Updated July 27, 2023
Common Stock Formula (Table of Contents)
What is Common Stock Formula?
The term “common stock” refers to the type of security for ownership of a corporation such that the holder of such securities has voting rights that can be exercised for various corporate events.
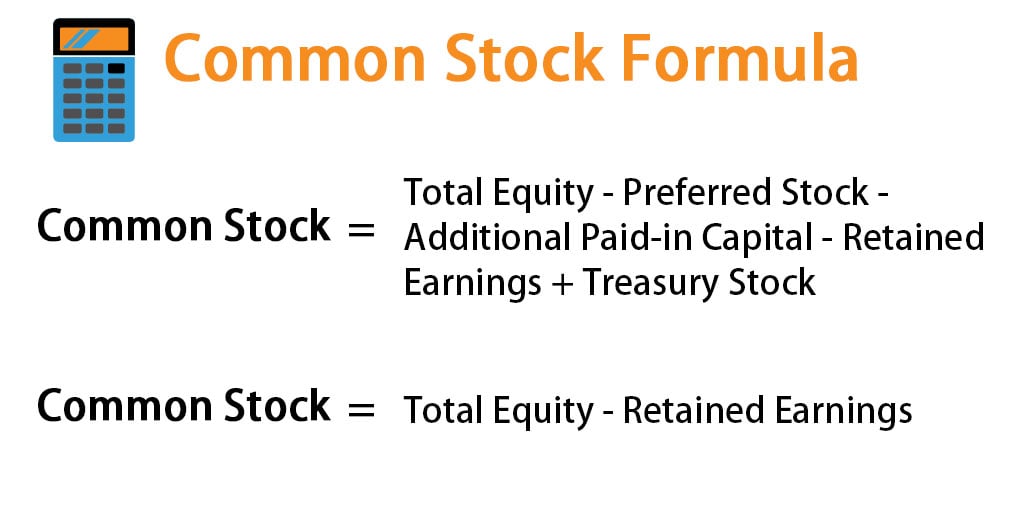
Examples of such events include a selection of the board of directors or other major corporate decisions. The formula for the common stock of a company can be derived by deducting preferred stock, additional paid-in capital, and retained earnings from the total equity while adding back the treasury stock. Mathematically, it is represented as,
However, in some cases where there is no preferred stock, additional paid-in capital, and treasury stock, the common stock formula becomes simply total equity minus retained earnings. This is the case with most smaller companies with only one class of stock.
Examples of Common Stock Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of Common Stock in a better manner.
Common Stock Formula – Example #1
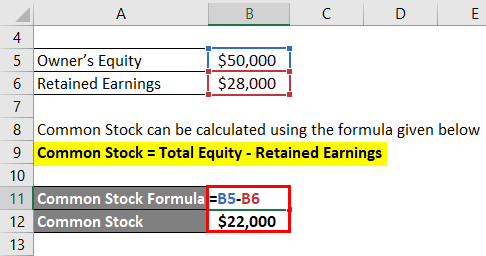
Let us take the example of the firm owned by John. As per the balance sheet as on December 31, 2018, the owner’s equity is $50,000 and the retained earnings are $28,000. Calculate the company’s common stock based on the given information.
Solution:
The formula to calculate Common Stock is as below:
Common Stock = Total Equity – Retained Earnings
- Common Stock = $50,000 – $28,000
- Common Stock = $22,000
Therefore, the company’s common stock stood at $22,000 on December 31, 2018.
Common Stock Formula – Example #2
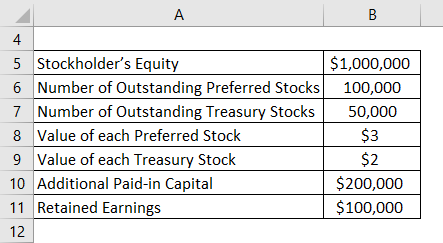
Let us take the example of a company named FGH Ltd. As per the balance sheet as on December 31, 2018, information is available. Calculate the company’s common stock based on the given information.
Solution:
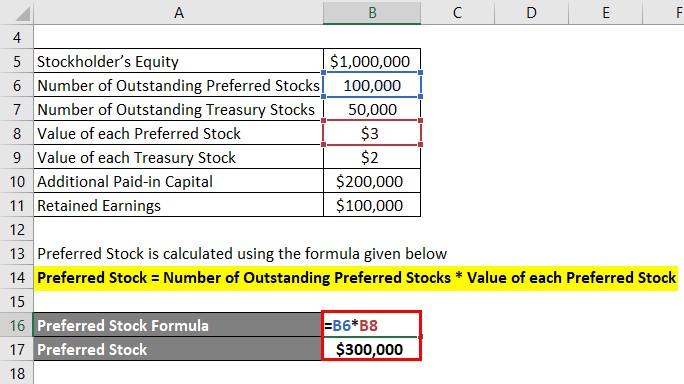
The formula to calculate Preferred Stock is as below:
Preferred Stock = Number of Outstanding Preferred Stocks * Value of each Preferred Stock
- Preferred Stock = 100,000 * $3
- Preferred Stock = $300,000
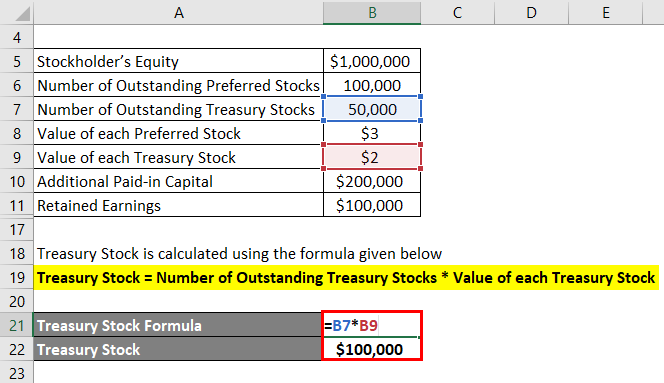
The formula to calculate Treasury Stock is as below:
Treasury Stock = Number of Outstanding Treasury Stocks * Value of each Treasury Stock
- Treasury Stock= 50,000 * $2
- Treasury Stock = $100,000
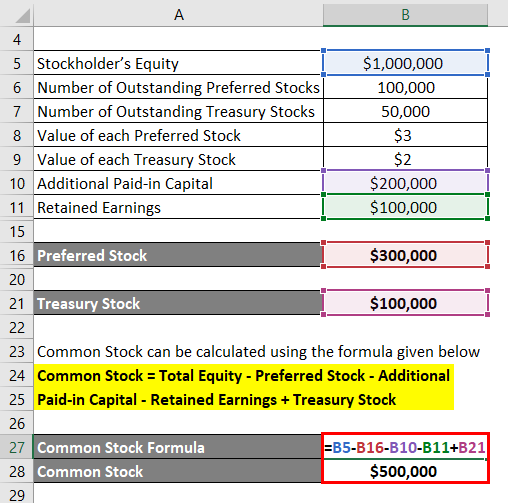
The formula to calculate Common Stock is as below:
Common Stock = Total Equity – Preferred Stock – Additional Paid-in Capital – Retained Earnings + Treasury Stock
- Common Stock = $1,000,000 – $300,000 – $200,000 – $100,000 + $100,000
- Common Stock = $500,000
Therefore, FGH Ltd’s common stock stood at $500,000 on December 31, 2018.
Explanation
The formula for common stock can be derived by using the following steps:
Step 1: Firstly, determine the value of the company’s total equity, which can be either in the form of owner’s or stockholder’s equity.
Step 2: Next, determine the number of outstanding preferred stocks and the value of each preferred stock. The product of both will give the value of the preferred stock.
Step 3: Next, determine the value of additional paid-in capital, which is the surplus value paid to the stock investors over and above the nominal price of the common stock.
Step 4: Next, determine the number of outstanding treasury stocks and each stock’s acquisition cost. The product of both will give the value of treasury stock.
Step 5: Next, determine the value of the retained earnings as of the reporting date. It is the accumulated account of the profit retained by the business to date.
Step 6: Finally, the formula for the common stock of a company can be derived by deducting preferred stock (step 2), additional paid-in capital (step 3), retained earnings (step 5) from the total equity (step 1), and adding the treasury stock (step 4) as shown below.
Relevance and Uses of Common Stock Formula
Common stock is vital for equity investors as it grants them voting rights. Common stockholders can vote on important corporate matters like acquisitions, board composition, and other significant decisions. Usually, each common stockholder gets one vote for every share. Another striking feature of common stock is that these stocks usually outperform other forms of securities, like bonds and preferred stocks, in the long run. However, common stock comes with a strong downside. In bankruptcy, the common stockholders receive nothing until the company fully pays off its creditors. The company prioritizes paying lenders, creditors, and other stakeholders when selling assets, with common stockholders receiving payment only if any funds are left after fulfilling these obligations. Common stock exemplifies the risk-return trade-off by offering potentially higher returns due to its higher risk than other securities.
Common Stock Formula Calculator
You can use the following Common Stock Calculator
| Total Equity | |
| Preferred Stock | |
| Additional Paid-in Capitala | |
| Retained Earnings | |
| Treasury Stock | |
| Common Stock | |
| Common Stock = | Total Equity - Preferred Stock - Additional Paid-in Capitala - Retained Earnings + Treasury Stock | |
| 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 + 0 = | 0 |
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Common Stock Formula. Here we discuss How to Calculate Common Stock along with practical examples. We also provide a Common Stock Calculator with a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –