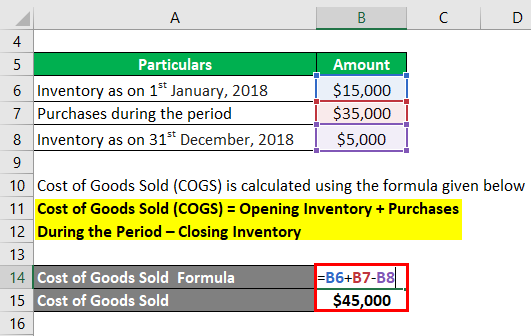
Patrick Inc. has the financial year beginning 1st January 2018 and ending 31st December 2018. Its inventory at the beginning of the year is $15,000. During the year, it makes purchases worth $35,000. Its inventory as of 31st December 2018 is $5,000. Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) during the year.
Solution:
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) = Opening Inventory + Purchases During the Period – Closing Inventory
- COGS = Inventory as of 1st January 2018 + Purchases during the period – Inventory as of 31st December 2018
- COGS = $15,000 + $35,000 – $5,000
- COGS = $45,000
The Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) during the year is $45,000.
Cost of Goods Sold – Example #2
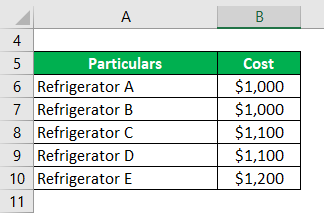
Kelly Inc. buys and sells refrigerators. The company buys Refrigerator A and Refrigerator B for $1,000 each. Then, it buys Refrigerators C and D for $1,100 each. Finally, it buys refrigerator E for $1,200. It then sells Refrigerators A and D. There are no refrigerators in Opening Stock.
Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold under:
- Specific Identification Method
- FIFO Method
- LIFO Method
Solution:
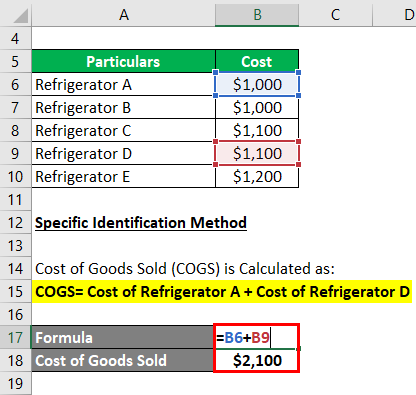
Under the Specific Identification method, we compute the costs of the refrigerators sold, which are A and D.
# Specific Identification Method
The cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is Calculated as follows:
Cost of Goods Sold = Cost of Refrigerator A + Cost of Refrigerator D
- COGS = $1,000 + $1,100
- COGS = $2,100
Thus, the Cost of Goods Sold under the Specific Identification Method is $2,100.
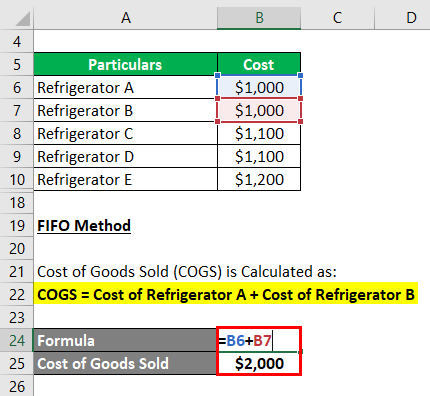
Under the FIFO method, we assume the refrigerators bought first are sold first. The costs of Refrigerator A and Refrigerator B are $1,000 each.
The cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is Calculated as follows:
Cost of Goods Sold = Cost of Refrigerator A + Cost of Refrigerator B
- COGS = $1,000 + $1,000
- COGS = $2,000
Thus, the Cost of Goods Sold under the FIFO method is $2,000
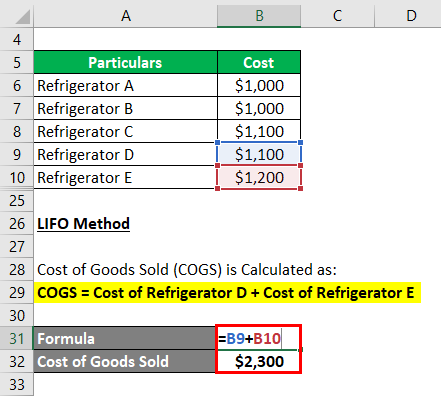
Under the LIFO method, we assume that the refrigerators bought last are sold first.
The cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is Calculated as follows:
Cost of Goods Sold = Cost of Refrigerator D + Cost of Refrigerator E
- COGS = $1,100 + $1,200
- COGS = $2,300
Thus, the cost of goods sold under the LIFO method is $2,300.
Cost of Goods Sold – Example #3
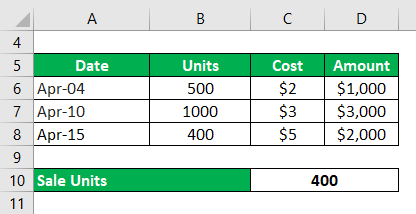
Hillary runs a cake shop. She has no cakes at the beginning of April. Below are some of the transactions:
- April 4 – She buys 500 cakes at $2 each
- April 10 – She buys 1,000 cakes at $3 each
- April 15 – She sells 400 cakes at $5 each
Compute the Cost of goods sold under the FIFO and LIFO methods. Also, calculate the Gross Profit and value of Closing Stock under both methods.
Solution:
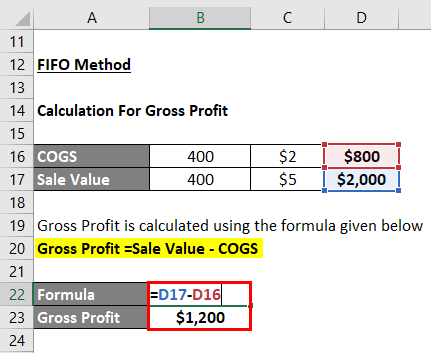
Under the FIFO method, 400 cakes are sold from the first lot of 500 cakes bought on April 4.
FIFO Method
The cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is Calculated as:
- COGS = 400*$2
- COGS = $800
The sale Value Calculates as:
- Sale Value = 400*$5
- Sale Value = $2,000
Gross Profit calculatea using the formula given below
Gross Profit =Sale Value – COGS
- Gross Profit =$2,000 – $800
- Gross Profit =$1,200
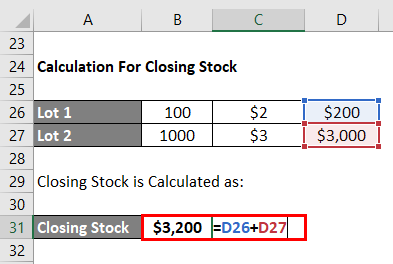
While calculating Closing Stock, we have 100 cakes (500-400) from the lot purchased on April 4 and 1,000 cakes from the lot purchased on April 10.
Closing Stock Calculates as:
- Closing Stock = 100*$2 + 1,000*$3
- Closing Stock = $200 + $3,000
- Closing Stock = $3,200
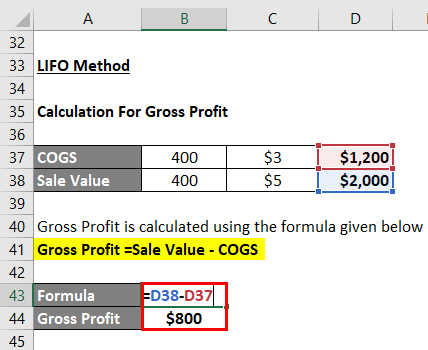
LIFO Method
Under the LIFO method, the 400 cakes are sold from the lot purchased on April 10.
The cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is Calculated as:
- COGS = 400*$3
- COGS = $1,200
The sale Value Calculates as:
- Sale Value = 400*$5
- Sale Value = $2,000
Gross Profit calculates by using the formula given below
Gross Profit =Sale Value – COGS
- Gross Profit = $2,000 – $1,200
- Gross Profit =$800
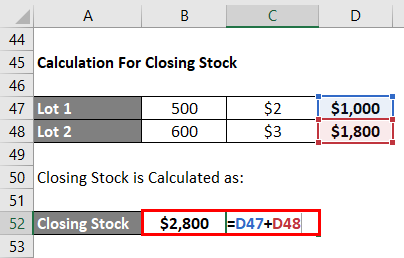
While calculating Closing Stock, we have 600 cakes (1000-400) from the lot purchased on April 10. In addition, we have the whole lot of 500 cakes purchased on April 4.
Closing Stock Calculates as:
- Closing Stock = 600*$3 + 500*$2
- Closing Stock = $1,800 +$1,000
- Closing Stock = $2,800
Cost of Goods Sold – Example #4
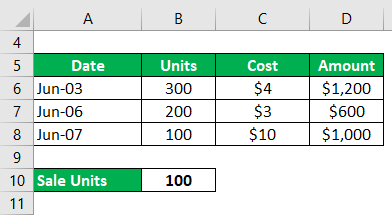
Eat Hungry Ltd is a biscuit shop. It carries out the following transactions in June:
- June 3 Purchase of 300 biscuits @ $4 each
- June 6 Purchase of 200 biscuits @ $3 each
- June 7 Sale of 100 biscuits @ $10 each
Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold on the basis of the Weighted Average Cost Method and the resultant Gross Profit.
Solution:
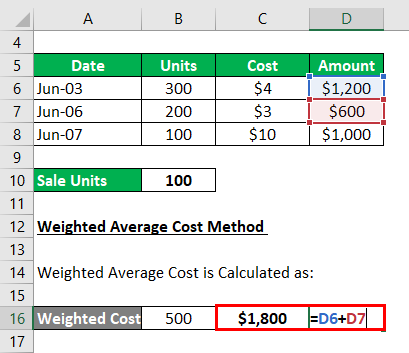
Weighted Average Cost Calculates as:
- Weighted Average Cost = 300*$4 + 200*$3
- Weighted Average Cost = $1,200 +$600
- Weighted Average Cost = $1,800
The total Number of Units Purchased Calculates as:
- Total Number of Units Purchased = 300 + 200
- Total Number of Units Purchased = 500 units
Cost Per Unit Calculate as:
- Cost Per Unit = $1,800/500
- Cost Per Unit = $3.6 per unit
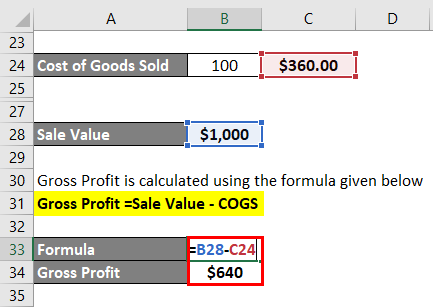
The cost of Goods Sold Calculates as:
- Cost of Goods sold = 100*$3.6
- Cost of Goods sold = $360
The sale Value Calculates as:
- Sale Value = 100*$10
- Sale Value = $1,000
Gross Profit calculate by using the formula given below
Gross Profit =Sale Value – COGS
Gross Profit = Sale Value – Cost of Goods Sold
- Gross Profit = $1,000 – $360.00
- Gross Profit = $640
Thus, the Cost of Goods Sold is $360, and the gross profit is $640.
Conclusion
Calculating the Cost of Goods Sold is to find the Gross Profit. The organization can also compare the Gross Profit Margin with its competitors. But, while interpreting the Cost of Goods Sold, certain factors must be considered. The Cost of Goods Sold depends upon the valuation method of inventories used. Thus, First in First Out (FIFO), Last in First Out (LIFO), and Weighted Average give different results for the Cost of Goods Sold. When using inventory valuation methods for external reporting, exercising care and ensuring that the method aligns with the prescribed Accounting Standards is important. All inventory valuation methods have their own advantages and disadvantages.
For instance, when using the FIFO method and experiencing inflation in the country, the prices for calculating the cost of goods sold (COGS) are lower and outdated. Similarly, various countries’ prescribed Accounting Standards prohibit using the LIFO method. While preparing a budget and comparing the actual results, it is possible to compute the cost of goods sold (COGS). If variations occur between the COGS number obtained for budget preparation and the actual results, it is important to identify the reasons and take corrective action in the next period.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Cost of Goods Sold Example. Here we discuss the overview and top 4 practical Cost of Goods Sold Example, a detailed explanation, and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –