Updated June 23, 2023

Introduction to CSS Position Relative
While designing pages in HTML, you might want to change the position of all of the elements of the page according to the page or layout. For example, when the page is loaded, one element will be positioned in one place, the other will be in another, or both elements should be placed relative to each other. To implement this, position properties allow you are indicating which type of position an element should have according to the required scenarios like “fixed”, “relative”, “sticky”, “absolute” etc., in your HTML code. In CSS Position Relative, we will see how we can position different elements in an HTML page by using the position properties of CSS in some examples.
Syntax:
position: value;Now the question is, what are the different values available? Those are different types of positions. Please find below a table describing various position types:
| Value | Description |
| static | If an element is defined as static, then the element will always have the position as per the normal page flow. This is the condition when nothing is defined as an element in an HTML page design. It is also the default value. The static element does not change its position. |
| fixed | If you define an element as static, it will always maintain a fixed position relative to the viewpoint or page. It always resides in the same place, even if we scroll the page. |
| absolute | Although the name is absolute, if an element is defined as absolute, it will always have a relative position with respect to its nearest neighbor element instead of the viewpoint or page. If there is no neighbor, it will be positioned relative to the body of the document, and its movement is in liaise with the scrolling of the page |
| relative | If an element is defined as relative, it will always have the position according to the defined values of its position, like: left, right, top, and bottom relative to the normal position, and its movement is in liaise with the page’s scrolling. |
| sticky | If an element is defined as relative, then the element will always follow the page’s scrolling and stick to scrolling. Sticky elements never leave the user as they scroll the webpage. |
How is Position Relative Done in CSS?
You need to mention the required value of the position as per the syntax in your HTML code to get that position in the output.
You can refer to the example section with code to see how you can implement relative positions of one or multiple element(s) in your HTML code by using different position values of CSS.
Examples to Implement of CSS Position Relative
Below are the examples of CSS Position Relative:
Example #1
In this example, you will see how you can arrange an element relative to another element in the absolute position.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#super {
position: relative;
width: 500px;
height: 400px;
background-color: grey;
font-size: 24px;
text-align: center;
}
#sub {
position: absolute;
right: 40px;
top: 100px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #fafafa;
font-size: 24px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="super">
<div id="sub"> I am sub in relative position of my parent</div>
I am super in absolute position</div>
</body>
</html>Output:

Example #2
This example demonstrates the arrangement of two distinct elements in relation to each other. We have positioned the second element 40 px left to the first element. The second element is also 150 px upper to the first element. See the codes carefully to understand how you can arrange multiple elements in one page according to our requirements when we are designing an HTML page with the help of the position values of CSS.
Code :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#fst_element {
position: relative;
left: 40px;
top: 150px;
height: 50px;
width: 400px;
background-color: white;
border: solid 3px red;
font-size: 25px;
text-align: center;
}
#snd_element {
position: relative;
height: 50px;
width: 450px;
background-color: white;
border: solid 3px blue;
font-size: 25px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="fst_element">1st element</div>
<div id="snd_element">2nd element</div>
</body>
</html>Output:

Example #3
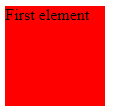
In this example, you can see that one element positions itself relative to the page layout based on the desired pixel values.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#myDIV {
position:relative;
width:100px;
height:100px;
background:red;
left:100px;
top:100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="myDIV">First element</div>
</body>
</html>Output:
Example #4
In this example, you will see another element positioned relative to the page layout per the desired px values. This element also uses border values and attributes such as top, bottom, height, and width to define its shape and position.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div.ExampleReltv {
position: relative;
left: 10px;
width: 200px;
border: 4px solid blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="ExampleReltv">
This element is in relative position;
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:

Example #5
In this example, once again, you will witness a situation where two distinct elements arrange relatively to another element, which holds an absolute position. See the codes carefully to understand how you can arrange one absolute element in one page and position a relative element on the same page according to our requirements when designing an HTML page with the help of position values of CSS.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div.reltv {
position: relative;
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
border: 4px solid blue;
}
div.abslt {
position: absolute;
top: 80px;
right: 20px;
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
border: 4px solid red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="reltv">I am located in relative position;
<div class="abslt">I am located in absolute position;</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:

Conclusion
This concludes our learning of the topic “CSS Position Relative” as you can see how we had implemented different positions in our HTML code examples by CSS. This article will be helpful for those associated with HTML designing webpages using CSS. Learning codes will be incomplete if you will not write code by yourself. Happy coding!!
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “CSS Position Relative” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


