The Role of Cybersecurity in E-Commerce for Protecting Data
E-commerce has become the preferred way for people to shop because it is fast, global, and convenient. However, with its rapid growth comes increasing vulnerability. Every transaction, customer account, and stored record can become a target. This is why cybersecurity in e-commerce is no longer optional it is essential for building trust, meeting compliance standards, and protecting revenue. This article explains how cybersecurity protects e-commerce data, the biggest threats online businesses face today, and practical steps merchants can take to secure their platforms.
Why E-commerce Security is Urgent Now?
The impact of a data breach on an online store is both rapid and complex. Attackers can steal payment details, customer data, purchase histories, and other sensitive business information meant only for your use. The cost of fixing the problem is high. The most recent study in the field found that the average price of a data breach was $4.88 million, and this number continues to rise. In that number, you can see the direct response costs, the legal and regulatory fallout, customer losses, and damage to your image. Online businesses really can not afford to make security a choice.
Beyond monetary considerations, consumers express their preferences through their purchasing choices. People want quick and easy checkouts, but they also want to feel safe. Reports indicate that safety and ease of use are two key factors that people look for in a payment method. This means that merchants who keep data secure while making checkout as simple as possible will win trust and sales.
Major Cybersecurity Risks That Threaten E-Commerce Businesses
Several types of attacks pose a threat to online stores.
- Payment fraud and card-not-present (CNP) attacks: As the number of online funds increases, so does the number of fraudsters. Global e-commerce fraud reports indicate that fraudsters are increasingly attempting new tactics and targeting businesses with more sophisticated scams.
- Account takeover and credential stuffing: Cybercriminals use stolen usernames and passwords from separate hacks to take over shoppers’ accounts, steal stored credit card information, or place fake orders.
- Breach of the supply chain and third parties: Plugins, payment gateways, and fulfillment partners are all critical parts of e-commerce platforms. If you work with a weak provider, they could get access to your data.
- Phishing and tricking people: These methods still allow access to admin accounts or expose staff to private controls.
- Misconfigurations and insider danger: A surprisingly frequent cause of data leaks is human error, such as leaving S3 buckets publicly accessible or choosing weak, easily guessable passwords.
Consequences for Merchants and Consumers
Cyber events not only lead to theft but also to chargebacks, legal fines, repairs, and, in some cases, long-term customer loss, all of which incur high costs. Recent studies on merchant-focused fraud and payments have shown that many e-commerce businesses are under constant attack from fraudsters. It is expensive for them to stop this, as they have to deal with declines, false positives, and human reviews, which cut into their profits. Local government crackdowns and increased reports of cyberfraud have made it more crucial for businesses in rapidly growing markets to enhance their defenses.
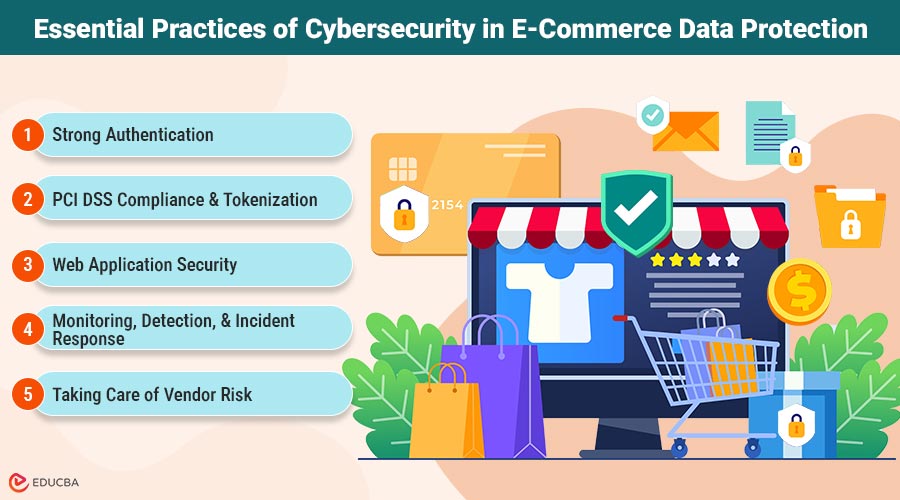
Essential Practices of Cybersecurity in E-Commerce Data Protection
To keep online shopping safe, you need to use a tiered, realistic strategy. These are the most important controls.
1. Strong Authentication (MFA & Password Security)
Multi-factor security makes it much less likely that someone will take over your account. Merchants and payment providers are making MFA the norm for both admin and customer accounts, driving rapid market growth and adoption rates. It is easy to add second factors for administrator portals and merchant dashboards that use SMS, apps, or hardware tokens.
2. PCI DSS Compliance & Tokenization
If you store cardholder data properly, such as through tokenization, vaulting, or PCI-compliant payment platforms, an attacker will be unable to steal as much of it. Many breaches are caused by poor card data storage or faulty processor connections, so start with PCI-compliant hosting and build up from there.
3. Web Application Security (WAF, Secure Code, Vulnerability Scanning)
In e-commerce, web apps, and APIs, the main entry points for hackers and common exploits like SQLi, XSS, and failed authentication are present. You need to regularly scan for vulnerabilities, review your code, and set up a web application firewall (WAF). For even stronger security, consider protecting your code repositories to ensure your development environment remains secure even in the event of an incident.
4. Monitoring, Detection, and Incident Response
Shortening dwell time and breach costs are both benefits of fast discovery. Continuous logging, anomaly detection, and a well-practiced incident response playbook can help you save time and money when incidents occur.
5. Taking Care of Vendor Risk
You can lower the risk associated with third parties by verifying your suppliers’ security, ensuring contracts include time frames for breach notifications, and separating vendors’ network access so they can only view what is necessary.
6. Training for Employees and Fake Hacking Attacks
Most of the time, human mistake is the weakest link. Regular role-based security training reduces the likelihood that phishing or a simple setup error will let someone in. Using HR platforms that centralize employee training and track compliance can significantly reduce human error.
Keeping Security and Change in Check
Many business owners worry that tighter security will hurt sales by making the checkout process more difficult. A better way to handle security is to base it on risk. For high-risk transactions such as a new shipping address, a large order, or an IP address that does not match the billing address add extra verification steps. For low-risk customers, there should be fewer checks.
Using tools that blend device fingerprinting, behavioral analytics, and real-time risk scoring, merchants can stop fraud and keep real buyers happy and moving quickly. Recent studies on fraud suggest that this layered, intelligence-driven approach is the most effective way to reduce losses without alienating customers.
Why Small and Medium Businesses Must Prioritize Cybersecurity?
Attackers often believe that small businesses are easy targets, and the numbers support this assumption. Smaller stores often lack the resources or expertise to invest in security, yet they still handle sensitive payment information and maintain customer records. For a small store, a breach can mean the end of the business: fines, chargebacks, lost customers, and the cost of recovering trust. Basic controls, such as multifactor authentication, PCI-compliant gateways, web application security measures, and backup and recovery plans, provide significant protection for a relatively small investment.
Practical Steps to Improve E-Commerce Security This Quarter
If you run an online business, these practical steps will help you quickly make your site safer.
- Transfer card data to a processor that works with PCI and uses tokenization.
- Make sure that all admin, vendor, and high-privilege users use MFA.
- Set up logging and centralized tracking, and conduct weekly vulnerability scans.
- Install a web application firewall to enhance API security.
- Remove unnecessary third-party plugins.
- Create an incident-handling plan and conduct phishing drills with your workers.
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity in e-commerce is not just about preventing data theft it is a strategic advantage. It is a benefit over the competition. When stores carefully protect their data, they experience fewer chargebacks, maintain better relationships with payment providers, avoid legal issues, and retain loyal customers. In an era when fraud schemes become increasingly sophisticated each year, and the average cost of a breach exceeds millions of dollars, it makes sense to integrate security into the product.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on cybersecurity in e-commerce helps you strengthen your online store’s protection. Explore these recommended articles for more tips and strategies to secure and grow your digital business.

