Updated June 9, 2023
Data Structures and Algorithms C++
Data Structures and Algorithms C++ – means arranging or organizing the elements in a particular way. When we say we have to arrange elements, those elements can be organized in different forms. For example, socks can be arranged in various different ways. You can just keep it in your cupboard all messed up. Or you can keep it neatly folded. The best way can be folding and arranging them color-wise. So for searching for a particular pair of socks, the third arrangement is perfect.
Similarly to the organization of socks, Data can also be organized in different ways or forms. These different ways of organizing data are called Data structures. Let’s see a formal definition of a data structure and the data structures and algorithms basics.
Data Structures And Algorithms C++
The logical or mathematical model of a particular organization of data.
OR
It is a particular way of organizing data in a computer so that it can be used.
Similarly to socks, the different organization of list data structures and algorithms C++ available is –
- Array
- Linked List
- Stack
- Queue
- Tree
- Graph
- Hash Table
- Heap
- Records
- Tables
These data structures and algorithms in C++ are very important while programming. A good programmer always gives emphasis on data structure rather than code. Each programming language works on various data structures and algorithms in C++. Data structures that are available in C++ are as follows.
- Array
- Linked List
- Stack
- Queue
- Tree
- Graph
- Hash Table
- Heap
Let’s discuss this one by one
#1 – Array
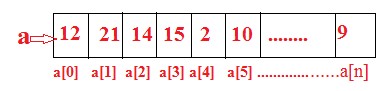
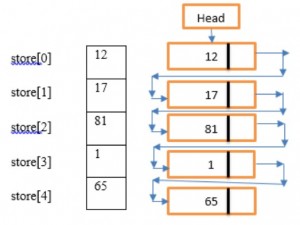
An array is the simplest type of data structure and algorithm in C++. The array is a Fix-size sequential collection of data elements of the same data type. E.g. a0=12, a1=21,a2=14,a3=15….We can represent a one-dimensional array as shown in the figure:
Where
0,1,2,3…..n is called subscript or index
a[1],a[2],…a[n] is called subscript variable
It can be 1-Dimensional, 2-Dimensional, 3-Dimensional, and so on multi-Dimensional.
In memory, an array is stored in contiguous memory locations.
The lowest address corresponds to the first element
The highest address corresponds to the last element
We can declare a 1-D (1-Dimensional) array in C++ as follows
dataType arrayName[arraySize];
E.g. int num[5];
Initializing Array in C++
num={23, 10, 12, 3, 6};
We can combine declaration and initialization into a single statement as follows.
int num={23, 10, 12, 3, 6};
When we want to dynamically allocate the size of an array, then we should use a new operator as follows
int * a= new int[size];
The disadvantage of the array is the insertion and deletion of elements are slow, as in an ordered array and its fixed-size storage.
#2 – Linked List
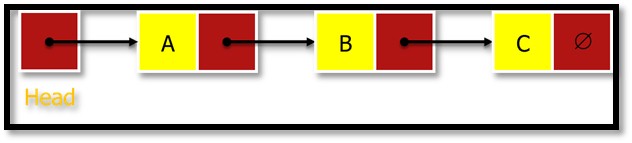
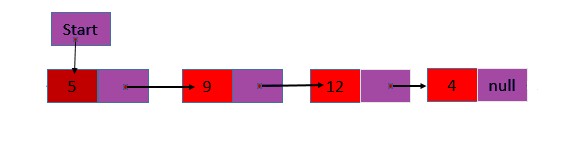
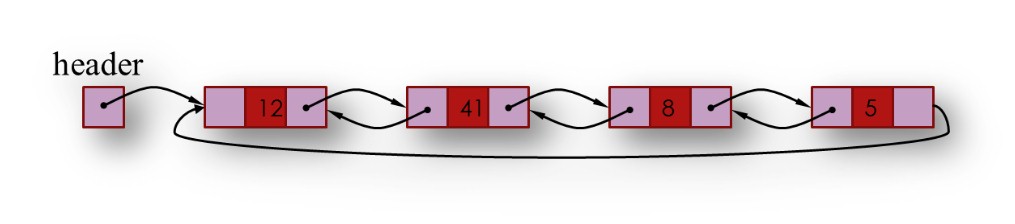
A list refers to a linear collection of items. A linked list is a series of connected nodes (data element), as shown in Figure 3. The header node points to the first node of the list, and the last node points to NULL, indicated byÆ as each node contains at least one.
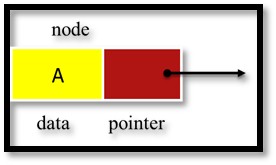
- A piece of data (any type)
- Pointer to the next node in the list
Linked List is represented in memory using two arrays. One array stores Information called info which is data to be stored, and the other stores the next-pointer field called LINK, which is the address of the next node.
An advantage of a linked list over an array:
An array and a linked list represent a list of items in memory. The important difference is the way in which the items are linked together. The main limitation of the array is element insertion into the array, and element deletion from the ordered array is difficult as the rest elements have to be moved. Insertion and deletion of elements from a linked list are very simple.
Types of Linked Lists
Below are the different types are as follows:
1. Singly linked list: Contains only one linked field, which holds the address of the next node in the list, and the info field, which holds information to be stored.
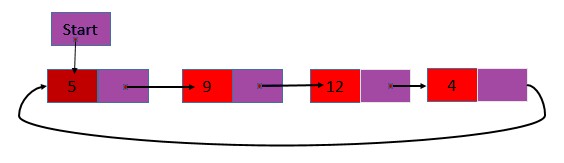
2. Single Circular Linked List: It is a single list only, but the last node of the list contains the address of the first node instead of null. That is the content of the head, and the next field of the last node is the same.
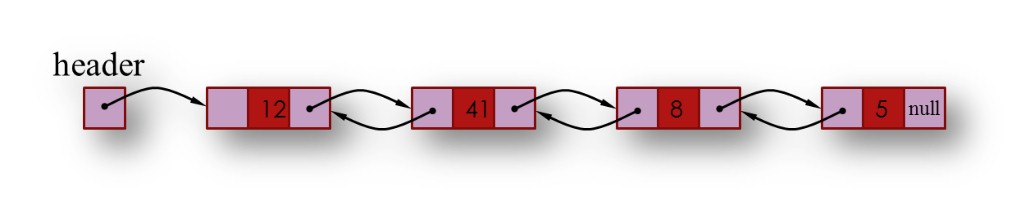
3. The doubly linked list: Contains two linked fields, previous and next. A previously linked field holds the address of the previous node in the list, the next linked field holds the address of the next node in the list, and the info field holds the information to be stored.
4. Double Circular Linked List: It is a doubly linked list, but the next field of the last node contains the address of the first node instead of null.
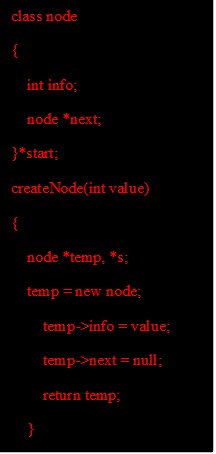
Implementing a linked list in C++ involves creating a node, deleting a node from the list, inserting a newly created node into the list, and searching for a node with a particular key.
The code for creation of the node is given as follows:
Inserting a node into the list
Inserting a node into the list involves three cases
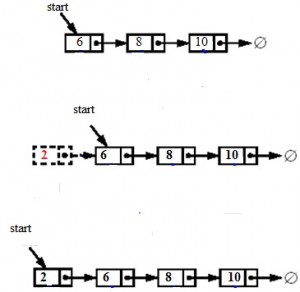
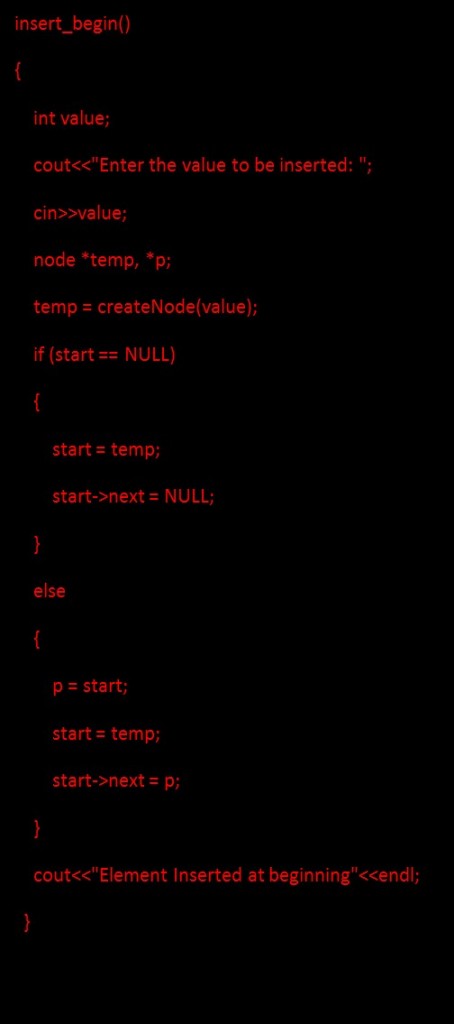
1. Inserting a node at the beginning means inserting the newly created node as starting node. For inserting a node at the beginning, first, create a new node and make the new node point to the old start, and then update starts to point to the new node as shown below figure:
Code for inserting a node at the beginning:
2. Inserting a node at the tail means inserting the newly created node as the last node. For inserting the node as a tail node have to create a new node and make the old last node point to the new node and then update the tail to point to the new node.
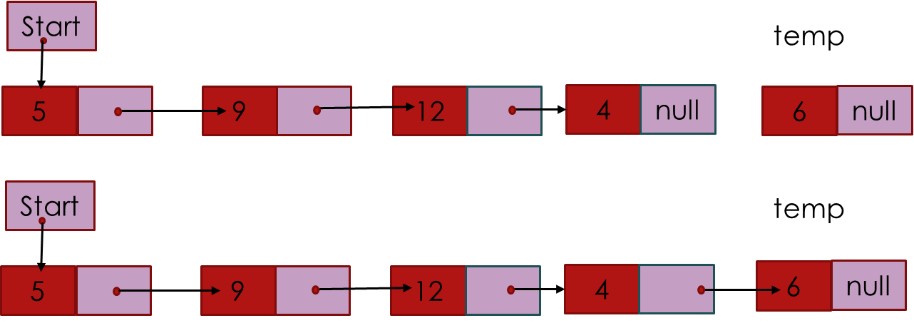
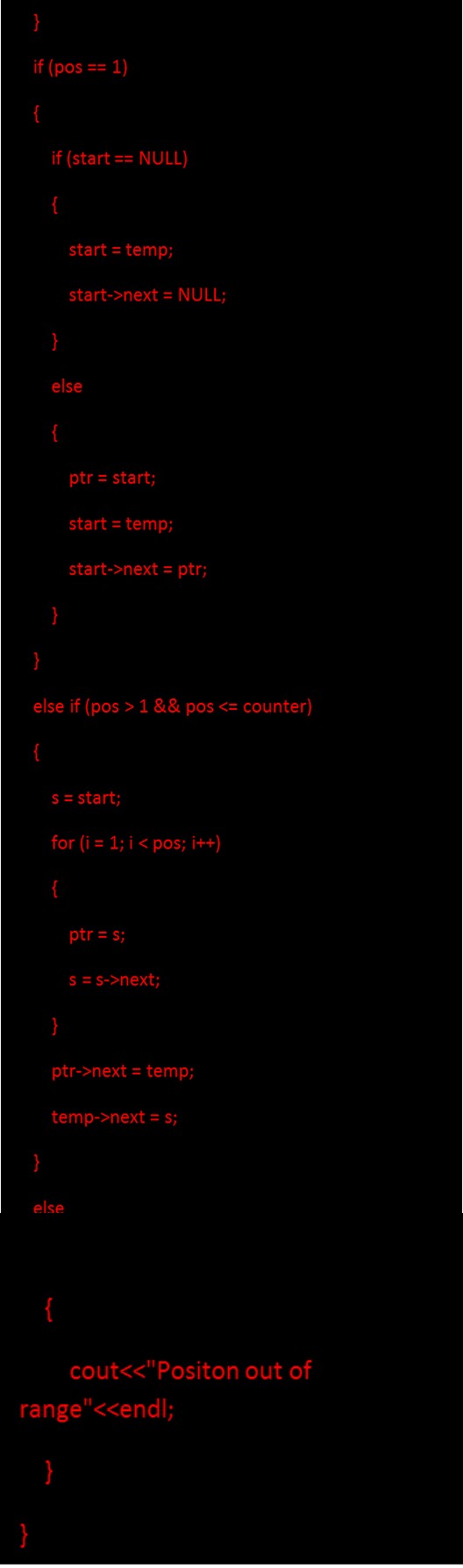
3. Inserting a node at a given position involves the creation of a new temp node; then have to find the position of insertion of the newly created node.
Code for insertion of the node at a given position:
Deleting a node from a list involves removing a node from the existing list. Deleting the node from the link list is simpler than inserting a node into the list. In C++, code for deletion of the node is as follows:
Traversing a node with a particular key (value) from a list will search a node from the list whose info will match with the key of a given node. The following C++ code will traverse a list. data structures and algorithms C++
#3 – Stack
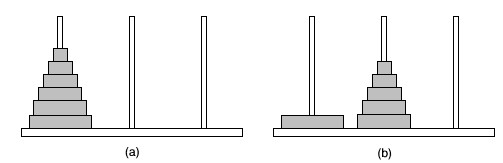
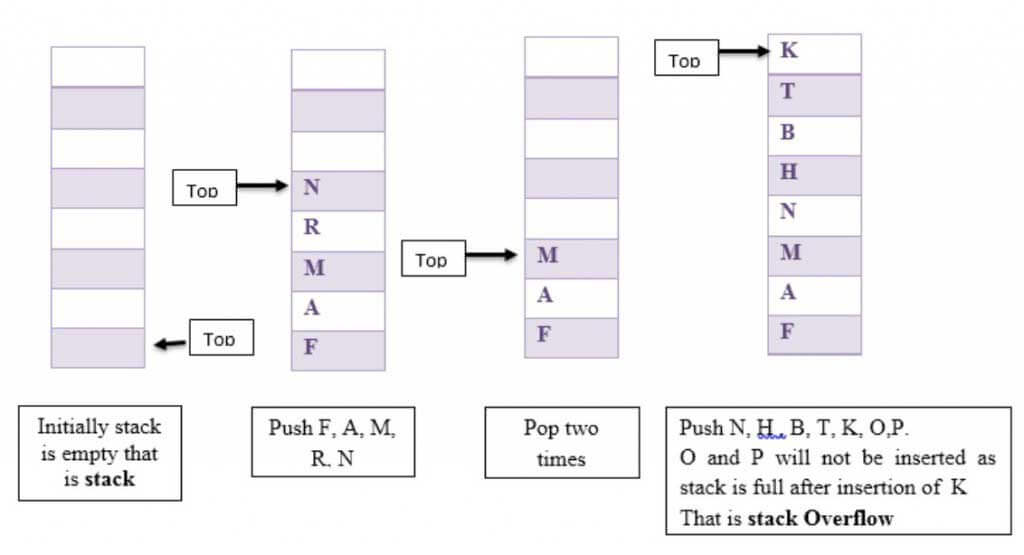
A stack is a list of elements in which an element may be inserted or deleted only at one end, called the top of the stack. Consider the example of a tower of Hanoi. Here when we have to insert a disc, we have to insert it from the top only, and similarly, removal of the disc takes place from the top only.
Stack uses the LIFO principle means it works in Last in First Out order. The last element added to the stack is the first element of removal. So there are four basic operations on the stack:
- Isempty: This operation sees whether the stack is empty.
- Push: This operation adds a new item to the stack.
- Pop: This operation removes an item from the recently added stack item.
- Top: This operation returns an item added to the stack most recently.
The following figure is an example of the stack where insertion into the stack and removal from a stack of the item takes place from the top of the stack and nowhere else.
Stack Overflow
The condition results from trying to push an element onto a full stack.
Stack underflow
The condition resulting from trying to pop an empty stack.
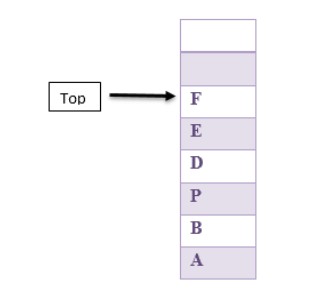
Here we have shown some push and pop operations on the stack. Suppose the initial stack is empty; then we add F, A, M, R, N. Then pop two times and push N, H, B, T, K, O, P.
Implementation of Stack
It executes using an array or linked list both.
The following code depicts how the stack is useful in C++ using Class. Here have defined one Class named a stack which created an array named a stick with dynamic size and two main functions, push and pop.
Stack Overflow: When top>=size-1
Stack underflow: When top <0
Recommended Articles
Here are some articles related to the data structures and algorithms of C++, which will help you to get more detail about the Algorithms of C++ and the data structures and algorithms, so kindly go through the link given below. If you like the article data structures and Algorithms C++, give us your valuable comment.